2.4inch LCD Module
| ||
Overview
Introduction
As a 2.4inch TFT display module with a resolution of 240 * 320, it uses the SPI interface for communication. LCD has an internal controller with basic functions, which can be used to draw points, lines, circles, and rectangles, and can display English, Chinese as well as pictures.
We provide complete supporting Raspberry Pi demos (BCM2835 library, WiringPi library, and python demos), STM32 demos, and Arduino demos.
Specification
- Operating voltage: 3.3V/5V (When using 5V power supply, the logic voltage is 5V; When using 3.3V power supply, the logic voltage is 3.3V.)
- Interface: SPI
- LCD Type: TFT
- Controller: IL9341
- Resolution: 240(V) x 320(H)RGB
- Display Size: 36.72(H)x 48.96(V)mm
- Pixel Size: 0.153(H)x 0.153(V)mm
- Dimension: 70.5 x 43.3(mm)
Interface Description
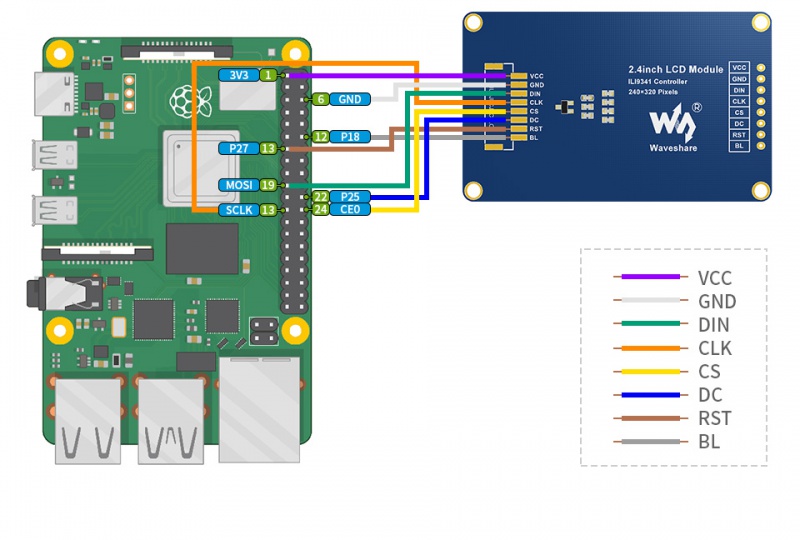
Raspberry Pi hardware connection
Please connect the LCD to your Raspberry Pi by the 8PIN cable according to the table below:
If you use the pin header or PH2.0 8PIN interface, you need to connect according to the following table.
| LCD | Raspberry Pi | |
| BCM2835 | Board | |
| VCC | 3.3V | 3.3V |
| GND | GND | GND |
| DIN | MOSI | 19 |
| CLK | SCLK | 23 |
| CS | CE0 | 24 |
| DS | 25 | 22 |
| RST | 27 | 13 |
| BL | 18 | 12 |
The 2.4inch LCD uses the PH2.0 8PIN interface, which can be connected to the Raspberry Pi according to the above table: (Please connect according to the pin definition table. The color of the wiring in the picture is for reference only, and the actual color shall prevail.)
STM32 Hardware Connection
The example we provide is based on STM32F103RBT6, and the connection method provided is also the corresponding pin of STM32F103RBT6. If you need to transplant the program, please connect according to the actual pin.
| LCD | STM32 |
| VCC | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| DIN | PA7 |
| CLK | PA5 |
| CS | PB6 |
| DC | PA8 |
| RST | PA9 |
| BL | PC7 |
Take the XNUCLEO-F103RB development board developed by our company as an example, the connection is as follows:

Arduino hardware connection
| LCD | UNO |
| VCC | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| DIN | D11 |
| CLK | D13 |
| CS | D10 |
| DC | D7 |
| RST | D8 |
| BL | D9 |
The connection diagram is as follows (click to enlarge):
Hardware Description
LCD and the controller
The LCD supports 12-bit, 16-bit, and 18-bit input color formats per pixel, namely RGB444, RGB565, and RGB666 three color formats, this demo uses RGB565 color format, which is also a commonly used RGB format.
For most LCD controllers, the communication mode of the controller can be configured, usually with an 8080 parallel interface, three-wire SPI, four-wire SPI, and other communication methods. This LCD uses a four-wire SPI communication interface, which can greatly save the GPIO port, and the communication speed will be faster.
Communication Protocol

Note: Different from the traditional SPI protocol, the data line from the slave to the master is hidden since the device only has a display requirement.
RESX: the reset pin, it should be low when powering the module and be higher at other times;
CSX: slave chip select, when CS is low, the chip is enabled.
D/CX: data/command control pin, when DC = 0, write command, when DC = 1, write data
SDA: the data pin for transmitting RGB data, it works as the MOSI pin of SPI interface;
SCL works as the SCLK pins of SPI interface.
SPI communication has data transfer timing, which is combined by CPHA and CPOL.
CPOL determines the level of the serial synchronous clock at idle state. When CPOL = 0, the level is Low. However, CPOL has little effect to the transmission.
CPHA determines whether data is collected at the first clock edge or at the second clock edge of serial synchronous clock; when CPHL = 0, data is collected at the first clock edge.
There are 4 SPI communication modes. SPI0 is commonly used, in which CPHL = 0, CPOL = 0.
Working with Raspberry Pi
Enable SPI interface
- Open the terminal, and use the command to enter the configuration page:
sudo raspi-config Choose Interfacing Options -> SPI -> Yes to enable the SPI interface.
sudo reboot
Please make sure the SPI is not occupied by other devices, you can check in the middle of /boot/config.txt.
Install Library
If you use the bookworm system, you can only use lgpio library, bcm2835 and wiringPi can't be installed and used.
BCM2835
#Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and run the following command wget http://www.airspayce.com/mikem/bcm2835/bcm2835-1.71.tar.gz tar zxvf bcm2835-1.71.tar.gz cd bcm2835-1.71/ sudo ./configure && sudo make && sudo make check && sudo make install # For more, you can refer to the official website at: http://www.airspayce.com/mikem/bcm2835/
WiringPi
#Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and run the following command cd sudo apt-get install wiringpi #For Raspberry Pi systems after May 2019 (earlier than that can be executed without), an upgrade may be required: wget https://project-downloads.drogon.net/wiringpi-latest.deb sudo dpkg -i wiringpi-latest.deb gpio -v # Run gpio -v and version 2.52 will appear, if it doesn't it means there was an installation error # Bullseye branch system using the following command: git clone https://github.com/WiringPi/WiringPi cd WiringPi . /build gpio -v # Run gpio -v and version 2.70 will appear, if it doesn't it means there was an installation error
lgpio
#Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and run the following command wget https://github.com/joan2937/lg/archive/master.zip unzip master.zip cd lg-master sudo make install #Raspberry Pi 5 sudo apt install python3-rpi-lgpio #For more details, you can refer to https://github.com/gpiozero/lg
Python
#python2 sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install python-pip -y sudo apt-get install python-pil -y sudo apt-get install python-numpy -y sudo pip install RPi.GPIO sudo pip install spidev #python3 sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install python3-pip -y sudo apt-get install python3-pil -y sudo apt-get install python3-numpy -y sudo pip3 install RPi.GPIO sudo pip3 install spidev
Download Examples
Open Raspberry Pi terminal and run the following command:
sudo apt-get install unzip -y sudo wget https://files.waveshare.com/upload/8/8d/LCD_Module_RPI_code.zip sudo unzip ./LCD_Module_RPI_code.zip cd LCD_Module_RPI_code/RaspberryPi/
Run the demo codes
Please go into the RaspberryPi directory (demo codes) first and run the commands in the terminal.
C codes
- Re-compile the demo codes.
cd c sudo make clean sudo make -j 8
- The test program of all screens can be called directly by entering the corresponding size.
sudo ./main Screen Size
Depending on the LCD, one of the following commands should be entered:
#0.96inch LCD Module sudo ./main 0.96 #1.14inch LCD Module sudo ./main 1.14 #1.28inch LCD Module sudo ./main 1.28 #1.3inch LCD Module sudo ./main 1.3 #1.47inch LCD Module sudo ./main 1.47 #1.54inch LCD Module sudo ./main 1.54 #1.8inch LCD Module sudo ./main 1.8 #2inch LCD Module sudo ./main 2 #2.4inch LCD Module sudo ./main 2.4
python
- Enter the Python program directory and run the command ls -l.
cd python/examples ls -l

