SIM800C GSM/GPRS HAT
| ||
Introduction
GSM/GPRS HAT for Raspberry Pi, Based on SIM800C.
| More |
Features
- Compatible with Raspberry Pi 2B/3B/3B+/Zero/Zero W.
- Supports SMS, GPRS, DTMF, HTTP, FTP, MMS, email, etc.
- Bluetooth 3.0, supports data transferring through Bluetooth.
- 2 x LEDs for indicating the module's working status.
- SIM card slot for 1.8V/3V SIM card.
- Baudrate auto detection (1200bps ~115200bps).
- Control via AT commands (3GPP TS 27.007, 27.005, and SIMCOM enhanced AT Commands).
- Supports SIM application toolkit: GSM 11.14 Release 99.
- Comes with online development resources and manual (examples for Raspberry Pi/Arduino/STM32).
GSM/GPRS
- Band
- GSM 850/EGSM 900/DCS 1800/PCS 1900 MHz
- Quad-band auto-search
- Compliant to GSM phase 2/2+
- Inputting power
- Class 4 (2W @ GSM 850/EGSM 900 MHz)
- Class 1 (1W @ DCS 1800/PCS 1900 MHz)
- GPRS connectivity
- GPRS multi-slot class 12 (default)
- GPRS multi-slot class 1~12 (configurable)
- GPRS data feature
- Downlink/Uplink speed: ≤ 85.6kbps
- Coding schemes: CS-1\CS-2\CS-3\CS-4
- Supports PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) for PPP connection
- Supports Packet Broadcast Control Channel (PBCCH)
- Supports Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD)
- SMS
- Supports: MT/MO/CB/Text/PDU mode
- SMS storage: SIM card
- Bluetooth
- Integrates AT commands
- Compliant to Bluetooth specification3.0 + EDR
- Supports SPP, OPP, HFP/HSP, etc.
- MISC
- Operating voltage: 5V
- Operating temperature: -40°C ~ 85°C
- Storage temperature: -45°C ~ 90°C
- Dimensions: 30.2mm x 65mm
Pinout
| PIN | Description |
|---|---|
| 5V | 5V power input |
| GND | Ground |
| RX1 | Serial port 1 Data receiver |
| Tx1 | Serial port 2 Data transmission |
| DTR | Sleep control pin. High: Sleep; Low: Wake-up (should set AT+CSCLK=1) |
| RI | Interrupt wake-up pin. this pin defaults to high and keeps low for 120ms when URCs are reported or SMS received. (should set "AT+CFGRI=1") |
| RX2 | Serial port 2 Data receiver |
| TX2 | Serial port 2 Data transmission |
| PWR | Power control pin |
| RESET | When power is on, you can reset the module by pulling down the reset pin. It is unavailable when power off |
Jumpers
| VCCIO | by change the jumper, you can set the working voltage to 3.3V or 5V. |
| PWR | Power control pin, connecting to P4 of Raspberry Pi by default. |
Indicators
| PWR | Light: Module is powered on with 5V voltage input. |
| NET | 64ms on / 800ms off - not registered on the network 64ms on/3000ms off - registered to the network 64ms on/300ms off - during data transmission Off - Shutdown or PSM sleep mode |
Working with PC
Hardware connection
In addition to the micro USB cable and GSM/Bluetooth antenna, users need to prepare the following before using the SIM800C module.
- A GPRS-compatible card.
- A serial module (TTL to USB like CP2102 USB UART Board).
- Insert the CPRS card into the card slot on the back of the module and connect the LTE antenna (The LTE antenna must be rotated to the outside of the board).
- Connect the CP2102 module to the corresponding serial port 1 (or serial port 2) of the SIM800C and use the USB cable to connect the module to the computer.
- Power the SIM800C module. At this time, the PWR light indicator should light up in red and the NET light should be off.
- Press the PWRKEY button and hold for about 1 second. Waiting for about 2 seconds. You should see that the NET light starts flashing. This means the module is powered on successfully.
- Open the serial assistant software, then select the corresponding serial port, and set the baud rate to 115200. Check the "Newlines" Options. By opening the extension you can see the already set AT commands. Click on the corresponding command to send it directly.
