RM500U-CN 5G HAT
| ||
| ||
| ||
Overview
Features
- Integrates extensive network protocols, with multi drivers and software support, compatible with different OS including Windows / Linux / Android.
- USB 3.1 port (USB 2.0 compatible) for connecting to PC, Raspberry Pi, or Jetson Nano host board to enable high-speed 5G communication.
- Standard M.2 B KEY slot, compatible with different 5G modules: RM500U-CN / RM500Q-GL / RM500Q-AE / RM502Q-AE series.
- Onboard UART, PWR, and RST control pin, built-in voltage level translator, enabled via DIP switch, for use with hosts like Raspberry Pi or Arduino.
- Onboard USB-C connector, enabled via a switch, for connecting the standalone power supply for the module, allows more loads, a stable and flexible power supply.
- Onboard power supply on/off switch, reset button, and LED indicator, easy to turn on/off the module or monitor the operating status.
- 2 x SIM card slot, dual card single standby, switchable via AT command. (Some 4G/5G modules do not support dual sim cards, depending on the actual supporting modules.)
- High-efficiency power supply circuit, up to 3A output current.
Version Options
This product is available with an optional 5G module and also with the optional case.


Selection Guide
| 5G Sub-6 | RM500U-CNV | RM500Q-GL 5G HAT | RM502Q-AE 5G HAT | RM520N-GL | RM530N-GL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Picture | 
|

|

|

|

| |
| 5G Standard | 3GPP R15 | 3GPP R16 | ||||
| 5G Chip | UNISOC | Qualcomm | ||||
| 5G | Sub-6 GHz | Sub-6 GHz & mmWave | ||||
| Region/Operator | China, EMEA, Asia-Pacific | except Americas | except China | Global | ||
| Operating Temperature | -30°C ~ +75°C | |||||
| Extension Temperature | -40°C ~ +85°C | |||||
| Module Size | 30.0 × 52.0 × 2.3 (mm) | |||||
| Module Weight | 8.8g | 8.7g | 8.8g | |||
| Power Supply | 3.3~4.4V, Typ. 3.7V | 3.135~4.4V, Typ. 3.7V | ||||
| Power Consumption | 78μA @ shutdown; 5.1mA @ hibernate; |
70μA @ shutdown; 4.0mA @ hibernate; |
80μA @ shutdown; 4.2mA @ hibernate; |
195μA @ shutdown; 4.7mA @ hibernate; |
173μA @ shutdown; 5.1mA @ hibernate; | |
| Frequency Band | ||||||
| 5G | 5G NR | - | n257, n258, n260, n261 | |||
| 5G NR NSA | n41, n78, n79 | n41, n77, n78, n79 | n1, n2, n3, n5, n7, n8, n12, n20, n25, n28, n38, n40, n41, n48, n66, n71, n77, n78, n79 | n1, n2, n3, n5, n7, n8, n12, n13, n14, n18, n20, n25, n26, n28, n29, n30, n38, n40, n41, n48, n66, n70, n71, n75, n76, n77, n78, n79 | ||
| 5G NR SA | n1, n2, n3, n5, n8, n28, n41, n77, n78, n79 | n1, n2, n3, n5, n7, n8, n12, n20, n25, n28, n38, n40, n41, n48, n66, n71, n77, n78, n79 | n1, n2, n3, n5, n7, n8, n12, n13, n14, n18, n20, n25, n26, n28, n29, n30, n38, n40, n41, n48, n66, n70, n71, n75, n76, n77, n78, n79 | |||
| LTE | LTE-FDD | B1, B3, B5, B8 | B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B7, B8, B12, B13, B14, B17, B18, B19, B20, B25, B26, B28, B29, B30, B32, B66, B71 | |||
| LTE-TDD | B34, B38, B39, B40, B41 | B34, B38, B39, B40, B41, B42, B43, B48 | ||||
| LAA | - | B46 | ||||
| UMTS | WCDMA | B1, B5, B8 | B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B8, B19 | B1, B2, B4, B5, B8, B19 | ||
| GNSS | - | GPS / GLONASS / BeiDou(Compass) / Galileo / QZSS (only RM520N-GL and RM530N-GL support) | ||||
| Data Rate | ||||||
| 5G mmWave | - | DL 4.0Gbps; UL 1.4Gbps | ||||
| 5G SA Sub-6 | DL 2Gbps; UL 1Gbps |
DL 2.1Gbps; UL 900Mbps |
DL 4.2Gbps; UL 450Mbps |
DL 2.4Gbps; UL 900Mbps | ||
| 5G NSA Sub-6 | DL 2.2Gbps; UL 575Mbps |
DL 2.5Gbps; UL 600/650Mbps |
DL 5Gbps; UL 650Mbps |
DL 3.4Gbps; UL 550Mbps | ||
| LTE | DL 600Mbps; UL 150Mbps |
DL 1.0Gbps; UL 200Mbps |
DL 2Gbps; UL 200Mbps |
DL 1.6Gbps; UL 200Mbps | ||