Test programs for all screens can be viewed, sorted by size:
0inch96_LCD_test.py: 0.96inch LCD test program
1inch14_LCD_test.py: 1.14inch LCD test program
1inch28_LCD_test.py: 1.28inch LCD test program
1inch3_LCD_test.py: 1.3inch LCD test program
1inch47_LCD_test.py: 1.47inch LCD test program
1inch54_LCD_test.py: 1.54inchLCD test program
1inch8_LCD_test.py: 1.8inch LCD test program
2inch_LCD_test.py: 2inch LCD test program
2inch4_LCD_test.py: 2inch4 LCD test program
- Just run the program corresponding to the screen, the program supports python2/3.
# python2 sudo python 0inch96_LCD_test.py sudo python 1inch14_LCD_test.py sudo python 1inch28_LCD_test.py sudo python 1inch3_LCD_test.py sudo python 1inch47_LCD_test.py sudo python 1inch54_LCD_test.py sudo python 1inch8_LCD_test.py sudo python 2inch_LCD_test.py sudo python 2inch4_LCD_test.py # python3 sudo python3 0inch96_LCD_test.py sudo python3 1inch14_LCD_test.py sudo python3 1inch28_LCD_test.py sudo python3 1inch3_LCD_test.py sudo python3 1inch47_LCD_test.py sudo python3 1inch54_LCD_test.py sudo python3 1inch8_LCD_test.py sudo python3 2inch_LCD_test.py sudo python3 2inch4_LCD_test.py
FBCP Porting
Framebuffer uses a video output device to drive a video display device from a memory buffer containing complete frame data. Simply put, a memory area is used to store the display content, and the display content can be changed by changing the data in the memory.
There is an open source project on Git Hub: fbcp-ili9341. Compared with other fbcp projects, this project uses partial refresh and DMA to achieve a speed of up to 60fps.
Download Drivers
sudo apt-get install cmake -y cd ~ wget https://files.waveshare.com/upload/1/18/Waveshare_fbcp.zip unzip Waveshare_fbcp.zip cd Waveshare_fbcp/ sudo chmod +x ./shell/*
Method 1: Use a script (recommended)
Here we have written several scripts that allow users to quickly use fbcp and run corresponding commands according to their own screen.
If you use a script and do not need to modify it, you can ignore the second method below.
Note: The script will replace the corresponding /boot/config.txt and /etc/rc.local and restart, if the user needs, please back up the relevant files in advance.
#0.96inch LCD Module sudo ./shell/waveshare-0inch96 #1.14inch LCD Module sudo ./shell/waveshare-1inch14 #1.3inch LCD Module sudo ./shell/waveshare-1inch3 #1.44inch LCD Module sudo ./shell/waveshare-1inch44 #1.54inch LCD Module sudo ./shell/waveshare-1inch54 #1.8inch LCD Module sudo ./shell/waveshare-1inch8 #2inch LCD Module sudo ./shell/waveshare-2inch #2.4inch LCD Module sudo ./shell/waveshare-2inch4
Method 2: Manual Configuration
Environment Configuration
Raspberry Pi's vc4-kms-v3d will cause fbcp to fail, so we need to close vc4-kms-v3d before installing it in fbcp.
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
Just block the statement corresponding to the picture below.

A reboot is then required.
sudo reboot
Compile and run
mkdir build cd build cmake [options] .. sudo make -j sudo ./fbcp
Replace it by yourself according to the LCD Module you use, above cmake [options] ..
#0.96inch LCD Module sudo cmake -DSPI_BUS_CLOCK_DIVISOR=20 -DWAVESHARE_0INCH96_LCD=ON -DBACKLIGHT_CONTROL=ON -DSTATISTICS=0 .. #1.14inch LCD Module sudo cmake -DSPI_BUS_CLOCK_DIVISOR=20 -DWAVESHARE_1INCH14_LCD=ON -DBACKLIGHT_CONTROL=ON -DSTATISTICS=0 .. #1.3inch LCD Module sudo cmake -DSPI_BUS_CLOCK_DIVISOR=20 -DWAVESHARE_1INCH3_LCD=ON -DBACKLIGHT_CONTROL=ON -DSTATISTICS=0 .. #1.54inch LCD Module sudo cmake -DSPI_BUS_CLOCK_DIVISOR=20 -DWAVESHARE_1INCH54_LCD=ON -DBACKLIGHT_CONTROL=ON -DSTATISTICS=0 .. #1.8inch LCD Module sudo cmake -DSPI_BUS_CLOCK_DIVISOR=20 -DWAVESHARE_1INCH8_LCD=ON -DBACKLIGHT_CONTROL=ON -DSTATISTICS=0 .. #2inch LCD Module sudo cmake -DSPI_BUS_CLOCK_DIVISOR=20 -DWAVESHARE_2INCH_LCD=ON -DBACKLIGHT_CONTROL=ON -DSTATISTICS=0 .. #2.4inch LCD Module sudo cmake -DSPI_BUS_CLOCK_DIVISOR=20 -DWAVESHARE_2INCH4_LCD=ON -DBACKLIGHT_CONTROL=ON -DSTATISTICS=0 ..
Set up to start automatically
sudo cp ~/Waveshare_fbcp/build/fbcp /usr/local/bin/fbcp sudo nano /etc/rc.local
Add fbcp& before exit 0. Note that you must add "&" to run in the background. Otherwise, the system may not be able to start.
Set the Display Resolution
Set the user interface display size in the /boot/config.txt file.
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
Then add the following lines at the end of the config.txt.
hdmi_force_hotplug=1 hdmi_cvt=[options] hdmi_group=2 hdmi_mode=1 hdmi_mode=87 display_rotate=0
Replace the above hdmi_cvt=[options] according to the LCD Module you are using.
#2.4inchinch LCD Module & 2inchinch LCD Module hdmi_cvt=640 480 60 1 0 0 0 #1.8inch LCD Module hdmi_cvt=400 300 60 1 0 0 0 #1.3inch LCD Module & 1.54inch LCD Module hdmi_cvt=300 300 60 1 0 0 0 #1.14inch LCD Module hdmi_cvt=300 170 60 1 0 0 0 #0.96inch LCD Module hdmi_cvt=300 150 60 1 0 0 0
And then reboot the system:
sudo reboot
After rebooting the system, the Raspberry Pi OS user interface will be displayed.
API Description
The RaspberryPi series can share a set of programs, because they are all embedded systems, and the compatibility is relatively strong.
The program is divided into bottom-layer hardware interface, middle-layer LCD screen driver, and upper-layer application;
C
Hardware Interface
We have carried out the low-level encapsulation, if you need to know the internal implementation can go to the corresponding directory to check, for the reason the hardware platform and the internal implementation are different.
You can open DEV_Config.c(.h) to see definitions, which in the directory RaspberryPi\c\lib\Config.
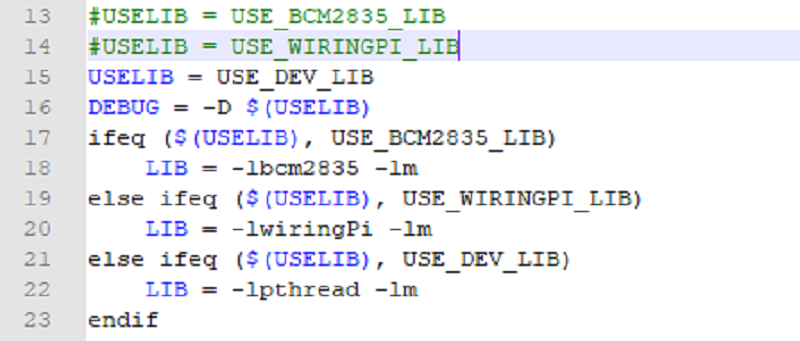
1. There are three ways for C to drive: BCM2835 library, WiringPi library, and Dev library respectively 2. We use Dev libraries by default. If you need to change to BCM2835 or WiringPi libraries, please open RaspberryPi\c\Makefile and modify lines 13-15 as follows:
- Data type:
#define UBYTE uint8_t #define UWORD uint16_t #define UDOUBLE uint32_t
- Module initialization and exit processing.
void DEV_Module_Init(void); void DEV_Module_Exit(void); Note: Here is some GPIO processing before and after using the LCD screen.
- GPIO read and write:
void DEV_Digital_Write(UWORD Pin, UBYTE Value); UBYTE DEV_Digital_Read(UWORD Pin);
- SPI write data:
void DEV_SPI_WriteByte(UBYTE Value);
Upper application
If you need to draw pictures or display Chinese and English characters, we provide some basic functions here about some graphics processing in the directory RaspberryPi\c\lib\GUI\GUI_Paint.c(.h).