Networking testing
The following table lists some common AT commands that can be used to quickly and easily detect whether the SIM800C's AT serial communication and network connection are normal. Before following the steps of the network communication demonstration described in the table below, it is recommended to do a simple network test to confirm that the target network connection is normal and operable.
| Commands | Description | Return |
|---|---|---|
| AT | AT Test Command | OK |
| ATE | ATE1: Turns on echoing; ATE0: Turns off e'choing. | OK |
| AT+CSQ | Network signal quality query, returns a signal value | OK |
| AT+CGMR | Request firmware version | OK |
| AT+CREG? | Request network registration status | OK |
| AT+CGATT? | Check for GPRS attachment service status | OK |
TCP/IP Communication
The TCP/IP application of the SIM800 serial module has two connection modes, which can be set by the command AT CIPMUX=<n>. When AT CIPMUX is set to 0 (AT+CIPMUX=0), it is in single link mode; when AT CIPMUX is set to 1 (AT+CIPMUX=1), it is in multi-link mode. The module is set as single link mode by default.
In single link mode, the SIM800 serial module can operate in both transparent and non-transparent modes. In both transmission modes, the module can be configured as a TCP/UDP client or as a TCP server.
In multi-link mode, the SIM800 serial module can only work in non-transparent mode.
In this mode, the module can work as an absolute TCP/UDP connection client, which can establish a total of 6 connections; it can also be configured as a TCP server, and can also be configured with 5 TCP/UDP clients. SIM800C TCP/IP defaults to a multi-client architecture that supports a total of five sockets, including TCP or UDP.
With the following demonstrations, we will focus on the client communication of the SIM800C, in single-link non-transparent mode and transparent mode.
【Client communication in non-transparent mode】
| AT Commands | Description | Return |
|---|---|---|
| AT+CGATT? | Check GPRS attachment service status | OK |
| AT+CSTT="CMNET" | Set APN | OK |
| AT+CIICR | Establish a wireless connection | OK |
| AT+CIFSR | Retrieve the local IP address | OK |
| AT+CIPSTART="TCP","118.190.93.84",2317 | Establish a TCP client connection | OK |
| AT+CIPSTART="UDP","118.190.93.84",2317 | Establish a UDP client connection | OK |
| AT+CIPSEND=<string length> | Send a specified string length | OK |
| AT+CIPCLOSE | Close the connection | OK |
| AT+CIPSHUT | Close PDP context connection | OK |
【Client communication in transparent transmission mode】
| AT Commands | Description | Return |
|---|---|---|
| AT+CGATT? | Check GPRS attachment service status | OK |
| AT+CIPMODE=1 | Set to transparent mode | OK |
| AT+CSTT="CMNET" | Set APN | OK |
| AT+CIICR | Establish a wireless connection | OK |
| AT+CIFSR | Retrieve the local IP address | OK |
| AT+CIPSTART="TCP","118.190.93.84",2317 | Establish a TCP client connection | OK |
| AT+CIPSTART="UDP","118.190.93.84",2317 | Establish a UDP client connection | OK |
| AT+CIPSEND=<string length> | Send a specified string length | OK |
| AT+CIPCLOSE | Close the connection | OK |
| AT+CIPSHUT | Close PDP context connection | OK |
You can switch the transparent transmission mode or the command mode by the following steps:
- The escape sequence can be used to exit from transparent mode if the fourth parameter of AT+CIPCCFG is 1. The default escape sequence is +++, and to use this sequence, there should be a 1000ms idle period before this sequence and a 1000ms idle period after this sequence. Besides, the interval between each + should not exceed 1000ms, otherwise, it will be treated as TCP/IP data.
- DTR line (pin) of serial port can also be used. To use this method, AT&D1 should be set first. Pull the DTR line to Low for at least 1 second and then pull up, the module will switch from data mode to command mode and an “OK” string will be returned indicating the module is in command mode.
- Unintentionally, for TCP client connection, if the remote server closes the connection, the module will switch back to command mode automatically.
- Conversely, for TCP server connection, if the remote client closes the connection, the module will switch back to command mode automatically.
- Restarting the module.
