SIM8200EA-M2 5G Router
| ||
Overview
Feature
- Supporting SIM8200EA-M2 core module, based on Qualcomm Snapdragon X55 platform with multi mode multi band support.
- Support 5G/4G/3G Internet access in various modes, which can be used in the fields of Internet of Networked Medical Treatment, Intelligent Agriculture, Smart City, Smart Robots, Security Monitoring Networking, Intelligent Bus Wi-Fi, etc.
- Enjoy High Speed 5G Networking Via The Gigabit Ethernet Port Or WiFi Connection.
- Onboard 1 WAN interface and 4 LAN interfaces, the interface is 10 / 100 / 1000M Ethernet port, adaptive MDI/MDIX.
- Onboard 1x M.2 connector, and 3x mini PCIE connectors, you can flexibly customize or upgrade the software/hardware by yourself.
- Onboard multi-function RS232/RS485 serial communication, support TCP/UDP transparent transmission, Modbus, and MQTT multi-mode work.
- Onboard one 4G-SIM card slot and one 5G-SIM card slot, support 1.8V and 3V SIM card.
- Onboard 16 LED indicators for easy viewing of module operating status.
- Support AT command control (based on 3GPP TS 27.007, 27.005, and V.25TER command set).
- Integrated multi-constellation system dual-frequency positioning: GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, Galileo and QZSS*
- Support operator private network access, adopt financial-grade data security standards, and data transmission is stable and reliable.
- Quality metal case, with multiple protections like ESD protection, surge protection, electric fast pulse protection, and power supply phase-reversal protection.
Specification
|
Frequency band | |
|
Sub-6G(SA) |
n1, n2, n3, n5, n7, n8, n12, n20, n28, n40, n41,n48, n66, n71, n77, n78, n79 (n79 is only available for SIM8202G-M2) |
|
Sub-6G(NSA) |
n41, n77, n78, n79 (n79 is only available for SIM8202G-M2) |
|
LTE-FDD |
B1/B2/B3/B4/B5/B7/B8/B12/B13/B14/B17/B18/B19/B20/B25/B26/B28/B29/B30/B66/B71 |
|
LTE-TDD |
B34/B38/B39/B40/B41/B42/B48 |
|
WCDMA |
B1/B2/B3/B4/B5/B8 |
|
GNSS |
GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, Galileo and QZSS |
|
Data rate | |
|
Sub-6G |
2.4 Gbps (DL) / 500 Mbps (UL) |
|
LTE |
1 Gbps (DL) / 200 Mbps (UL) |
|
HSPA |
42 Mbps (DL) / 5.76 Mbps (UL) |
|
Software enviroment | |
|
OS |
Windows/Linux/Android |
|
Protocol |
TCP/IP/IPV4/IPV6/Multi-PDP/FTP/FTPS/HTTP/HTTPS/MQTTS/DNS/SSL3.0 |
|
SMS |
Support MT, MO, CB, Text, PDU |
|
Firmware upgrade |
Support to upgrade firmware via USB interface |
|
Hardware | |
|
SIM Card |
1.8V/3.0V |
|
Antenna interface |
6 × IPEX-4 interfaces for 3G/4G/5G/GNSS |
|
Power supplay |
5V 3A |
|
Applications | |
|
Available area |