| UMTS | DL 42.2Mbps; UL 11Mbps |
DL 42Mbps; UL 5.76Mbps | ||||
What's On Board
| Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ① | Raspberry Pi GPIO Header | Easily connect to Raspberry Pi |
| ② | Switch | Enable the corresponding pin |
| ③ | M.2 Interface | Compatible with RM500U-CN/RM500Q-CN/RM500Q-GL/RM50XQ-AE and other series of 5G modules |
| ④ | SIM Card Holder | Onboard two SIM card slots, dual card single standby. The default SIM1 card slot works, SIM2 is on the back, requires module support and must be switched through AT commands |
| ⑤ | USB 3.1 Connector | Backward compatible with USB 2.0, can be used to connect to PC/Raspberry Pi/Jetson Nano, etc. |
| ⑥ | USB Type-C Connector | 5V 3A input; stable and flexible power supply |
| ⑦ | Audio Port | SIM82XX series support audio function, RM50XX series do not support this audio function |
| ⑧ | Antenna Connector | Onboard four-way antenna, strong signal |
| ⑨ | Reset Switch | One-key reset |
| ⑩ | Power Switch | To facilitate the power supply mode of the control module:
——If set to USB, the module will provide power through the "⑤.USB3.1 interface"; |
| ⑪ | Cooling Fan | Cool down the Raspberry Pi and 5G module at the same time |
| ⑫ | Indicator | Check the module running status anytime, anywhere |
| Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ⑬ | Cooling Fan | Simultaneously cooling Raspberry Pi and 5G modules |
| ⑭ | SIM Card Slot 2 | Switchable via AT command (module is required) |
| ⑮ | Module Setting Switch | Switch A to ON for SIM7600X/A7906X/IM7906X/SIM7912X series 4G M.2 module; Switch B to ON, for SIM8202X/SIM8200EA/SIM8262X series 5G M.2 module; Switch C to ON, for RM50X/RM520N-GL/EM06X series 5G/LTE-A M.2 module |
| ⑯ | USB Interface Pad | USB 2.0 interface pad |
| ⑰ | NAU8810X Audio Chip | For SIMN7600X/SIM8XXX series module, does support RM5XX and EM06XX series module |
| ⑱ | Fan Header | 5V power supply for cooling fan |
Pinout Definition
After connecting to Raspberry Pi, these pins (TX, RX, D4 and D6) can be connected or not through the DIP switch:

4G/5G modules function testing
| Category | 4G/5G Module | Network Communication | GNSS Positioning | Voice calls through Earphone Port |
Dual SIMs | UART Interface | External Power Supply? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5G | SIM8202G-M2 | 5G/4G/3G | Support | Support | Support | Support | Optional, but recommended |
| 5G | SIM8200EA-M2 | 5G/4G/3G | Support | Support | Support | Support | Optional, but recommended |
| 5G | RM500U-CN | 5G/4G/3G | NOT Support | NOT Support | Support | Support | Recommended |
| 5G | RM500Q-GL | 5G/4G/3G | Support | NOT Support | Support | NOT Support | Recommended |
| 5G | RM500Q-AE | 5G/4G/3G | Support | NOT Support | NOT Support | NOT Support | Recommended |
| 5G | RM502Q-AE | 5G/4G/3G | Support | NOT Support | NOT Support | NOT Support | Recommended |
| LTE-A | EM06-E | LTE-A/4G/3G | NOT Support | NOT Support | NOT Support | NOT Support | Optional |
| LTE-A | A7906E | LTE-A/4G/3G | NOT Support | NOT Support | NOT Support | NOT Support | Optional |
| 4G | SIM7600G-H-M2 | 4G/3G/2G | Support | Support | NOT Support | Support | Optional |
4G/5G Module Compatibility
If you need to use the M.2 TO 4G/5G HAT for other 4G/5G modules, you can refer to the M.2 connection diagram below, check whether there is any pin conflict, and then connect to test:

Working With Windows
Install Drivers
- After connecting the RM500U-CN 5G HAT to the computer through a double-ended usb3.0 data cable, there will be a series of devices without drivers installed on other devices:
- Download the driver to your computer and unzip the compressed package.