The fonts can be found in RaspberryPi\c\lib\Fonts directory.

- New Image Properties: Create a new image buffer, this property includes the image buffer name, width, height, flip Angle, and color.
void Paint_NewImage(UBYTE *image, UWORD Width, UWORD Height, UWORD Rotate, UWORD Color)
Parameters:
Image: the name of the image buffer, which is actually a pointer to the first address of the image buffer;
Width: image buffer Width;
Height: the Height of the image buffer;
Rotate: Indicates the rotation Angle of an image
Color: the initial Color of the image;
- Select image buffer: The purpose of the selection is that you can create multiple image attributes, there can be multiple images buffer, you can select each image you create.
void Paint_SelectImage(UBYTE *image)
Parameters:
Image: the name of the image buffer, which is actually a pointer to the first address of the image buffer;
- Image Rotation: Set the rotation Angle of the selected image, preferably after Paint_SelectImage(), you can choose to rotate 0, 90, 180, 270.
void Paint_SetRotate(UWORD Rotate)
Parameters:
Rotate: ROTATE_0, ROTATE_90, ROTATE_180, and ROTATE_270 correspond to 0, 90, 180, and 270 degrees.
- Image mirror flip: Set the mirror flip of the selected image. You can choose no mirror, horizontal mirror, vertical mirror, or image center mirror.
void Paint_SetMirroring(UBYTE mirror)
Parameters:
Mirror: indicates the image mirroring mode. MIRROR_NONE, MIRROR_HORIZONTAL, MIRROR_VERTICAL, MIRROR_ORIGIN correspond to no mirror, horizontal mirror, vertical mirror, and image center mirror respectively.
- Set points of the display position and color in the buffer: here is the core GUI function, processing points display position and color in the buffer.
void Paint_SetPixel(UWORD Xpoint, UWORD Ypoint, UWORD Color)
Parameters:
Xpoint: the X position of a point in the image buffer
Ypoint: Y position of a point in the image buffer
Color: indicates the Color of the dot
- Image buffer fill color: Fills the image buffer with a color, usually used to flash the screen into blank.
void Paint_Clear(UWORD Color)
Parameters:
Color: fill Color
- The fill color of a certain window in the image buffer: the image buffer part of the window filled with a certain color, usually used to fresh the screen into blank, often used for time display, fresh the last second of the screen.
void Paint_ClearWindows(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, UWORD Xend, UWORD Yend, UWORD Color)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-starting coordinate of the window
Ystart: the y-starting coordinate of the window
Xend: the x-end coordinate of the window
Yend: the y-end coordinate of the window
Color: fill Color
- Draw point: In the image buffer, draw points on (Xpoint, Ypoint), you can choose the color, the size of the point, the style of the point.
void Paint_DrawPoint(UWORD Xpoint, UWORD Ypoint, UWORD Color, DOT_PIXEL Dot_Pixel, DOT_STYLE Dot_Style)
Parameters:
Xpoint: indicates the X coordinate of a point.
Ypoint: indicates the Y coordinate of a point.
Color: fill Color
Dot_Pixel: The size of the dot, the demo provides 8 size pointss by default.
typedef enum {
DOT_PIXEL_1X1 = 1, // 1 x 1
DOT_PIXEL_2X2 , // 2 X 2
DOT_PIXEL_3X3 , // 3 X 3
DOT_PIXEL_4X4 , // 4 X 4
DOT_PIXEL_5X5 , // 5 X 5
DOT_PIXEL_6X6 , // 6 X 6
DOT_PIXEL_7X7 , // 7 X 7
DOT_PIXEL_8X8 , // 8 X 8
} DOT_PIXEL;
Dot_Style: the size of a point that expands from the center of the point or from the bottom left corner of the point to the right and up.
typedef enum {
DOT_FILL_AROUND = 1,
DOT_FILL_RIGHTUP,
} DOT_STYLE;
- Draw line: In the image buffer, draw line from (Xstart, Ystart) to (Xend, Yend), you can choose the color, the width and the style of the line.
void Paint_DrawLine(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, UWORD Xend, UWORD Yend, UWORD Color, LINE_STYLE Line_Style , LINE_STYLE Line_Style)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-starting coordinate of a line
Ystart: the y-starting coordinate of the a line
Xend: the x-end coordinate of a line
Yend: the y-end coordinate of a line
Color: fill Color
Line_width: The width of the line, the demo provides 8 sizes of width by default.
typedef enum {
DOT_PIXEL_1X1 = 1, // 1 x 1
DOT_PIXEL_2X2 , // 2 X 2
DOT_PIXEL_3X3 , // 3 X 3
DOT_PIXEL_4X4 , // 4 X 4
DOT_PIXEL_5X5 , // 5 X 5
DOT_PIXEL_6X6 , // 6 X 6
DOT_PIXEL_7X7 , // 7 X 7
DOT_PIXEL_8X8 , // 8 X 8
} DOT_PIXEL;
Line_Style: line style. Select whether the lines are joined in a straight or dashed way.
typedef enum {
LINE_STYLE_SOLID = 0,
LINE_STYLE_DOTTED,
} LINE_STYLE;
- Draw rectangle: In the image buffer, draw a rectangle from (Xstart, Ystart) to (Xend, Yend), you can choose the color, the width of the line, whether to fill the inside of the rectangle.
void Paint_DrawRectangle(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, UWORD Xend, UWORD Yend, UWORD Color, DOT_PIXEL Line_width, DRAW_FILL Draw_Fill)
Parameters:
Xstart: the starting X coordinate of the rectangle
Ystart: the starting Y coordinate of the rectangle
Xend: the x-end coordinate of the rectangle
Yend: the y-end coordinate of the rectangle
Color: fill Color
Line_width: The width of the four sides of a rectangle. And the demo provides 8 sizes of width by default.
typedef enum {
DOT_PIXEL_1X1 = 1, // 1 x 1
DOT_PIXEL_2X2 , // 2 X 2
DOT_PIXEL_3X3 , // 3 X 3
DOT_PIXEL_4X4 , // 4 X 4
DOT_PIXEL_5X5 , // 5 X 5
DOT_PIXEL_6X6 , // 6 X 6
DOT_PIXEL_7X7 , // 7 X 7
DOT_PIXEL_8X8 , // 8 X 8
} DOT_PIXEL;
Draw_Fill: Fill, whether to fill the inside of the rectangle
typedef enum {
DRAW_FILL_EMPTY = 0,
DRAW_FILL_FULL,
} DRAW_FILL;
- Draw circle: In the image buffer, draw a circle of Radius with (X_Center Y_Center) as the center. You can choose the color, the width of the line, and whether to fill the inside of the circle.
void Paint_DrawCircle(UWORD X_Center, UWORD Y_Center, UWORD Radius, UWORD Color, DOT_PIXEL Line_width, DRAW_FILL Draw_Fill)
Parameters:
X_Center: the x-coordinate of the center of the circle
Y_Center: the y-coordinate of the center of the circle
Radius: indicates the Radius of a circle
Color: fill Color
Line_width: The width of the arc, with a default of 8 widths
typedef enum {
DOT_PIXEL_1X1 = 1, // 1 x 1
DOT_PIXEL_2X2 , // 2 X 2
DOT_PIXEL_3X3 , // 3 X 3
DOT_PIXEL_4X4 , // 4 X 4
DOT_PIXEL_5X5 , // 5 X 5
DOT_PIXEL_6X6 , // 6 X 6
DOT_PIXEL_7X7 , // 7 X 7
DOT_PIXEL_8X8 , // 8 X 8
} DOT_PIXEL;
Draw_Fill: fill, whether to fill the inside of the circle
typedef enum {
DRAW_FILL_EMPTY = 0,
DRAW_FILL_FULL,
} DRAW_FILL;
- Write Ascii character: In the image buffer, use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write an Ascii character, you can select Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
void Paint_DrawChar(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, const char Ascii_Char, sFONT* Font, UWORD Color_Foreground, UWORD Color_Background)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-coordinate of the left vertex of a character
Ystart: the Y-coordinate of the left vertex of a character
Ascii_Char: indicates the Ascii character
Font: Ascii visual character library, in the Fonts folder the demo provides the following Fonts:
Font8: 5*8 font
Font12: 7*12 font
Font16: 11*16 font
Font20: 14*20 font
Font24: 17*24 font
Color_Foreground: Font color
Color_Background: indicates the background color
- Write English string: In the image buffer, use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of English characters, you can choose Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
void Paint_DrawString_EN(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, const char * pString, sFONT* Font, UWORD Color_Foreground, UWORD Color_Background)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-coordinate of the left vertex of a character
Ystart: the Y coordinate of the font's left vertex
PString: string, string is a pointer
Font: Ascii visual character library, in the Fonts folder the demo provides the following Fonts:
Font8: 5*8 font
Font12: 7*12 font
Font16: 11*16 font
Font20: 14*20 font
Font24: 17*24 font
Color_Foreground: Font color
Color_Background: indicates the background color
- Write Chinese string: in the image buffer, use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of Chinese characters, you can choose character font, font foreground color, and font background color of the GB2312 encoding.
void Paint_DrawString_CN(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, const char * pString, cFONT* font, UWORD Color_Foreground, UWORD Color_Background)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-coordinate of the left vertex of a character
Ystart: the Y coordinate of the font's left vertex
PString: string, string is a pointer
Font: GB2312 encoding character Font library, in the Fonts folder the demo provides the following Fonts:
Font12CN: ASCII font 11*21, Chinese font 16*21
Font24CN: ASCII font24 *41, Chinese font 32*41
Color_Foreground: Font color
Color_Background: indicates the background color
- Write numbers: In the image buffer,use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of numbers, you can choose Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