Applicable For Regions With 5G Sub-6G Signal Coverage Including China, US, Japan, South Korea, Europe, The Middle East, Latin America... |
|
Classic application |
CPE/Intelligent router/UAL/Live video/Telehealth/Intelligent Security |
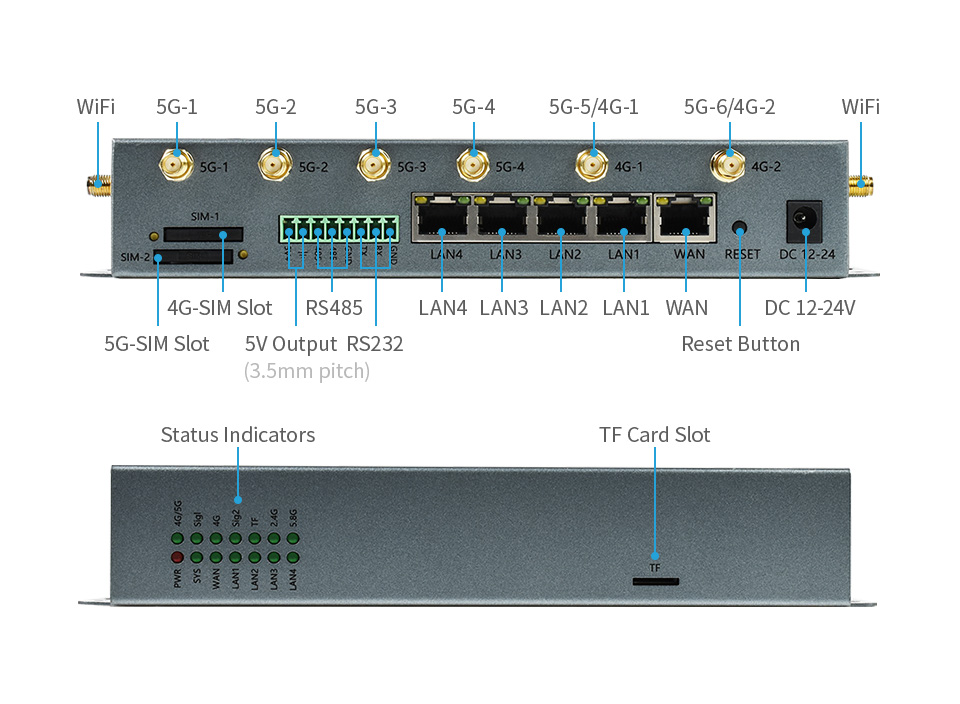
Interfaces
|
Interface Type | |
|
M.2 |
1x connector, comes with 1x SIM8200EA-M2 module by default, supports other 5G modules |
|
Mini PCIE |
3x connectors, comes with 1x 2.4GHz WiFi module, allows connecting one more 4G module and one more 5.8GHz WiFi module |
|
WAN |
1x 10/100/1000M Ethernet, auto-negotiation MDI/MDIX, embedded 1.5KV electromagnetic isolation protection (the WAN RJ45 can be used as LAN RJ45 port, so there could be totally 5x LAN RJ45 port) |
|
LAN |
4x 10/100/1000M Ethernet, auto-negotiation MDI/MDIX, embedded 1.5KV electromagnetic isolation protection |
|
Serial port |
1x RS232 + 1x RS485, embedded ESD protection |
|
SIM/UIM card slot |
drawer SIM card slot, prevents the SIM card from dropping out, embedded 15KV ESD protection |
|
Antenna connector |
SMA standard antenna connector, comes with 6x 5G antennas, 2x WiFi antennas by default |
|
TF card slot |
for external storage |
|
Power supply |
standard power supply interface, supply 12~24V input, embedded power supply phase-reversal protection and over-voltage protection |
|
Reset button |
Press and hold it for 5~10s then release, restores the router to factory setting |
| Indicators |
PWR, SYS, 5G, 4G, WAN, LAN, TF, 2.4G, 5.8G status indicators |
About the Speed
Due to the fact that there will be many inconsistencies between actual and laboratory conditions, the 5G speed will not be ideal and stable to maintain 100MBPS. There are several reasons:
- Distance: The closer to the 5G base station, the better the signal and the faster the speed.
- Load: The fewer people use it, the faster the speed will be, and in rush hour it will be slower.
- Number: Due to the spectrum, the equivalent 4G coverage rate requires double 5G base stations.
- Operator: You need to confirm whether your 5G card is limited in speed, you can periodically ask the operator to reset your network.
- The area: Because of building penetration attenuation, and indoor diffraction attenuation, the signal will be better outdoors.
PS: The current number of base stations still does not have good coverage, and the speed measurement in different locations is not the same.
Log in
- Connect the SIM card to the SIM-2 card slot (SIM-1 card slot corresponds to the 4G module) -> Install the antenna -> Connect the computer and router with a network cable -> Open the browser and enter 192.168.8.1 -> Login interface -> User name and The initial value of the password is admin.