- Enter the RM500U_Driver directory.
- Click setup.exe to install the driver. After the installation is complete, the device manager will generate the following devices:
Common AT Commands
EM25X, EM06E and RM50X series 4G/5G module support AT command control, some basic AT commands are shown in the table below:
| Command | Description | Return |
|---|---|---|
| AT | AT Test Command | OK |
| ATE | ATE1 sets echo ATE0 turns off echo |
OK |
| AT+CGMI | Query module manufactor | OK |
| AT+CGMM | Query module model | OK |
| AT+CGSN | Query product serial number (IMEI) | OK |
| AT+CSUB | Query module version and chip | OK |
| AT+QGMR | Query firmware version serial number | OK |
| AT+IPR? | Set module hardware serial port baudrate | +IPR: OK |
| AT+CFUN=1,1 | Reset module | OK |
| AT+QUIMSLOT? | Query SIM card selection: Return 1, select SIM card 1; Return 2, select SIM card 2 |
+QUIMSLOT: 1/2 OK |
| AT+CPIN? | Query SIM card status, return READY, SIM card can normally identify | +CPIN: READY |
| AT+COPS? | Query the current operator, after normally connecting to the network, it will return the operator's information | +COPS: OK |
| AT+CEREG? | Query the network registration status | +CEREG: OK |
| AT+C5GREG? | Query 5G network registration status | +C5GREG: OK |
| AT+QENG="servingcell" | Query UE system information | |
| AT+QNWPREFCFG="mode_pref",AUTO | Auto-network mode | OK |
| AT+QNWPREFCFG="mode_pref",NR5G | Prioritize 5G network | OK |
| AT+QNWPREFCFG="nr5g_band",79 | Fixed N79 frequency band | OK |
| AT+QNWPREFCFG="mode_pref",LTE | Prioritize 4G network | OK |
SIM Card Selection
The 5G HAT has two SIM card slots onboard, a dual SIM card, and single standby, which can be switched and enabled by AT command.
- SIM card 1 is selected by default, You can use the following command to query and confirm:
AT+QUIMSLOT?
- To switch SIM card 2, please use the following command:
AT+QUIMSLOT=2
- Switch back to SIM card 1, please use the following command:
AT+QUIMSLOT=1
- Check whether the corresponding card slot recognizes the SIM card:
AT+CPIN?
Windows System
RM500U-CNV MBIM Dial-up Network Access
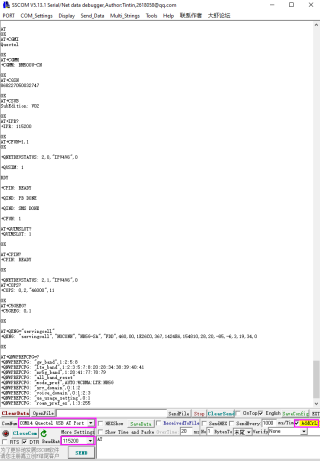
AT+CPIN? AT+QCFG="usbnet",2 AT+CFUN=1,1 AT+QNETDEVCTL=2,3,1
RNDIS Dial-up Internet Access
- Open the RM50X AT port and send the following commands to dial up the Internet:
AT+QENG="servingcell" AT+QCFG="ethernet",0 AT+QCFG="nat",1 AT+QCFG="usbnet",3 AT+QNETDEVCTL=2,3,1 AT+CFUN=1,1
- And then you can find that there are some unrecognized devices in the Device Manager on the computer, such as RNDIS (with an exclamation mark).