HTTP Communication
This chapter introduces the HTTP communication function of SIM800C module, which is mainly divided into HTTP GET and HTTP POST. For more details information about the HTTP and FTP communication, please refer to SIM800C Series_IP_Application_Note
【HTTP GET】
| AT Commands | Description | Return |
|---|---|---|
| AT+SAPBR=3,1,"Contype","GPRS" | Configure bearer profile 1 | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=3,1,"APN","CMNET" | Configure the bearer profile APN | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=1,1 | Open a GPRS context | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=2,1 | Query a GPRS context | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=0,1 | Close the GPRS context | OK |
| AT+HTTPINIT | Check the HTTP connection status | OK |
| AT+HTTPPARA="CID",1 | Set parameters for HTTP session | OK |
| AT+HTTPPARA="URL","www.sim.com" | Set parameters for HTTP session | OK |
| AT+HTTPACTION=0 | GET session start | OK |
| AT+HTTPREAD | Read the data of the HTTP server | OK |
| AT+HTTPTERM | End HTTP service | OK |
【HTTP Post】
| AT Commands | Description | Return |
|---|---|---|
| AT+SAPBR=3,1,"Contype","GPRS" | Configure bearer profile 1 | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=3,1,"APN","CMNET" | Configure the bearer profile APN | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=1,1 | Open a GPRS context | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=2,1 | Query a GPRS context | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=0,1 | Close the GPRS context | OK |
| AT+HTTPINIT | Check the HTTP connection status | OK |
| AT+HTTPPARA="CID",1 | Set parameters for HTTP session | OK |
| AT+HTTPPARA="URL","www.sim.com" | Set parameters for HTTP session | OK |
| AT+HTTPDATA=100,10000 | Upload 100 bytes data, waiting for 10000ms | OK |
| AT+HTTPACTION=0 | GET session start | OK |
| AT+HTTPREAD | Read the data of the HTTP server | OK |
| AT+HTTPTERM | End HTTP service | OK |
Sending and receiving emails
The TCP/IP application of the SIM800 serial module has two connection modes, which can be set by the command AT+CIPMUX=<n>.
【Sending emails】
For sending emails some of the features this module offers are sending ordinary emails, set the email Carbon-copy; it can also email attachments, send it encoded as UTF-8 etc. We provide a simple operation demonstration of how to send an ordinary email.
| AT Commands | Description | Return |
|---|---|---|
| AT+SAPBR=3,1,"Contype","GPRS" | Configure bearer profile 1 | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=3,1,"APN","CMNET" | Configure the bearer profile APN. | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=1,1 | Open a GPRS context | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=2,1 | Query a GPRS context | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=0,1 | Close the GPRS context. | OK |
| AT+EMAILCID=1 | Configure email parameters | OK |
| AT+EMAILTO=30 | Set time value of the server response | OK |
| AT+SMTPSRV="smtp.ym.163.com",25 | Set SMTP server address and port | OK |
| AT+SMTPAUTH=1,"[email protected]","123456" | Set username and password | OK |
| AT+SMTPFROM="[email protected]","kaloha" | Set the sender address and name | OK |
| AT+SMTPRCPT=0,0,"[email protected]","kallanlw" | Set a recipient | OK |
| AT+SMTPRCPT=1,0,"[email protected]","john" | Set the CC email and name | OK |
| AT+SMTPSUB="Test" | Set the email subject | OK |
| AT+SMTPBODY=19 | Set the message body | OK |
| This is a new Email | Content of the email | OK |
| AT+SMTPSEND | Send the email | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=3,1,"Contype","GPRS" | Configure bearer profile 1 | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=3,1,"APN","CMNET" | Configure the bearer profile APN. | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=1,1 | Activate a GPRS context | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=2,1 | Query GPRS context | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=0,1 | Close the GPRS context. | OK |
| AT+EMAILCID=1 | Configures email parameters | OK |
| AT+EMAILTO=30 | Set time value of the server response | OK |
| AT+SMTPSRV="smtp.ym.163.com",25 | Set SMTP server address and port | OK |
| AT+SMTPAUTH=1,"[email protected]","123456" | Set username and password | OK |
| AT+SMTPFROM="[email protected]","kaloha" | Set sender address and name | OK |
| AT+SMTPRCPT=0,0,"[email protected]","kallanlw" | Set the email recipient address and name | OK |
| AT+SMTPRCPT=1,0,"[email protected]","john" | Set the email CC address and name | OK |
| AT+SMTPSUB="Test" | Set the email subject | OK |
| AT+SMTPBODY=19 | Set the message body | OK |
| This is a new Email | Content of email | OK |
| AT+SMTPSEND | Send email | OK |
【Receiving emails】
| AT Commands | Description | Return |
|---|---|---|
| AT+SAPBR=3,1,"Contype","GPRS" | Configure bearer profile 1 | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=3,1,"APN","CMNET" | Configure the bearer profile APN. | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=1,1 | Activate a GPRS context | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=2,1 | Query a GPRS context | OK |
| AT+SAPBR=0,1 | Close the GPRS context. | OK |
| AT+EMAILCID=1 | Configure email parameters | OK |
| AT+EMAILTO=30 | Set time value of the server response | OK |
| AT+POP3SRV="pop.ym.163.com","[email protected]","123456",110 | Set POP3 server address and account information | OK |
| AT+POP3IN | Log in to the POP3 server | OK |
| AT+POP3NUM | Get the total number of messages and its total size | OK |
| AT+POP3LIST=1 | Get the size of first email | OK |
| AT+POP3CMD=4,1 | Read the first message | OK |
| AT+POP3READ=1460 | Read the message content | OK |
【SMS sending and receiving】
The TCP/IP application of the SIM800 serial module has two connection modes, which can be set by the command AT+CIPMUX=<n>.