Summary
The page shows the number of client access, network connection status, network speed and CPU usage:

- Summary: Display the current basic status of the gateway, mainly connection status and real-time traffic, number of terminals, wireless name channel, CPU memory load;
- Resources: Details of gateway system resources;
- Interface: Details of all network interfaces of the gateway;
- Network: Common network settings, such as 4G network, local network, routing table, port mapping, firewall and other basic network settings;
- Wireless: Wireless SSID settings;
- Station Control: terminal management, Internet access control, access control, traffic management, etc.;
- Application: Various applications, various application software in the gateway will be displayed in this menu item;
- System: Management configuration for the gateway, such as upgrade, configuration management, password management, etc.;
- Debug: Some functions that engineers and technicians need to debug or develop.
Interface
The working status of the network port, operator information, signal value, network type, IP address information and related information of the module are displayed here:

Note: The interface for selecting the same working mode is different. For details, please refer to the settings in the system settings section. The 5G router mode is selected here.
Network
- Log in to the router -> Network -> 4G/5G network, after successfully connecting to the 5G network, the status is connected successfully, and the network type is NR5G:
- Network -> turn on 2.4G AP Client -> scan WIFI hotspots -> select available hotspots -> enter password -> apply:
Wireless
- Wireless -> SSID -> Open WiFi 2.4G -> Apply.
Station Control
- Station Control -> Station list interface displays the devices and working status information that have been connected to the router:
- Station access control -> check the corresponding host -> enable Staion Access Control -> add ACL Rule Settings
4G/5G module terminal
- Debug -> Terminal command line -> 4G/5G module terminal -> Send AT command to debug -> Click close before leave:
Dynamic Domain Name Server (DDNS)
DDNS is to map the user's dynamic IP address to a fixed domain name resolution service. Every time the user connects to the network, the Client program will transfer the dynamic IP address of the host through information transmission. It is transmitted to the server program located on the host of the service provider, and the Server program is responsible for providing DNS services and implementing dynamic domain name resolution.
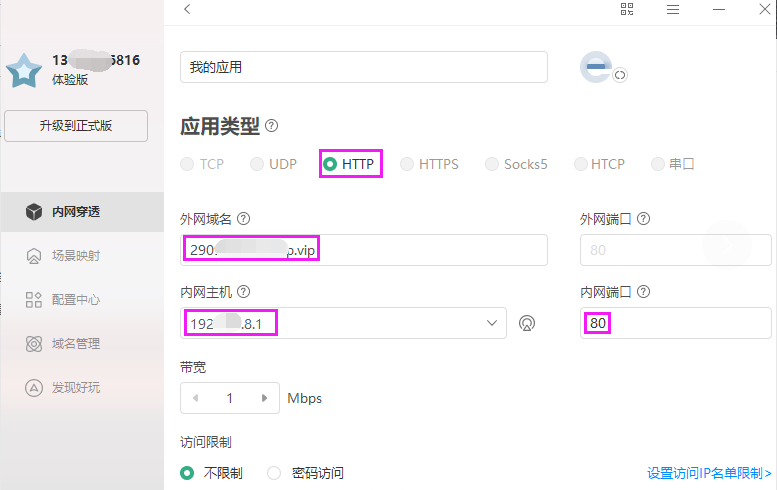
For example, to map the login IP of the 5G router—192.168.8.1 to the domain name of Oray, we can also log in to the router through the computer outside the LAN through the domain name:
- Register Oray -> download client (or Oray console) -> intranet penetration -> apply for HTTP domain name -> fill in intranet host IP (router login IP) and port number (80).
- Application -> DDNS->Status on -> Select service provider (here select Oray) -> Fill in the mapped domain name, login account, and password of Oray -> click Apply.
- Internet-connected browsers worldwide -> enter the domain name mapped by Oray -> log in to the router (the effect is equivalent to logging in to 192.168.8.1 in the local area network).
Application
File Sharing
- Application -> File Sharing -> FTP Server -> Status Enabled -> Login Method Select username and password to log in -> Enable writable:
- When the computer is connected to the 5G router -> open the file manager file or browser -> enter ftp://192.168.8.1:21 -> enter the router shared file directory.
Serial (232)
- Application -> Serial#(232) -> Open Status -> Select data transparent forwarding mode -> Configure baud rate 115200 -> Data center address (set to 120.79.2.0 here, you can build your own TCP server).
- Application -> Serial#(232) keep-alive packets are sent to the server regularly -> the content is aa(hex) -> the time interval is set to 2 seconds here.