- Right-click the 'RNDIS', search "Update Divers" and select "Let me pick from a list of available drivers on my computer", then select "Network adapters" from the device list.
- Select "Microsoft" in the manufacturer list of the Network adapters window, and then select "Remote NDIS Compatible Device" in the list on the right, which is the remote NDIS compatible device.
- Click 'Next' and wait for the installation to finish, the RNDIS Kitl device will be installed successfully.
- If it cannot connect to the network, please set it to obtain the IP automatically.
Network Speed Test
- Install speed testing software, such as Internet speed manager and other speed testing software, you can choose to download the speed test at www.speedtest.cn/pc/download.
About the speed testing
As there will be many inconsistencies between actual and laboratory conditions that will result in 5G speeds that are not ideally stable at 100MBPS, there are the following.
- Base station distance, the closer to the 5G base station the better the signal and the faster the speed.
- Base station load, the fewer people using it the faster it will be, and the slower it will be during peak commuting periods.
- Number of base stations: due to the spectrum, an equal amount of 4G coverage requires double the number of 5G base stations.
- Operator: you need to confirm your 5G card, and whether the speed is limited, you can regularly ask the operator to reset your network.
- Indoor is worse than outdoor: building penetration attenuation, and indoor bypass attenuation.
PS: The current number of base stations still does not have good coverage, and the speed measurement is not quite the same in different locations.
Working with Raspberry Pi
Ubuntu System Use
- Raspberry Pi programming Ubuntu 22.04 system image.
- Confirm system version information:
sudo apt-get install screenfetch screen fetch uname -r
The USB device descriptor needs to be loaded for the first use
In order to identify a module, the module's VID and PID needs to be added to the file [kernel].
- Check the VID and PID of RM500U.
lsusb
- Install gcc and make tools
sudo apt-get install gcc sudo apt-get install make
- Add VID and PID:
sudo su sudo modprobe option sudo sh -c 'echo "2c7c 0900" > /sys/bus/usb-serial/drivers/option1/new_id' sudo echo 2c7c 0900 > /sys/bus/usb-serial/drivers/generic/new_id
ECM Dial-up
- Open minicom:
sudo apt-get install minicom sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyUSB2
- Send the following commands in minicom for ECM dialing:
AT+CPIN? AT+QENG="servingcell" AT+QCFG="ethernet",0 AT+QCFG="usbnet",1 AT+QNETDEVCTL=1,3,1 AT+QNETDEVCTL=1,1,1 AT+QCFG="nat",0 AT+CFUN=1,1
- After configuring the ECM mode, CTRL+A -> X -> Yes to exit minicom.
- Use the following commands to get IP and set DNS:
sudo dhclient -v enxe2f1fbfdd5e7 sudo apt-get install udhcpc sudo udhcpc -i enxe2f1fbfdd5e7 sudo route add -net 0.0.0.0 enxe2f1fbfdd5e7
- After dialing, the Raspberry Pi can see that enxe2f1fbfdd5e7 has obtained the IP through the following command (different systems are different, so the actual obtained IP shall prevail):
ifconfig
- Test enxe2f1fbfdd5e7 network status:
ping -I enxe2f1fbfdd5e7 www.baidu.com
Working with Raspberry Raspbian System
Add VID and PID
- Add the following drivers for the mainstream systems:
sudo su sudo modprobe option sudo sh -c 'echo "2c7c 0900" > /sys/bus/usb-serial/drivers/option1/new_id' sudo echo 2c7c 0900 > /sys/bus/usb-serial/drivers/generic/new_id
- For other systems, you need to compile ko file to input the kernel to drive the driver:
sudo apt-get install unzip wget https://files.waveshare.com/wiki/RM500U-CN/Driver/Linux/RM500U_FOR_RPI.zip unzip RM500U_FOR_RPI.zip sudo chmod 777 -R RM500U_FOR_RPI cd RM500U_FOR_RPI sudo ./install.sh
- After adding PID and rebooting the Raspberry Pi, you need to input the following commands on the command line interface for USB0-USB4 USB device descriptors:
ls /dev/ttyUSB*
RNDIS Dial-up Internet
- Open minicom.