【Sending message】
- AT+CMGF=1: Sets the SMS mode to TEXT
- AT+CMGS="phone number"<Enter>, sets the recipient's mobile number, and then returns: ">"
- To send the required content, such as "Send massage test!", there is no need to press enter at the end.
- After editing the short message, send a “1A” in hexadecimal format for sending the message.
(1A is the key value of "CTRL+Z", which is used to tell the module to perform the “send” operation. To cancel the operation, send 1B or "ESC")
- After the transmission is done, the module returns +CMGS:15 to confirm the transmission is successful.
【Receiveing message】
- Send this message on the phone: "This is a receiving test for SIM7600X!" to the test module
- When receiving the information, the serial port will brake down the report to specific format, such as "SM", 20. This means that there are 20 messages in the SM, and the message sent is the 20th one.
- For reading messages use AT+CMGR=20. This reads the 20th message (AT+CMGL="ALL" reads all messages)
- For deleting messages: AT+CMGD=20, as shown in the picture below
- The displayed information is converted to text by a transcoder.
Bluetooth Debugging
The SIM800 serial module supports Bluetooth 3.0 and other profiles such as SPP, OPP and HFP/HSP.
The commands in the table below mainly demonstrates the Bluetooth SPP serial communication functionality.
For more information about Bluetooth, please refer to SIM800C_Series_BT_Application_Note
| AT Commands | Description | Return |
|---|---|---|
| AT+BTPOWER=1 | Turn on the Bluetooth power | OK |
| AT+BTHOST? | Query Bluetooth name and address | Returns the bluetooth name and MAC address |
| AT+BTSCAN=1,10 | Search for nearby Bluetooth devices | Returns the searched Bluetooth device information |
| AT+BTPAIR=1,1 | Digital confirmation mode response pairing | OK |
| AT+BTACPT=1 | Accept client connection request | OK |
| AT+BTSPPSEND | Send data | Return > to start entering data,
Send hexadecimal 1A to end sending |
| AT+BTPOWER=0 | Turn off the Bluetooth power | OK |
Test steps:
- 1. Prepare an Android cellphone and install the Bluetooth serial APP: Serial Bluetooth
- 2. On the module, send an AT command to turn on the Bluetooth power: AT+BTPOWER=1
- 3. Inquiry the module's own Bluetooth name and address: AT+BTHOST?
- 4. Turn on the Bluetooth of your Android cellphone, search for nearby Bluetooth devices, find the Bluetooth name and address of the module, and initiate a connection request.
- 5. At this time, the serial port of the module will receive a prompt (+BTPAIRING: “Mobile Bluetooth Name”, address, pairing code), then send confirmation pair: AT+BTPAIR=1,1
- 6. Open the Serial Bluetooth APP on your cellphone (or scan the QR code below), switch to Device, and select to connect SIM800 Bluetooth.
- 7. Then the module's serial port receives the prompts (+BTCONNECTING: "Address", "SPP"), and sends the request of receiving the connection: AT+BTACPT=1.
- 8. After Bluetooth communicates, disconnect the power of the Bluetooth: AT+BTPOWER=0
Working with Raspberry Pi
Hardware connection
SIM800C GSM GPRS HAT has 40PIN header on board, compatible with any revision of Raspberry Pi.
| SIM800C GMS/GPRS HAT | Raspberry Pi |
|---|---|
| 5V | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| RXD | TXD (BCM P14) |
| TXD | RXD (BCM P15) |
| PWR | P7 (BCM P4) |
Software Setting
【Pin initialization】
The default PWR pin of the module is to jump to the P4 pin of raspberry pi by placing a jumper cap. In order to ensure that SIM800C GSM/GPRS HAT can work properly after it is connected to raspberry pi, it is necessary to initialize the level output of raspberry pi board pin.