void Paint_DrawNum(UWORD Xpoint, UWORD Ypoint, double Nummber, sFONT* Font, UWORD Digit, UWORD Color_Foreground, UWORD Color_Background) Parameters: Xpoint: the x-coordinate of the left vertex of a character Ypoint: the Y coordinate of the left vertex of the font Nummber: indicates the number displayed, which can be a decimal Digit: It's a decimal number Font: Ascii visual character library, in the Fonts folder the demo provides the following Fonts: Font8: 5*8 font Font12: 7*12 font Font16: 11*16 font Font20: 14*20 font Font24: 17*24 font Color_Foreground: Font color Color_Background: indicates the background color
- Display time: in the image buffer,use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, display time,you can choose Ascii visual character font, font foreground color, font background color.
void Paint_DrawTime(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, PAINT_TIME *pTime, sFONT* Font, UWORD Color_Background, UWORD Color_Foreground)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-coordinate of the left vertex of a character
Ystart: the Y coordinate of the font's left vertex
PTime: display time, A time structure is defined here, as long as the hours, minutes, and seconds are passed to the parameters;
Font: Ascii visual character library, in the Fonts folder the demo provides the following Fonts:
Font8: 5*8 font
Font12: 7*12 font
Font16: 11*16 font
Font20: 14*20 font
Font24: 17*24 font
Color_Foreground: Font color
Color_Background: indicates the background color
- Read the local bmp image and write it to the cache.
For Linux operating systems such as Raspberry Pi, you can read and write pictures. For Raspberry Pi, in the directory: RaspberryPi\c\lib\GUI\GUI_BMPfile.c(.h).
UBYTE GUI_ReadBmp(const char *path, UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart)
parameter:
path: the relative path of the BMP image
Xstart: The X coordinate of the left vertex of the image, generally 0 is passed by default
Ystart: The Y coordinate of the left vertex of the picture, generally 0 by default
Testing Code for Users
For Raspberry Pi, in the directory: RaspberryPi\c\examples, for all the test code;
If you need to run the 0.96-inch LCD test program, you need to add 0.96 as a parameter when running the main demo.
Re-execute in Linux command mode as follows:
make clean make sudo ./main 0.96
Python (for Raspberry Pi)
Works with python and python3.
For python, his calls are not as complicated as C.
Raspberry Pi: RaspberryPi\python\lib\
lcdconfig.py
- Module initialization and exit processing.
def module_init() def module_exit() Note: 1. Here is some GPIO processing before and after using the LCD screen. 2. The module_init() function is automatically called in the INIT () initializer on the LCD, but the module_exit() function needs to be called by itself.
- GPIO read and write:
def digital_write(pin, value) def digital_read(pin)
- SPI write data.
def spi_writebyte(data)
- xxx_LCD_test.py (xxx indicates the size, if it is a 0.96inch LCD, it is 0inch96_LCD_test.py, and so on)
python is in the following directory:
Raspberry Pi: RaspberryPi\python\examples\
If your python version is python2 and you need to run the 0.96inch LCD test program, re-execute it as follows in linux command mode:
sudo python 0inch96_LCD_test.py
If your python version is python3 and you need to run the 0.96inch LCD test program, re-execute the following in linux command mode:
sudo python3 0inch96_LCD_test.py
About Rotation Settings
If you need to set the screen rotation in the python program, you can set it by the statement im_r= image1.rotate(270).
im_r= image1.rotate(270)
GUI Functions
Python has an image library PIL official library link, it does not need to write code from the logical layer like C and can directly call to the image library for image processing. The following will take a 1.54-inch LCD as an example, we provide a brief description of the demo.
- It needs to use the image library and install the library.
sudo apt-get install python3-pil
And then import the library
from PIL import Image,ImageDraw,ImageFont.
Among them, Image is the basic library, ImageDraw is the drawing function, and ImageFont is the text function.
- Define an image cache to facilitate drawing, writing, and other functions on the picture.
image1 = Image.new("RGB", (disp.width, disp.height), "WHITE")
The first parameter defines the color depth of the image, which is defined as "1" to indicate the bitmap of one-bit depth. The second parameter is a tuple that defines the width and height of the image. The third parameter defines the default color of the buffer, which is defined as "WHITE".
- Create a drawing object based on Image1 on which all drawing operations will be performed on here.
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image1)
- Draw a line.
draw.line([(20, 10),(70, 60)], fill = "RED",width = 1)
The first parameter is a four-element tuple starting at (0, 0) and ending at (127,0). Draw a line. Fill ="0" means the color of the line is white.
- Draw a rectangle.
draw.rectangle([(20,10),(70,60)],fill = "WHITE",outline="BLACK")
The first argument is a tuple of four elements. (20,10) is the coordinate value in the upper left corner of the rectangle, and (70,60) is the coordinate value in the lower right corner of the rectangle. Fill =" WHITE" means BLACK inside, and outline="BLACK" means the color of the outline is black.
- Draw a circle.
draw.arc((150,15,190,55),0, 360, fill =(0,255,0)
Draw an inscribed circle in the square, the first parameter is a tuple of 4 elements, with (150, 15) as the upper left corner vertex of the square, (190, 55) as the lower right corner vertex of the square, specifying the level median line of the rectangular frame is the angle of 0 degrees, the second parameter indicates the starting angle, the third parameter indicates the ending angle, and fill = 0 indicates that the color of the line is white. If the figure is not square according to the coordination, you will get an ellipse.
Besides the arc function, you can also use the chord function for drawing a solid circle.
draw.ellipse((150,65,190,105), fill = 0)
The first parameter is the coordination of the enclosing rectangle. The second and third parameters are the beginning and end degrees of the circle. The fourth parameter is the fill color of the circle.
- Character.
The ImageFont module needs to be imported and instantiated:
Font1 = ImageFont.truetype("../Font/Font01.ttf",25)
Font2 = ImageFont.truetype("../Font/Font01.ttf",35)
Font3 = ImageFont.truetype("../Font/Font02.ttf",32)
You can use the fonts of Windows or other fonts which is in ttc format..
Note: Each character library contains different characters; If some characters cannot be displayed, it is recommended that you can refer to the encoding set ro used.
To draw English characters, you can directly use the fonts; for Chinese characters, you need to add a symbol u:
draw.text((40, 50), 'WaveShare', fill = (128,255,128),font=Font2) text= u"微雪电子" draw.text((74, 150),text, fill = "WHITE",font=Font3)
The first parameter is a tuple of 2 elements, with (40, 50) as the left vertex, the font is Font2, and the fill is the font color. You can directly make fill = "WHITE", because the regular color value is already defined Well, of course, you can also use fill = (128,255,128), the parentheses correspond to the values of the three RGB colors so that you can precisely control the color you want. The second sentence shows Waveshare Electronics, using Font3, the font color is white.
- read local image
image = Image.open('../pic/LCD_1inch28.jpg')
The parameter is the image path.
- Other functions.
For more information, you can refer to http://effbot.org/imagingbook pil
Using with STM32
Software description
- The demo is developed based on the HAL library. Download the demo, find the STM32 program file directory, and open the LCD_demo.uvprojx in the STM32\STM32F103RBT6\MDK-ARM directory to check the program.
- Open main.c, you can see all the test programs, remove the comments in front of the test programs on the corresponding screen, and recompile and download.
LCD_0in96_test() 0.96inch LCD test program
LCD_1in14_test() 1.14inch LCD test program
LCD_1in28_test() 1.28inch LCD test program
LCD_1in3_test() 1.3 inch LCD test program
LCD_1in54_test() 1.54inch LCD test program
LCD_1in8_test() 1.8inch LCD test program
LCD_2in_test() 2inch LCD test program
Program description
Underlying hardware interface
- Data type:
#define UBYTE uint8_t #define UWORD uint16_t #define UDOUBLE uint32_t
- Module initialization and exit processing:
UBYTE System_Init(void); void System_Exit(void); Note: 1. Here is some GPIO processing before and after using the LCD screen. 2. After the System_Exit(void) function is used, the OLED display will be turned off.
- Write and read GPIO.
void DEV_Digital_Write(UWORD Pin, UBYTE Value); UBYTE DEV_Digital_Read(UWORD Pin);
- SPI writes data:
UBYTE SPI4W_Write_Byte(uint8_t value);
The upper application
For the screen, if you need to draw pictures, display Chinese and English characters, display pictures, etc., you can use the upper application to do, and we provide some basic functions here about some graphics processing in the directory STM32\STM32F103RB\User\GUI_DEV\GUI_Paint.c(.h)
Note: Because of the size of the internal RAM of STM32 and arduino, the GUI is directly written to the RAM of the LCD.