sudo apt-get install minicom sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyUSB2
- Send the following command RNDIS dial in minicom:
AT+QCFG="nat",1 AT+CPIN? AT+QENG="servingcell" AT+QCFG="usbnet",3 AT+QNETDEVCTL=2,3,1 AT+CFUN=1,1
- If the IP is not obtained or the network is not connected, you can use the following commands to get it:
sudo dhclient -v usb0 sudo apt-get install udhcpc sudo udhcpc -i usb0 sudo route add -net 0.0.0.0 usb0 auto usb0 iface usb0 inet dhcp
Raspberry Pi Serial Port Enable
Since the Raspberry Pi serial port is used for terminal debugging by default, if you need to use the serial port, you need to modify the Raspberry Pi settings. Execute the following command to enter the Raspberry Pi configuration:
sudo raspi-config
Select Interfacing Options ->Serial ->NO ->YES to disable serial debugging.

Open the /boot/config.txt file, and find the following configuration statement to enable the serial port, if not, add it at the end of the file:
enable_uart=1
Restart to take effect:
1. Insert the module into the Raspberry Pi, and turn the S_TX and S_RX of the DIP switch to ON:

2. Install minicom, minicom is a serial debugging tool for the Linux platform:
sudo apt-get install minicom
3. Open ttyS0 through minicom——ttyS0 is the serial port of Raspberry Pi 3B/3B+/4B, the default baud rate is 115200;
sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyS0
4. For Raspberry Pi 2B/zero, the user serial device number is ttyAMA0; you can use the following command line to confirm, serial0 is the selected serial device number, as shown below:

OpenWrt
Introduction
Soft routing is using desktops or servers and other equipment with software. It mainly depends on the settings of the software to achieve the functions of the router. The hard routing is a unique hardware device, including a processor, power supply, and embedded software to provide router functionality.
OpenWrt is a very popular soft routing system. It is a highly modular and highly automated embedded Linux system with powerful network components and scalability. It is often used in industrial control equipment, routers, and other equipment.
In addition to the functions of general home routers, OpenWrt soft routing can also achieve port forwarding, intranet penetration, 4G networking, FTP server, and more powerful functions.
Burn the image
Download the RPI OpenWrt system, unzip the system in the Imgs directory, and use the burning tool to burn the system to the SD card.
Login and initial settings
- After the OpenWrt system is turned on, the Raspberry Pi is equivalent to a router. Therefore, use a network cable to connect the Raspberry Pi to the computer according to the use of the router (you can also use the mobile phone to search for WIFI, the default name is "OpenWrt").
- You can set the language to auto first.
- Enter 192.168.1.1 on the web page, the default user name: root, and the default password: password, enter the OpenWrt web management interface.
- Set WIFI password: Network —> Wireless —> interface configuration —> Wireless security.
- Create the new interface: Network -> Interface -> Create interface.