- Download demo codes from wiki page. Extract and copy the SIM800C folder to /home/pi of Raspberry Pi
- Open Terminal,enter /home/pi/ then execute commands below
chmod 777 pi_gpio_init.sh
- Set the script to auto-run after booting.
sudo nano /etc/rc.local
- Add command before exit 0
sh /home/pi/SIM800C/pi_gpio_init.sh
【Serial port setting】
The serial port of Raspberry Pi is set for shell login by default. Therefore, we need to disable shell login function and enable hardware serial
- Enter configuration page
sudo raspi-config
- Choose Interfacing Options->Serial->no->yes
- Open /boot/config.txt file, make sure the state below is added to the file:
enable_uart=1
- reboot Raspberry Pi
Minicom Debugging
Press the PWRKEY button and hold for about 1 second. Waiting for about 2 seconds. You should see that the NET light starts flashing. This means the module is powered on successfully.
Install minicom on your Raspberry
sudo apt-get install minicom
Then execute command minicom -D /dev/ttyS0 to run the minicom
Note that the defualt baud rate is 115200, serial port is ttyS0 (for Raspberry Pi 3B/3B+ is ttyS0, for Raspberry Pi Zero/2B it should be ttyAMA0)
PPP networking
About the PPP networing, you can refer to this page: SIM868 PPP Dail-up Networking
BCM2835 Demo
Download the sample program, copy the entire BCM2835 folder to the Raspberry Pi, for example, put it under /home/pi/, and change the name to SIM800C.
BCM2835 Installation
Enter the bcm2835 directory under SIM800C, compile and install the bcm2835 library, and execute the command:
./configure & make & sudo make check & sudo make install
Compile and Run
The following is an example of compiling and running the AT sample program:
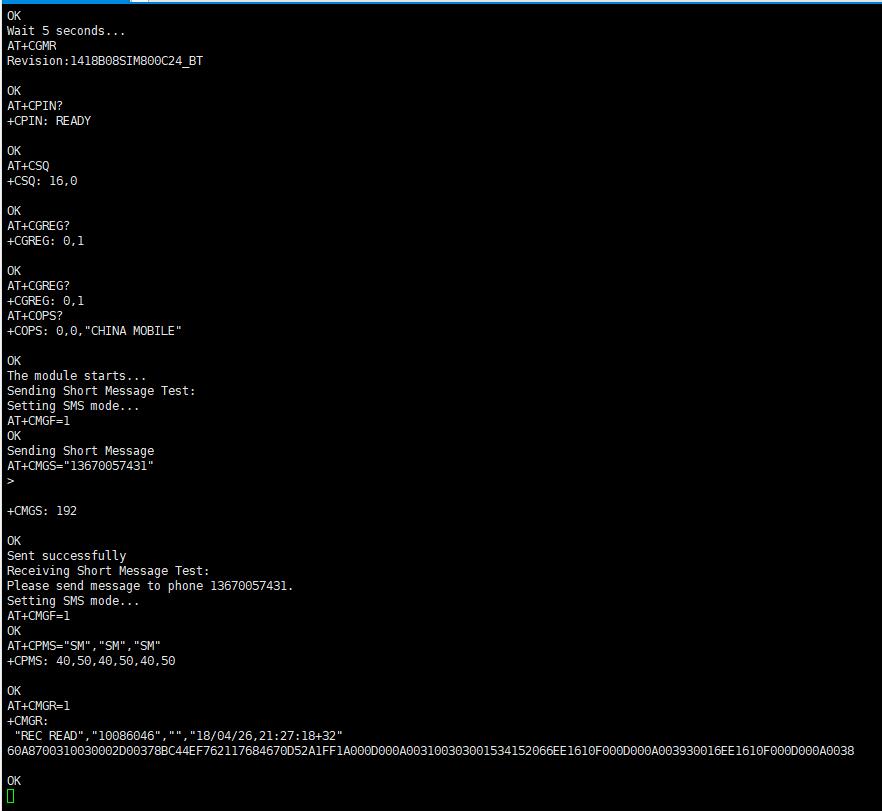
cd /home/pi/SIM800C/bcm2835/examples/AT sudo make clean && sudo make && sudo ./main
- Sample program test screenshot:
Python Demo
Enter the python directory under SIM800C and execute the corresponding sample program, such as send_message.py:
python send_message.py
Work with Arduino
Hardware Connection
Hardware connection to the development board UNO PLUS / Arduino UNO:
| SIM800C GSM/GPRS HAT | UNO PLUS / Arduino UNO |
|---|---|
| 5V | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| TX1 | 2 |
| RX1 | 3 |
Arduino Example
Work with Jetson Nano
Hardware Connection
Jetson Nano has an onboard 40Pin GPIO interface, SIM800C GSM/GPRS HAT can be directly connected and used, and Jetson Nano's terminal access serial port does not affect the serial communication with SIM800C GSM/GPRS HAT (ie Pin10 and Pin8).