The character font which GUI dependent is in the directory STM32\STM32F103RB\User\Fonts

- New Image Properties: Create a new image property, this property includes the image buffer name, width, height, flip Angle, color.
void Paint_NewImage(UWORD Width, UWORD Height, UWORD Rotate, UWORD Color)
Parameters:
Width: image buffer Width;
Height: the Height of the image buffer;
Rotate: Indicates the rotation Angle of an image
Color: the initial Color of the image;
- Set the clear screen function, usually call the clear function of LCD directly.
void Paint_SetClearFuntion(void (*Clear)(UWORD));
parameter:
Clear : Pointer to the clear screen function, used to quickly clear the screen to a certain color;
- Set the drawing pixel function
void Paint_SetDisplayFuntion(void (*Display)(UWORD,UWORD,UWORD));
parameter:
Display: Pointer to the pixel drawing function, which is used to write data to the specified location in the internal RAM of the LCD;
- Select image buffer:the purpose of the selection is that you can create multiple image attributes, image buffer can exist multiple, you can select each image you create.
void Paint_SelectImage(UBYTE *image)
Parameters:
Image: the name of the image cache, which is actually a pointer to the first address of the image buffer
- Image Rotation: Set the selected image rotation Angle, preferably after Paint_SelectImage(), you can choose to rotate 0, 90, 180, 270.
void Paint_SetRotate(UWORD Rotate)
Parameters:
Rotate: ROTATE_0, ROTATE_90, ROTATE_180, and ROTATE_270 correspond to 0, 90, 180, and 270 degrees respectively;
- Image mirror flip: Set the mirror flip of the selected image. You can choose no mirror, horizontal mirror, vertical mirror, or image center mirror.
void Paint_SetMirroring(UBYTE mirror)
Parameters:
Mirror: indicates the image mirroring mode. MIRROR_NONE, MIRROR_HORIZONTAL, MIRROR_VERTICAL, MIRROR_ORIGIN correspond to no mirror, horizontal mirror, vertical mirror, and about image center mirror respectively.
- Set points of display position and color in the buffer: here is the core GUI function, processing points display position and color in the buffer.
void Paint_SetPixel(UWORD Xpoint, UWORD Ypoint, UWORD Color)
Parameters:
Xpoint: the X position of a point in the image buffer
Ypoint: Y position of a point in the image buffer
Color: indicates the Color of the dot
- Image buffer fill color: Fills the image buffer with a color, usually used to flash the screen into blank.
void Paint_Clear(UWORD Color)
Parameters:
Color: fill Color
- Image buffer part of the window filling color: the image buffer part of the window filled with a certain color, generally as a window whitewashing function, often used for time display, whitewashing on a second
void Paint_ClearWindows(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, UWORD Xend, UWORD Yend, UWORD Color)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-starting coordinate of the window
Ystart: indicates the Y starting point of the window
Xend: the x-end coordinate of the window
Yend: indicates the y-end coordinate of the window
Color: fill Color
- Draw points: In the image buffer, draw points on (Xpoint, Ypoint), you can choose the color, the size of the point, the style of the point.
void Paint_DrawPoint(UWORD Xpoint, UWORD Ypoint, UWORD Color, DOT_PIXEL Dot_Pixel, DOT_STYLE Dot_Style)
Parameters:
Xpoint: indicates the X coordinate of a point
Ypoint: indicates the Y coordinate of a point
Color: fill Color
Dot_Pixel: The size of the dot, providing a default of eight size points
typedef enum {
DOT_PIXEL_1X1 = 1, // 1 x 1
DOT_PIXEL_2X2 , // 2 X 2
DOT_PIXEL_3X3 , // 3 X 3
DOT_PIXEL_4X4 , // 4 X 4
DOT_PIXEL_5X5 , // 5 X 5
DOT_PIXEL_6X6 , // 6 X 6
DOT_PIXEL_7X7 , // 7 X 7
DOT_PIXEL_8X8 , // 8 X 8
} DOT_PIXEL;
Dot_Style: the size of a point that expands from the center of the point or from the bottom left corner of the point to the right and up
typedef enum {
DOT_FILL_AROUND = 1,
DOT_FILL_RIGHTUP,
} DOT_STYLE;
- Line drawing: In the image buffer, line from (Xstart, Ystart) to (Xend, Yend), you can choose the color, line width, line style.
void Paint_DrawLine(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, UWORD Xend, UWORD Yend, UWORD Color, LINE_STYLE Line_Style , LINE_STYLE Line_Style)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-starting coordinate of a line
Ystart: indicates the Y starting point of a line
Xend: x-terminus of a line
Yend: the y-end coordinate of a line
Color: fill Color
Line_width: The width of the line, which provides a default of eight widths
typedef enum {
DOT_PIXEL_1X1 = 1, // 1 x 1
DOT_PIXEL_2X2 , // 2 X 2
DOT_PIXEL_3X3 , // 3 X 3
DOT_PIXEL_4X4 , // 4 X 4
DOT_PIXEL_5X5 , // 5 X 5
DOT_PIXEL_6X6 , // 6 X 6
DOT_PIXEL_7X7 , // 7 X 7
DOT_PIXEL_8X8 , // 8 X 8
} DOT_PIXEL;
Line_Style: line style. Select whether the lines are joined in a straight or dashed way
typedef enum {
LINE_STYLE_SOLID = 0,
LINE_STYLE_DOTTED,
} LINE_STYLE;
- Draw rectangle: In the image buffer, draw a rectangle from (Xstart, Ystart) to (Xend, Yend), you can choose the color, the width of the line, whether to fill the inside of the rectangle.
void Paint_DrawRectangle(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, UWORD Xend, UWORD Yend, UWORD Color, DOT_PIXEL Line_width, DRAW_FILL Draw_Fill)
Parameters:
Xstart: the starting X coordinate of the rectangle
Ystart: indicates the Y starting point of the rectangle
Xend: X terminus of the rectangle
Yend: specifies the y-end coordinate of the rectangle
Color: fill Color
Line_width: The width of the four sides of a rectangle. Default eight widths are provided
typedef enum {
DOT_PIXEL_1X1 = 1, // 1 x 1
DOT_PIXEL_2X2 , // 2 X 2
DOT_PIXEL_3X3 , // 3 X 3
DOT_PIXEL_4X4 , // 4 X 4
DOT_PIXEL_5X5 , // 5 X 5
DOT_PIXEL_6X6 , // 6 X 6
DOT_PIXEL_7X7 , // 7 X 7
DOT_PIXEL_8X8 , // 8 X 8
} DOT_PIXEL;
Draw_Fill: Fill, whether to fill the inside of the rectangle
typedef enum {
DRAW_FILL_EMPTY = 0,
DRAW_FILL_FULL,
} DRAW_FILL;
- Draw circle: In the image buffer, draw a circle of Radius with (X_Center Y_Center) as the center. You can choose the color, the width of the line, and whether to fill the inside of the circle.
void Paint_DrawCircle(UWORD X_Center, UWORD Y_Center, UWORD Radius, UWORD Color, DOT_PIXEL Line_width, DRAW_FILL Draw_Fill)
Parameters:
X_Center: the x-coordinate of the center of a circle
Y_Center: Y coordinate of the center of a circle
Radius: indicates the Radius of a circle
Color: fill Color
Line_width: The width of the arc, with a default of 8 widths
typedef enum {
DOT_PIXEL_1X1 = 1, // 1 x 1
DOT_PIXEL_2X2 , // 2 X 2
DOT_PIXEL_3X3 , // 3 X 3
DOT_PIXEL_4X4 , // 4 X 4
DOT_PIXEL_5X5 , // 5 X 5
DOT_PIXEL_6X6 , // 6 X 6
DOT_PIXEL_7X7 , // 7 X 7
DOT_PIXEL_8X8 , // 8 X 8
} DOT_PIXEL;
Draw_Fill: fill, whether to fill the inside of the circle
typedef enum {
DRAW_FILL_EMPTY = 0,
DRAW_FILL_FULL,
} DRAW_FILL;
- Write Ascii character: In the image buffer, at (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write an Ascii character, you can select Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
void Paint_DrawChar(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, const char Ascii_Char, sFONT* Font, UWORD Color_Foreground, UWORD Color_Background)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-coordinate of the left vertex of a character
Ystart: the Y coordinate of the font's left vertex
Ascii_Char: indicates the Ascii character
Font: Ascii visual character library, in the Fonts folder provides the following Fonts:
Font8: 5*8 font
Font12: 7*12 font
Font16: 11*16 font
Font20: 14*20 font
Font24: 17*24 font
Color_Foreground: Font color
Color_Background: indicates the background color
- Write English string: In the image buffer, use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of English characters, can choose Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
void Paint_DrawString_EN(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, const char * pString, sFONT* Font, UWORD Color_Foreground, UWORD Color_Background)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-coordinate of the left vertex of a character
Ystart: the Y coordinate of the font's left vertex
PString: string, string is a pointer
Font: Ascii visual character library, in the Fonts folder provides the following Fonts:
Font8: 5*8 font
Font12: 7*12 font
Font16: 11*16 font
Font20: 14*20 font
Font24: 17*24 font
Color_Foreground: Font color
Color_Background: indicates the background color
- Write Chinese string: in the image buffer, use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of Chinese characters, you can choose GB2312 encoding character font, font foreground color, font background color.
void Paint_DrawString_CN(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, const char * pString, cFONT* font, UWORD Color_Foreground, UWORD Color_Background)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-coordinate of the left vertex of a character
Ystart: the Y coordinate of the font's left vertex
PString: string, string is a pointer
Font: GB2312 encoding character Font library, in the Fonts folder provides the following Fonts:
Font12CN: ASCII font 11*21, Chinese font 16*21
Font24CN: ASCII font24 *41, Chinese font 32*41
Color_Foreground: Font color
Color_Background: indicates the background color
- Write numbers: In the image buffer,use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of numbers, you can choose Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
void Paint_DrawNum(UWORD Xpoint, UWORD Ypoint, double Nummber, sFONT* Font, UWORD Digit, UWORD Color_Foreground, UWORD Color_Background)
Parameters:
Xpoint: the x-coordinate of the left vertex of a character
Ypoint: the Y coordinate of the left vertex of the font
Nummber: indicates the number displayed, which can be a decimal
Digit: It's a decimal number
Font: Ascii visual character library, in the Fonts folder provides the following Fonts:
Font8: 5*8 font
Font12: 7*12 font
Font16: 11*16 font
Font20: 14*20 font
Font24: 17*24 font
Color_Foreground: Font color
Color_Background: indicates the background color
- Display time: in the image buffer,use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, display time,you can choose Ascii visual character font, font foreground color, font background color.
void Paint_DrawTime(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, PAINT_TIME *pTime, sFONT* Font, UWORD Color_Background, UWORD Color_Foreground)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-coordinate of the left vertex of a character
Ystart: the Y coordinate of the font's left vertex
PTime: display time, here defined a good time structure, as long as the hour, minute and second bits of data to the parameter;
Font: Ascii visual character library, in the Fonts folder provides the following Fonts:
Font8: 5*8 font
Font12: 7*12 font
Font16: 11*16 font
Font20: 14*20 font
Font24: 17*24 font
Color_Foreground: Font color
Color_Background: indicates the background color
Arduino software description
Note: The demos are all tested on Arduino uno. If you need other types of Arduino, you need to determine whether the connected pins are correct.
Run program
In the product encyclopedia interface download the program, and then unzip it. The Arduino program is located at ~/Arduino/…

Please select the corresponding program according to the LCD screen model to open.

You can view test programs for all screen sizes, sorted by size:
For example, 1.54inch LCD Module. Open the LCD_1inch54 folder and run the LCD_1inch54.ino file.
Open the program, select the development board model Arduino UNO.