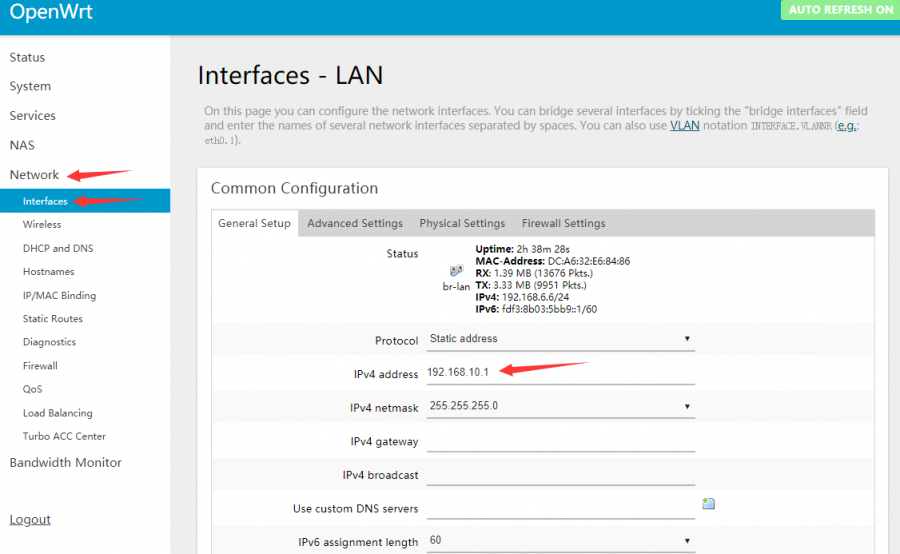
- Modify the IPv4 address of the LAN port to a different IP that is not the same as the LAN port IP of other routers in your home. (Many routers default the LAN port IP to 192.168.1.1. If you do not modify the IP of the OpenWrt, it will easily lead to conflicts and failure to connect to the Internet).
If necessary, it is also recommended to disable the IPv6 allocation length. After the modification is completed, click "Save & Apply", and re-use 192.168.10.1 to access the OpenWrt console.
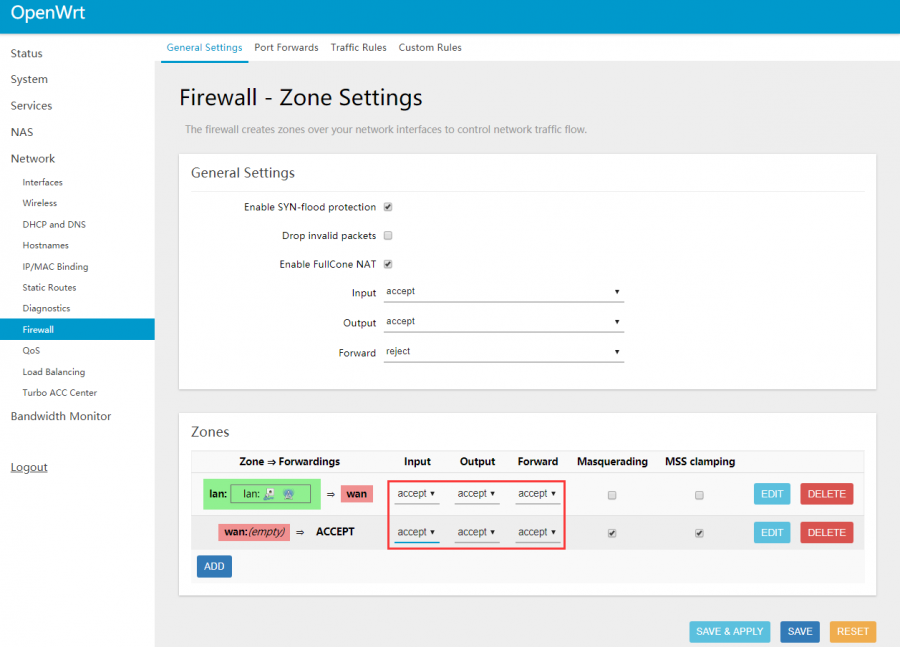
- In addition, it is recommended to adjust the Firewall setting to connect the OpenWrt terminal and Web management interface through the local area.