| SIM800C GSM/GPRS HAT | Jetson Nano |
|---|---|
| 5V | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| TXD | 10 (Board encoding) |
| RXD | 8 (Board encoding) |
| PWRKEY | 7 (Board code) |
Jetson Nano Minicom Serial Debugging
1. Connect the SIM800C GSM/GPRS HAT to the Jetson Nano, press the PWRKER key for two seconds, and then turn it on.
2. Use SERIAL to log in to the Jetson Nano terminal, install minicom, and enter:
sudo apt-get install minicom
3. Run minicom for serial port debugging, enter in the terminal:
sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyTHS1 -b 115200
4. Send the AT command to test, press the PWRKEY button for three seconds to start the shutdown when exiting, and exit the minicom, first press Ctrl+A, then press X, and finally press ENTER:

Python Demo
- After installing the library function:
sudo apt-get python3-pip sudo pip3 install pyserial sudo apt-get install p7zip
- Use the wget tool to download the source code to the specified folder of Jetson Nano, and copy the following command:
mkdir -p ~/Documents/SIM800C_GSM_GPRS wget -P ~/Documents/SIM800C_GSM_GPRS/ https://files.waveshare.com/upload/9/96/SIM800C_GSM-GPRS_HAT_Code.7z
Enter the directory where the source code was just created and downloaded, and use the p7zip tool to unzip it to the current directory:
cd ~/Documents/SIM800C_GSM_GPRS/ sudo p7zip --uncompress SIM800C_GSM-GPRS_HAT_Code.7z sudo chmod 777 -R Jetson\ Nano
AT
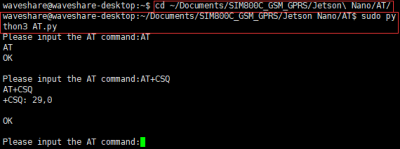
Connect SIM800C GSM/GPRS HAT to Jetson Nano, connect to the antenna, press and hold the PWRKEY button for two seconds to power on, and press Ctrl+C when exiting. Enter the Jetson Nano/AT directory and execute the command:
cd ~/Documents/SIM800C_GSM_GPRS/Jetson\ Nano/AT/ sudo python3 AT.py
SMS
The SIM800C GSM/GPRS HAT is connected to Jetson Nano, and the small pepper antenna is connected. The demo uses software to start and shut down, and there is no need to press the button to turn on and off the machine. This demo will automatically shut down the software after sending the information www.waveshare.com to the specified number. When users use SMS demo, they must first use tools such as vim to change the number on line 10 in the SMS.py file, replace * with numbers, and keep the ' symbol.
Enter the Jetson Nano/SMS directory and execute the following command:
cd ~/Documents/SIM800c_GSM_GPRS/Jetson\ Nano/SMS/ sudo python3 SMS.py
TCP
The SIM800C GSM GPRS HAT is connected to the Jetson Nano, and the pepper antenna is connected. The routine uses the software to turn on and off, and there is no need to press the button to turn on and off the machine.
Enter the Jetson Nano/TCP directory and execute the command:
cd ~/Documents/SIM800C_GSM_GPRS/Jetson\ Nano/TCP sudo python3 TCP.py
Resources
Document
Demo
Related Instruction
Tools
SIM800C Datasheets
- SIM800 Series_AT Command Manual_V1.10
- SIM800 Series_Bluetooth_Application Note_V1.08
- SIM800 Series_Email_Application Note_V1.01
- SIM800 Series_IP_Application Note_V1.03
- SIM800 Series_MMS_Application Note_V1.01
- SIM800 Series_NTP_Application Note_V1.02
- SIM800 Series_Serial Port_Application Note_V1.01
- SIM800 Series_SSL_Application Note_V1.02
- SIM800 Series_TCPIP_Application Note_V1.02
- SIM800C_Hardware_Design_V1.05
- SIM800 Series_Multiplexer_Application Note_V1.02
- More...
FAQ
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 PM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)