Select the corresponding COM port

Then click to compile and download

Program Description
Document Introduction
Take Arduino UNO controlling a 1.54-inch LCD as an example, open the Arduino\LCD_1inch54 directory:

Of which:
LCD_1inch54.ino: open with Arduino IDE;
LCD_Driver.cpp(.h): is the driver of the LCD screen;
DEV_Config.cpp(.h): It is the hardware interface definition, which encapsulates the read and writes pin levels, SPI transmission data, and pin initialization;
font8.cpp, font12.cpp, font16.cpp, font20.cpp, font24.cpp, font24CN.cpp, fonts.h: fonts for characters of different sizes;
image.cpp(.h): is the image data, which can convert any BMP image into a 16-bit true color image array through Img2Lcd (downloadable in the development data).
The program is divided into bottom-layer hardware interface, middle-layer LCD screen driver, and upper-layer application;
Underlying hardware interface
The hardware interface is defined in the two files DEV_Config.cpp(.h), and functions such as read and write pin level, delay, and SPI transmission are encapsulated.
- write pin level
void DEV_Digital_Write(int pin, int value)
The first parameter is the pin, and the second is the high and low levels.
- Read pin level
int DEV_Digital_Read(int pin)
The parameter is the pin, and the return value is the level of the read pin.
- Delay
DEV_Delay_ms(unsigned int delaytime)
millisecond level delay.
- SPI output data
DEV_SPI_WRITE(unsigned char data)
The parameter is char type, occupying 8 bits.
The upper application
For the screen, if you need to draw pictures, display Chinese and English characters, display pictures, etc., you can use the upper application to do, and we provide some basic functions here about some graphics processing in the directory GUI_Paint.c(.h)
Note: Because of the size of the internal RAM of STM32 and Arduino, the GUI is directly written to the RAM of the LCD.

The fonts used by the GUI all depend on the font*.cpp(h) files under the same file