Network —> Firewall, change all "reject" to "accept", and click "Save & Apply" after modification, as shown in the picture below:
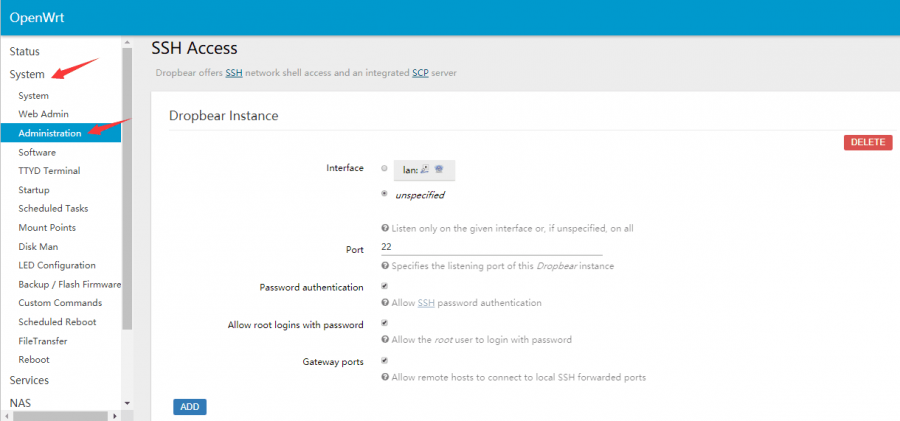
- And then select System -> Administration, modify the allowed interface for SSH access to "unspecified" (that is, any interface can be accessed by ssh), check the Gateway port, and click "Save & Apply" after the modification is completed.
At this point, you can connect to the OpenWrt web management interface or terminal through the IP address of the LAN port or wan port.
Configure networking
- Insert the SIM card into the slot of the communication module -> All 5G antennas are connected, after connecting to the Raspberry Pi 4B via USB -> Power on;
- Change the mobile communication module to RNDIS mode (USB network sharing mode), which can be changed in Openwrt by sending the following command via minicom:
sh -c 'echo "2c7c 0900" > /sys/bus/usb-serial/drivers/option1/new_id' sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyUSB2 AT+QENG="servingcell" AT+QCFG="usbnet",3 AT+QNETDEVCTL=2,3,1
AT+QCFG="usbnet",1
- Add new interface: Network -> Interfaces -> Add New Interface.
- Create new interface: name of new interface - SIM8202G; protocol of new interface - DHCP client; include the following interfaces - ethernet adapter: "usb0"; submit.
- Configuration interface: Firewall settings - wan; save & apply.
- Wireless configuration: Network -> Wireless -> Modify -> Interface Configuration -> Basic Settings -> Check SIM8202G (Defined by yourself) and lan in Network; Save & Apply.
Working with Jetson Nano
Hardware Connection
Connect the RM500U-CN with a double-ended usb3.0 data cable, and connect an external 5V power supply to the Type-C power supply port of the RM500U-CN 5G HAT, as shown in the figure:

Load USB Device Descriptor
In order to identify the module, the module's VID and PID information needs to be added to the file [kernel].
- View VID and PID of RM500U:
lsusb
sudo apt-get install unzip wget https://files.waveshare.com/upload/9/93/RM500U_CN_For_Jetson_nano.zip unzip RM500U_CN_For_Jetson_nano.zip sudo chmod 777 -R RM500U_CN_For_Jetson_nano cd RM500U_CN_For_Jetson_nano sudo ./install.sh sudo reboot
After successfully adding the PID and restarting Jetson nano, enter the following command in the command line interface to display five device symbols USB0-USB4.
ls /dev/ttyUSB*
RNDIS
- Enable minicom.
sudo apt-get install minicom sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyUSB2
- Send the following command ECM in minicom.
AT+CPIN? AT+QCFG="usbnet",3 AT+QNETDEVCTL=2,3,1 AT+CFUN=1,1

After the module restarts and the NET light is on, use the following command to check the network status (optional).
AT+QENG="servingcell"
Get the IP and set the DNS with the following commands:
sudo dhclient -v usb1 sudo apt-get install udhcpc sudo udhcpc -i usb1 sudo route add -net 0.0.0.0 usb1
After dialing, you can see that usb1 gets the IP through the following command:
ip route
ping -I usb1 www.baidu.com
Resources
Program
Assembly drawing
Software
Datasheet
Related Application Cases
FAQ
RM500U-CN and RM500Q-GL modules support installing two SIM cards at the same time, and you can enable one SIM card to work with AT commands:
*Select SIM card 1 by default, and check it with the following command: AT+QUIMSLOT? *Switch it to SIM card 2 with the following command: AT+QUIMSLOT=2 *Switch it to SIM card 1 with the following command: AT+QUIMSLOT=1 *Query whether the corresponding card slot identify the SIM card: AT+CPIN?