- Connect the RS232 interface of USB to RS232/485/TTL to the RS232 interface of the router (TXD-RXD, RXD-TXD) -> upload the data sent by the serial port to the server -> send the data from the server to the serial port.

Note: The RS232 serial port is used as an example here, and the same is true for the RS485 serial port test.
System
Device
- System->Device->Modify->Modify the Device Name yourself;
- Copy from computer -> get time from computer and synchronize with computer time;
- System Reboot->The device will reboot after confirmation;
- Operation Mode->LTE/NR Modem->Select the third LTE/NR gateway mode here (5G module is installed by default on the device, please select a mode that can use 5G network);
- Language Settings -> You can set "Chinese" or "English" (default is English)";
- Time zone -> select the time zone corresponding to your location;
Software management
- System->Software Management -> View Version Number -> Firmware Version (4.3.3w-052221) -> Software Update -> Choose -> Select the corresponding firmware version to upgrade.
Password management
- System -> Software -> New Password -> Repeat New Password -> Modify.
SSH server
- Open SSH Server -> Open Remote SSH Access -> set the port number to 22 -> Apply.
- After the SSH server is enabled -> you can log in to the terminal through the SSH tool (xshell here) -> the account password is the same as that used to log in to the router (all are admin here).
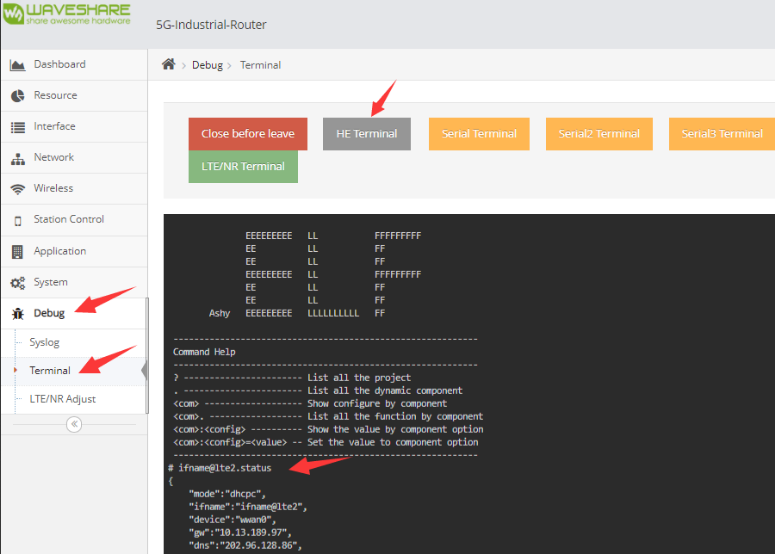
Debug
HE terminal
- Debug -> Terminal command line -> HE terminal -> Send HE command to control the device -> Click close before leaving:
[email protected] // Get 5G module network status information [email protected] // Get client information [email protected] //Get device LAN port information
4G/5G module terminal
- Debug -> Terminal command line -> 4G/5G module terminal -> Send AT command to debug -> Click close before leaving:
Resource
Develop software
FAQ
{{{5}}}
enable_uart=1
For Raspberry Pi 3B users, the serial port is used for Bluetooth and needs to be commented out:
#dtoverlay=pi3-miniuart-bt
Then reboot the Raspberry Pi:
sudo reboot
Make sure that both sides of the Raspberry Pi are handled in this way, the two modules of the A and B corresponding connection.
If you are using other 485 devices, make sure that the connection of A-A and B-B.
{{{5}}}
- Please enable the SPI of the Raspberry Pi.
- Considering the gold finger contact is poorly caused, please press down the tail and then access the test, so that the module and module good fit.
{{{5}}}
- SX1303 has lower power consumption than SX1202.
- SX1303 supports fine time stamps, which can be used for network positioning based on calculated time differences, while SX1302 does not support this function.
{{{5}}}
- Make sure the router has been powered on and enter the corresponding IP (if you have not changed the IP, the default is 192.1686.8.1).
- If you have forgotten the IP, please press the reset RESET button for about 30 seconds, all the lights; after lighting up, restore the factory settings, wait for the router to reboot, and then log in with the default IP.
{{{5}}}
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 PM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)