- New Image Properties: Create a new image property, this property includes the image buffer name, width, height, flip Angle, and color.
void Paint_NewImage(UWORD Width, UWORD Height, UWORD Rotate, UWORD Color)
Parameters:
Width: image buffer Width;
Height: the Height of the image buffer;
Rotate: Indicates the rotation Angle of an image
Color: the initial Color of the image;
- Set the clear screen function, usually call the clear function of LCD directly.
void Paint_SetClearFuntion(void (*Clear)(UWORD));
parameter:
Clear: Pointer to the clear screen function, used to quickly clear the screen to a certain color;
- Set the drawing pixel function.
void Paint_SetDisplayFuntion(void (*Display)(UWORD,UWORD,UWORD));
parameter:
Display: Pointer to the pixel drawing function, which is used to write data to the specified location in the internal RAM of the LCD;
- Select image buffer: the purpose of the selection is that you can create multiple image attributes, image buffer can exist multiple, and you can select each image you create.
void Paint_SelectImage(UBYTE *image)
Parameters:
Image: the name of the image cache, which is actually a pointer to the first address of the image buffer
- Image Rotation: Set the selected image rotation Angle, preferably after Paint_SelectImage(), you can choose to rotate 0, 90, 180, 270.
void Paint_SetRotate(UWORD Rotate)
Parameters:
Rotate: ROTATE_0, ROTATE_90, ROTATE_180, and ROTATE_270 correspond to 0, 90, 180, and 270 degrees respectively;
- Image mirror flip: Set the mirror flip of the selected image. You can choose no mirror, horizontal mirror, vertical mirror, or image center mirror.
void Paint_SetMirroring(UBYTE mirror)
Parameters:
Mirror: indicates the image mirroring mode. MIRROR_NONE, MIRROR_HORIZONTAL, MIRROR_VERTICAL, MIRROR_ORIGIN correspond to no mirror, horizontal mirror, vertical mirror, and about image center mirror respectively.
- Set points of display position and color in the buffer: here is the core GUI function, processing points display position and color in the buffer.
void Paint_SetPixel(UWORD Xpoint, UWORD Ypoint, UWORD Color)
Parameters:
Xpoint: the X position of a point in the image buffer
Ypoint: Y position of a point in the image buffer
Color: indicates the Color of the dot
- Image buffer fill color: Fills the image buffer with a color, usually used to flash the screen into blank.
void Paint_ClearWindows(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, UWORD Xend, UWORD Yend, UWORD Color)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-starting coordinate of the window
Ystart: indicates the Y starting point of the window
Xend: the x-end coordinate of the window
Yend: indicates the y-end coordinate of the window
Color: fill Color
- Draw points: In the image buffer, draw points on (Xpoint, Ypoint), you can choose the color, the size of the point, the style of the point.
void Paint_DrawPoint(UWORD Xpoint, UWORD Ypoint, UWORD Color, DOT_PIXEL Dot_Pixel, DOT_STYLE Dot_Style)
Parameters:
Xpoint: indicates the X coordinate of a point
Ypoint: indicates the Y coordinate of a point
Color: fill Color
Dot_Pixel: The size of the dot, providing a default of eight size points
typedef enum {
DOT_PIXEL_1X1 = 1, // 1 x 1
DOT_PIXEL_2X2 , // 2 X 2
DOT_PIXEL_3X3 , // 3 X 3
DOT_PIXEL_4X4 , // 4 X 4
DOT_PIXEL_5X5 , // 5 X 5
DOT_PIXEL_6X6 , // 6 X 6
DOT_PIXEL_7X7 , // 7 X 7
DOT_PIXEL_8X8 , // 8 X 8
} DOT_PIXEL;
Dot_Style: the size of a point that expands from the center of the point or from the bottom left corner of the point to the right and up
typedef enum {
DOT_FILL_AROUND = 1,
DOT_FILL_RIGHTUP,
} DOT_STYLE;
- Line drawing: In the image buffer, line from (Xstart, Ystart) to (Xend, Yend), you can choose the color, line width, line style.
void Paint_DrawLine(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, UWORD Xend, UWORD Yend, UWORD Color, LINE_STYLE Line_Style , LINE_STYLE Line_Style)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-starting coordinate of a line
Ystart: indicates the Y starting point of a line
Xend: x-terminus of a line
Yend: the y-end coordinate of a line
Color: fill Color
Line_width: The width of the line, which provides a default of eight widths
typedef enum {
DOT_PIXEL_1X1 = 1, // 1 x 1
DOT_PIXEL_2X2 , // 2 X 2
DOT_PIXEL_3X3 , // 3 X 3
DOT_PIXEL_4X4 , // 4 X 4
DOT_PIXEL_5X5 , // 5 X 5
DOT_PIXEL_6X6 , // 6 X 6
DOT_PIXEL_7X7 , // 7 X 7
DOT_PIXEL_8X8 , // 8 X 8
} DOT_PIXEL;
Line_Style: line style. Select whether the lines are joined in a straight or dashed way
typedef enum {
LINE_STYLE_SOLID = 0,
LINE_STYLE_DOTTED,
} LINE_STYLE;
- Draw a rectangle: In the image buffer, draw a rectangle from (Xstart, Ystart) to (Xend, Yend), you can choose the color, the width of the line, and whether to fill the inside of the rectangle.
void Paint_DrawRectangle(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, UWORD Xend, UWORD Yend, UWORD Color, DOT_PIXEL Line_width, DRAW_FILL Draw_Fill)
Parameters:
Xstart: the starting X coordinate of the rectangle
Ystart: indicates the Y starting point of the rectangle
Xend: X terminus of the rectangle
Yend: specifies the y-end coordinate of the rectangle
Color: fill Color
Line_width: The width of the four sides of a rectangle. Default eight widths are provided
typedef enum {
DOT_PIXEL_1X1 = 1, // 1 x 1
DOT_PIXEL_2X2 , // 2 X 2
DOT_PIXEL_3X3 , // 3 X 3
DOT_PIXEL_4X4 , // 4 X 4
DOT_PIXEL_5X5 , // 5 X 5
DOT_PIXEL_6X6 , // 6 X 6
DOT_PIXEL_7X7 , // 7 X 7
DOT_PIXEL_8X8 , // 8 X 8
} DOT_PIXEL;
Draw_Fill: Fill, whether to fill the inside of the rectangle
typedef enum {
DRAW_FILL_EMPTY = 0,
DRAW_FILL_FULL,
} DRAW_FILL;
- Draw circle: In the image buffer, draw a circle of Radius with (X_Center Y_Center) as the center. You can choose the color, the width of the line, and whether to fill the inside of the circle.
void Paint_DrawCircle(UWORD X_Center, UWORD Y_Center, UWORD Radius, UWORD Color, DOT_PIXEL Line_width, DRAW_FILL Draw_Fill)
Parameters:
X_Center: the x-coordinate of the center of a circle
Y_Center: Y coordinate of the center of a circle
Radius: indicates the Radius of a circle
Color: fill Color
Line_width: The width of the arc, with a default of 8 widths
typedef enum {
DOT_PIXEL_1X1 = 1, // 1 x 1
DOT_PIXEL_2X2 , // 2 X 2
DOT_PIXEL_3X3 , // 3 X 3
DOT_PIXEL_4X4 , // 4 X 4
DOT_PIXEL_5X5 , // 5 X 5
DOT_PIXEL_6X6 , // 6 X 6
DOT_PIXEL_7X7 , // 7 X 7
DOT_PIXEL_8X8 , // 8 X 8
} DOT_PIXEL;
Draw_Fill: fill, whether to fill the inside of the circle
typedef enum {
DRAW_FILL_EMPTY = 0,
DRAW_FILL_FULL,
} DRAW_FILL;
- Write Ascii character: In the image buffer, at (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write an Ascii character, you can select Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