- If the corresponding SIM card can not be identified, it may because the DIP switch has not enable the corresponding module, please make the DIP switch corresponding to C turn on:
{{{5}}}
Quectel/Qualcomm:
AT+QENG="servingcell" at+qcfg="pcie/mode",1 at+qcfg="data_interface",1,0 at+qeth="eth_driver","r8125",1 AT+QMAPWAC=1 at+qmap="mpdn_rule",0,1,0,1,1,"FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF"
Quectel/Spreadtrum:
AT+QCFG="pcie/mode",1 AT+QCFG="ethernet",1 AT+QNETDEVCTL=1,1,1 AT+QCFG="ethernet",1 AT+QCFG="nat",0
{{{5}}}
Please use the following commands to set it to the stable router mode:
AT+QCFG="nat",1
{{{5}}}
- The following modules that support it after testing:
Fibocom: FM650-CN FM160-EAU SIMCOM: SIM8202G-M2 SIM8262E-M2 SIM8262A-M2 Quectel: (AA version) RM500U-CNV RM500Q-GL/RM502Q-AE RM520N-GL RM530N-GL
- 5G modules are NOT included. If used with other modules and the pin compatibility should be tested.
{{{5}}}
RM500U-CN: based on Spreadtrum platform.
RM500Q-GL: based on Qualcomm platform, supports GNSS positioning, mainly for domestic use.
RM500Q-AE/RM502Q-AE: based on Qualcomm platform, support GNSS positioning, mainly used abroad.
{{{5}}}
It is because the 5G power consumption is high, and the Raspberry Pi is limited in power supply, you can power it with 5V (3A) through Type-C interface.
{{{5}}}
When using the external power supply, the Raspberry Pi reboots and RM500U does not reboot. You can use the command to reboot the RS500U.
{{{5}}}
Use the following command to turn on the echo, and press Enter after entering: (Blind typing is required here):
ATE1
{{{5}}}
There are the following dial types:
AT+QCFG="usbnet",0 driver type is NDIS(QMI)); AT+QCFG="usbnet",1 The driver type is ECM; AT+QCFG="usbnet",2 The driver type is MBIM; (RM5XXQ support) AT+QCFG="usbnet",3 The driver type is RNDIS AT+QCFG="usbnet",5 The driver type is NCM;
{{{5}}}
Yes.
{{{5}}}
Please use the following command to enable the Ethernet port to access the network.
AT+GTUSBMODE=36 AT+GTAUTOCONNECT=1
{{{5}}}
- For ABS modules, you can manually update it with the driver.
- For Qualcommm modules, you can manually install the driver.
- Ensure the module is normally on -> Open Device Manager -> Other Devices -> "Corresponding file folder after unzipping the drivers" -> Update the driver demo -> Browse the PC to find the corresponding driver demo files -> Select a path to store the driver file according to your system -> Finish.
{{{5}}}
Jetson Nano series can be supported, the hardware structure is customized for ordinary JETSON-NANO-LITE-DEV-KIT, if you use other Jetson nano version, the adapter needs to be changed to a dual male adapter cable to connect; if it is an orin nano, please use this verified Jetpack 6.0 (Ubuntu) version of the system, some of the validation is not possible, some of them are not suitable for Jetson nano. Ubuntu 22.04), some system drivers are not supported.
{{{5}}}
- USB TO M.2 B KEY does not include a module by default, you need to add a module before using.
- For example, after adding SIM8262E-M2 module, it can support Linxu and Windows system devices, if your router is OPenwrt and other Linux systems, it can be supported.
- Openwrt router configuration steps reference.
{{{5}}}
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 PM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)