void Paint_DrawChar(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, const char Ascii_Char, sFONT* Font, UWORD Color_Foreground, UWORD Color_Background)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-coordinate of the left vertex of a character
Ystart: the Y coordinate of the font's left vertex
Ascii_Char: indicates the Ascii character
Font: Ascii visual character library, in the Fonts folder provides the following Fonts:
Font8: 5*8 font
Font12: 7*12 font
Font16: 11*16 font
Font20: 14*20 font
Font24: 17*24 font
Color_Foreground: Font color
Color_Background: indicates the background color
- Write English string: In the image buffer, use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of English characters, can choose Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
void Paint_DrawString_EN(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, const char * pString, sFONT* Font, UWORD Color_Foreground, UWORD Color_Background)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-coordinate of the left vertex of a character
Ystart: the Y coordinate of the font's left vertex
PString: string, string is a pointer
Font: Ascii visual character library, in the Fonts folder provides the following Fonts:
Font8: 5*8 font
Font12: 7*12 font
Font16: 11*16 font
Font20: 14*20 font
Font24: 17*24 font
Color_Foreground: Font color
Color_Background: indicates the background color
- Write Chinese string: in the image buffer, use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of Chinese characters, you can choose GB2312 encoding character font, font foreground color, font background color.
void Paint_DrawString_CN(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, const char * pString, cFONT* font, UWORD Color_Foreground, UWORD Color_Background)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-coordinate of the left vertex of a character
Ystart: the Y coordinate of the font's left vertex
PString: string, string is a pointer
Font: GB2312 encoding character Font library, in the Fonts folder provides the following Fonts:
Font12CN: ASCII font 11*21, Chinese font 16*21
Font24CN: ASCII font24 *41, Chinese font 32*41
Color_Foreground: Font color
Color_Background: indicates the background color
- Write numbers: In the image buffer,use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of numbers, you can choose Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
void Paint_DrawNum(UWORD Xpoint, UWORD Ypoint, double Nummber, sFONT* Font, UWORD Digit, UWORD Color_Foreground, UWORD Color_Background)
Parameters:
Xpoint: the x-coordinate of the left vertex of a character
Ypoint: the Y coordinate of the left vertex of the font
Nummber: indicates the number displayed, which can be a decimal
Digit: It's a decimal number
Font: Ascii visual character library, in the Fonts folder provides the following Fonts:
Font8: 5*8 font
Font12: 7*12 font
Font16: 11*16 font
Font20: 14*20 font
Font24: 17*24 font
Color_Foreground: Font color
Color_Background: indicates the background color
- Write numbers with decimals: at (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of numbers with decimals, you can choose Ascii code visual character font, font foreground color, font background color
void Paint_DrawFloatNum(UWORD Xpoint, UWORD Ypoint, double Nummber, UBYTE Decimal_Point, sFONT* Font, UWORD Color_Foreground, UWORD Color_Background);
parameter:
Xstart: the X coordinate of the left vertex of the character
Ystart: Y coordinate of the left vertex of the font
Nummber: the displayed number, which is saved in double type here
Decimal_Point: Displays the number of digits after the decimal point
Font: Ascii code visual character font library, the following fonts are provided in the Fonts folder:
Font8: 5*8 font
Font12: 7*12 font
Font16: 11*16 font
Font20: 14*20 font
Font24: 17*24 font
Color_Foreground: font color
Color_Background: background color
- Display time: in the image buffer, use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, display time,you can choose Ascii visual character font, font foreground color, font background color.
void Paint_DrawTime(UWORD Xstart, UWORD Ystart, PAINT_TIME *pTime, sFONT* Font, UWORD Color_Background, UWORD Color_Foreground)
Parameters:
Xstart: the x-coordinate of the left vertex of a character
Ystart: the Y coordinate of the font's left vertex
PTime: display time, here defined a good time structure, as long as the hour, minute and second bits of data to the parameter;
Font: Ascii visual character library, in the Fonts folder provides the following Fonts:
Font8: 5*8 font
Font12: 7*12 font
Font16: 11*16 font
Font20: 14*20 font
Font24: 17*24 font
Color_Foreground: Font color
Color_Background: indicates the background color
- Display image: at (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, display an image whose width is W_Image and height is H_Image;
void Paint_DrawImage(const unsigned char *image, UWORD xStart, UWORD yStart, UWORD W_Image, UWORD H_Image)
parameter:
image: image address, pointing to the image information you want to display
Xstart: the X coordinate of the left vertex of the character
Ystart: Y coordinate of the left vertex of the font
W_Image: Image width
H_Image: Image height
VisionFive2
Adaptive Model
- 0.96inch LCD Module
- 1.14inch LCD Module
- 1.28inch LCD Module
- 1.3inch LCD Module
- 1.54inch LCD Module
- 1.8inch LCD Module
- 2inch LCD Module
- 2.4inch LCD Module
Hardware Connection
| LCD | VisionFive2 Board Pin No. |
| VCC | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| DIN | 19 |
| CLK | 23 |
| CS | 24 |
| DC | 22 |
| RST | 13 |
| BL | 12 |
Install Corresponding Libraries
apt-get install pip pip install VisionFive.gpio apt-get install python3-numpy apt-get install python3-pil
Demo Download
apt-get install p7zip-full wget https://files.waveshare.com/upload/e/e9/LCD_Module_code.7z 7z x LCD_Module_code.7z -o./LCD_Module_code cd LCD_Module_code/VisionFive/python/example/
Run the Corresponding Demo According to the Screen You Purchased
python3 0inch96_LCD_test.py python3 1inch14_LCD_test.py python3 1inch28_LCD_test.py python3 1inch3_LCD_test.py python3 1inch54_LCD_test.py python3 1inch8_LCD_test.py python3 2inch_LCD_test.py python3 2inch4_LCD_test.py
Resource
Docuemnts
Software
Demo codes
3D Drawing
2D Drawing
FAQ
b) Check the output of the BL pin, if it doesn't have any value, please try to disconnect it.
If you use Python codes, you can use the rotate(Rotate) function to change the orientation in any angle.
When using an Arduino, please make sure it is plugged into a 5v power supply.
{{{5}}}
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 PM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)