Difference between revisions of "Template:PI4B Senser Kit User Manual"
(Created page with "=<span style="color:#FF0000;">Configure Raspberry Pi</span>= {{RPI open i2c}} {{RPI open spi}} {{RPI open uart}} ==Install libraries== {{RPI C lib}} *python <pre> sudo apt-g...") |
|||
| Line 152: | Line 152: | ||
hwclock -s #(Synchronize the system time and RTC) | hwclock -s #(Synchronize the system time and RTC) | ||
| − | == | + | ==AD(Onboard TLC1543)== |
| − | === | + | ===Configure A0 Pin=== |
| − | 1) | + | 1) Install libraries (ignore if you have done)<br /> |
| − | 2) | + | 2) Set REF voltage:<br /> |
| − | * | + | *Connect REF to 5V: the REF voltage of the AD chip is 5V (Default) |
| − | * | + | *Connect REF连 to 3V3: the REF voltage of the AD chip is 3.3V. |
| − | + | You can only choose one setting when configure the REF voltage.<br /> | |
[[file:ARPI600_13.png|300px]]<br /> | [[file:ARPI600_13.png|300px]]<br /> | ||
| − | 3) | + | 3) Copy the program/AD_TLC1543 folder to Raspberry Pi and go into it. Run wit the following commands<br /> |
sudo make | sudo make | ||
sudo ./tlc1543 | sudo ./tlc1543 | ||
| − | 4) | + | 4) The data sent from AD0 pin will be printed.<br /> |
| − | 5) | + | 5) Connect the T_A0 pin to A0, then you can connect the A0 pin to any sensors for Analog signal reading:<br /> |
[[file:ARPI600_14.png|300px]]<br /> | [[file:ARPI600_14.png|300px]]<br /> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Configure AD pins=== |
| − | 1) | + | 1) If you want to read the data of other AD pins, you can modify tlc1543.c file:<br /> |
sudo nano tlc1543.c | sudo nano tlc1543.c | ||
| − | + | Find the line:<br /> | |
re=ADCSelChannel(0); | re=ADCSelChannel(0); | ||
| − | + | Change 0 to other number of pin for testing other AD pins (for example: re=ADCSelChannel(1); <br /> | |
| − | + | Save and exti (Ctrl+X, Y)<br /> | |
| − | 2) | + | 2)Run the following commands to test:<br /> |
sudo make | sudo make | ||
sudo ./tlc1543 | sudo ./tlc1543 | ||
| − | |||
==接口说明== | ==接口说明== | ||
Revision as of 06:16, 17 September 2020
Configure Raspberry Pi
Enable I2C Interface
Open a terminal and run the following commands:
sudo raspi-config Choose Interfacing Options -> I2C -> Yes.
Reboot Raspberry Pi:
sudo reboot
Enable SPI interface
- Open the terminal, and use the command to enter the configuration page.
sudo raspi-config Choose Interfacing Options -> SPI -> Yes to enable the SPI interface
sudo reboot
Make sure that the SPI is not occupied by other devices, you can check in the middle of the /boot/config .txt.
Enable UART
Execute the following command to enter the Raspberry Pi configuration:
sudo raspi-config
Choose Interfacing Options -> Serial -> No -> Yes:
You need to disable the login shell and enable the srial port hardware:
Reboot Raspberry Pi:
sudo reboot
Open the /boot/config.txt file and find the following configuration statement to enable the serial port, if not, add it at the end of the file:
enable_uart=1
Reboot to take effect.
Install libraries
Install Library
If you use the bookworm system, you can only use lgpio library, bcm2835 and wiringPi can't be installed and used.
BCM2835
#Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and run the following command wget http://www.airspayce.com/mikem/bcm2835/bcm2835-1.71.tar.gz tar zxvf bcm2835-1.71.tar.gz cd bcm2835-1.71/ sudo ./configure && sudo make && sudo make check && sudo make install # For more, you can refer to the official website at: http://www.airspayce.com/mikem/bcm2835/
WiringPi
#Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and run the following command cd sudo apt-get install wiringpi #For Raspberry Pi systems after May 2019 (earlier than that can be executed without), an upgrade may be required: wget https://project-downloads.drogon.net/wiringpi-latest.deb sudo dpkg -i wiringpi-latest.deb gpio -v # Run gpio -v and version 2.52 will appear, if it doesn't it means there was an installation error # Bullseye branch system using the following command: git clone https://github.com/WiringPi/WiringPi cd WiringPi . /build gpio -v # Run gpio -v and version 2.70 will appear, if it doesn't it means there was an installation error
lgpio
#Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and run the following command wget https://github.com/joan2937/lg/archive/master.zip unzip master.zip cd lg-master sudo make install # You can refer to the official website for more: https://github.com/gpiozero/lg
- python
sudo apt-get updata sudo apt-get install ttf-wqy-zenhei sudo apt-get install python-pip sudo pip install RPi.GPIO sudo pip install spidev sudo apt-get install python-smbus sudo apt-get install python-serial sudo pip install rpi_ws281x
Download Demo codes
sudo apt-get install p7zip wget http://www.waveshare.com/w/upload/3/37/ARPI600.7z 7zr x ARPI600.7z -r -o./ARPI600 sudo chmod 777 -R ARPI600 cd ARPI600/RaspberryPi/ARPI600_Code
Control sensors by Serial port
Configure Serial Port
1) Open a terminal and run the following commands:
sudo nano /boot/cmdline.txt
Change the line below:
wc_otg.lpm_enable=0 console=ttyAMA0,115200 kgdboc=ttyAMA0,115200 console=tty1 root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 rootfstype=ext4 elevator=deadline rootwait
to:
dwc_otg.lpm_enable=0 console=tty1 root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 rootfstype=ext4 elevator=deadline rootwait
Save and exit (Ctrl+X, Y)
2) Run the following command:
sudo nano /etc/inittab
Modify the line below:
#Spawn a getty on Raspberry Pi serial line T0:23:respawn:/sbin/getty -L ttyAMA0 115200 vt100
to:
#Spawn a getty on Raspberry Pi serial line #T0:23:respawn:/sbin/getty -L ttyAMA0 115200 vt100
Save and exit (Ctrl+X, Y)
3) Reboot Raspberry Pi:
sudo reboot
After rebooting, the hardware serial of Raspberry Pi is enabled and the login shell function is disabled. If you want to access Raspberry Pi via serial port, you need to reset all the setting and reboot.
Print data via serial Port
1) Users should configure the jumpers on board for enable serial port:
- Connect CP_RX to P_TX
- Connect CP_TX to P_RX
2)Run putty software in host PC and configure:
- Serial line: Select the COM port according the Devive Manager
- Speed: Set the buad rate to
- Connection type: Choose Serial。
3) Copy the program/Xbee/send folder to Raspberry Pi and go into send folder, run the following commands:
sudo make sudo ./serialTest
The serial port will print data as below:

Set up a wireless network with 2 Xbee modules
Preparation
1) Two Xbee modules
2) Two ARPI600 modules
3) Two Raspberry Pi
- We divide them to A group and B group (XBee-A,ARPI600-A,XBee-B,ARPI600-B)
Install X-CRU tool
1) Install software/X-CTU V5.2.8.6.exe in host PC
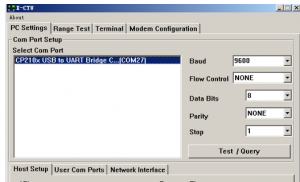
2) Configure XBee mdoule
- Baud: 9600
- Data Bite: 8
- Parity: NONE
- Stop: 1
Test XBee in host PCe
1) Connect XBee-A to ARPI600-A. Connect XBee-B to ARPI600-B.
2) Configure jumpers to enable the XBee:

- Connect XB_RX to CP_RX
- Connect CP_TX to XB_TX
3) Power on the Raspberry Pi
4) Click Test/Query button to check if the XBee module is connected successfully:

5) The module is connected normally if you get the following result:

Configure XBee-A
1) Click Modem Configuration Option, and click Read button to read the parameter of XBee:

2) Select ZIBGEE ROUTER/END DEVICE AT from Function Set box:
![]()
3) Configure Networking parameter as below:
- ID: 234
- DH: 0
- DL: 0
4) Click Write button to save the settings of XBee-A.
Configure XBee-B
1) Click Modem Configuration Option, and click the Read button to read the parameter of XBee.
2) Select ZIGBEE COORDINATOR AT from Function Set box:
![]()
3) Configure Networking parameter as below:
- ID: 234
- DH: 0
- DL: ffff
4) Click the Write button to save the settings of XBee-B.
5) After setting, run two X-CTU windows in the host PC and select the corresponding COM port in the PC Setting option, then you can test the point to point communication between two XBee modules.
6) In the terminal of X-CTU (XBee-A), input the data and the data will be transmitted to XBee-B and printed in terminal of X-CTU software (Bee-B), Blue is the data transmitted and Red is the data Received.

Wireless Communicating Between XBee Modules
Set up and configure XBee modules as above guides first. Then we can configure Raspberry Pi for wireless communicating.
1) Configure jumers of ARPI600:
- Connect XB_RX to P_TX
- Connect XB_TX to P_RX

2) Testing:
Run the following commands:
cd /Xbee/getdata sudo make sudo ./serialTest
Data will be printed as below:
![]()
Go into the send folder and run the following commands:
sudo make sudo ./serialTest
The receiver will printed the data received:

RTC
1) Connectg the RTC JMPjumpers
2) Run the LXTerminal and input:
i2cdetect -y 1
3) The i2c address of PCF8563 should be printed.

4)Run the following commands in LXTerminal terminal:
modprobei2c-dev echo pcf8563 0x51 > /sys/class/i2c-adapter/i2c-1/new_device hwclock -r#(Read the RTC time)
The time of PCF8563 is printed in LXTerminal, it may be different with system time
5) Run the following commands in LXTerminal:
hwclock -w #(Write the system time to PCF8563) hwclock -r #(Read the PCF8563 time) hwclock -s #(Synchronize the system time and RTC)
AD(Onboard TLC1543)
Configure A0 Pin
1) Install libraries (ignore if you have done)
2) Set REF voltage:
- Connect REF to 5V: the REF voltage of the AD chip is 5V (Default)
- Connect REF连 to 3V3: the REF voltage of the AD chip is 3.3V.
You can only choose one setting when configure the REF voltage.

3) Copy the program/AD_TLC1543 folder to Raspberry Pi and go into it. Run wit the following commands
sudo make sudo ./tlc1543
4) The data sent from AD0 pin will be printed.
5) Connect the T_A0 pin to A0, then you can connect the A0 pin to any sensors for Analog signal reading:

Configure AD pins
1) If you want to read the data of other AD pins, you can modify tlc1543.c file:
sudo nano tlc1543.c
Find the line:
re=ADCSelChannel(0);
Change 0 to other number of pin for testing other AD pins (for example: re=ADCSelChannel(1);
Save and exti (Ctrl+X, Y)
2)Run the following commands to test:
sudo make sudo ./tlc1543
接口说明
接口概述
1) 默认情况下,Arduino接口数字控制脚对应树莓派IO如下:
| Arduino接口 | 树莓派IO |
| D0 | P_RX |
| D1 | P_TX |
| D2 | P0 |
| D3 | P1 |
| D4 | P2 |
| D5 | P3 |
| D6 | P4 |
| D7 | P5 |
| D8 | P6 |
| D9 | P7 |
| D10 | CE0 |
| D11 | MOSI |
| D12 | MISO |
| D13 | SCK |
2) 模块电路板上有配置APRI600的D11, D12, D13管脚的跳线。它们之间通过0Ω电阻短接。如下图所示:

出厂时跳线连接如下:
- SCK连接D13
- MISO连接D12
- MOSI连接D11
如果连接:
- D13连接P26
- D12连接IO_SD
- D11连接IO_SC
则相当于使D11, D12, D13管脚接到树莓派普通IO控制脚。
注意:用户可以根据需要更改这些跳线,但是此操作需要用到焊接器材。在没有我司工作人员指导下擅自更改,将视为放弃保修。
3) APRI600的A0-A5管脚可以配置为IO控制功能或者ADC功能。

a) 当A0-A5连接到 1处时,则A0-A5作为IO控制管脚,和树莓派管脚对应关系参见下表:
| Arduino接口 | 树莓派IO |
| A0 | CE1 |
| A1 | P5 |
| A2 | P6 |
| A3 | P7 |
| A4 | CE0 |
| A5 | MOSI |
b) 当A0-A5连接到 3处时,则A0-A5作为AD转换脚。
4) 用户可以连接A4和P_SCL,A5和P_SDA(如图 22.),以作为树莓派的I2C控制脚,默认断开。
注意:用户可以根据更改这些跳线,但是此操作需要用到焊接器材。在没有我司工作人员指导下擅自更改,将视为放弃保修。

5) ARPI600提供传感器接口,如图引出4P的传感器接口:

其中:
- A处接TLC1543芯片的AD转换(A6-A10)管脚。
- D处接树莓派的P0-P4 IO控制脚。
方便用户接入多种传感器。
ARPI600连接传感器套件(需另外选购)
以下操作都需把ARPI600插上树莓派使用。如果只有ARPI600和传感器套件,却没有树莓派的话,那么是无法使用的。
- Color Sensor
1) 把ARPI600插入到树莓派。
2) 按照下表连接传感器和ARPI600的管脚:
| Color Sensor接口 | ARPI600 |
| LED | 3.3V |
| OUT | P0 |
| S3 | P4 |
| S2 | P3 |
| S1 | P2 |
| S0 | P1 |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
3) 把Color_Sensor文件夹复制到树莓派系统内,上电之后,终端执行:
cd Color_Sensor sudo ./Color_Sensor
4) 程序会对芯片的白平衡进行调整,时间大概为2s,调整结束以后即可把三原色的频率经过终端输出,对照RGB颜色对照表,即可知道所测得颜色。
5) 按Ctrl+C结束程序。
- Flame Sensor
1) 把ARPI600插入到树莓派。
2) 按照下表连接传感器和ARPI600的管脚:
| Flame Sensor管脚 | ARPI600 |
| DOUT | NC |
| AOUT | T_A6 |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
3) 把Flame_Sensor文件夹复制到树莓派系统内,上电之后,终端执行:
cd Flame_Sensor sudo ./General_Sensor
4) 传感器靠近火焰时,模块上的信号指示灯点亮。传感器远离火焰时,模块上的信号指示灯熄灭。
5) 随着传感器与火焰距离的改变,终端输出的数据也会发生改变。
6) 按Ctrl+C结束程序
注意:该传感器主要用于感知火焰,但其自身并不防火。因此使用时请与火焰保持一定距离,以免烧坏传感器。
- Metal Sensor
1) 把ARPI600插入到树莓派。 2) 按照下表连接传感器和ARPI600的管脚:
| Metal Sensor管脚 | ARPI600 |
| DOUT NC | |
| AOUT T_A6 | |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
3) 把Metal_Sensor文件夹复制到树莓派系统内,上电之后,终端执行:
cd Metal_Sensor sudo ./General_Sensor
4) 传感器接触带电金属时,模块上的信号指示灯点亮。传感器远离金属时,模块上的信号指示灯熄灭。
5) 随着传感器与金属接触与分离,终端输出的数据会发生相应改变。
6) 按Ctrl+C结束程序。
- Hall Sensor
1) 把ARPI600插入到树莓派。
2) 按照下表连接传感器和ARPI600的管脚:
| Hall Sensor管脚 | ARPI600 |
| NC | |
| AOUT | T_A6 |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
3) 把Hall Sensor文件夹复制到树莓派系统内,上电之后,终端执行:
cd Hall_Sensor sudo ./General_Sensor
4) 传感器靠近磁铁时,模块上的信号指示灯点亮。传感器远离磁铁时,模块上的信号指示灯熄灭。
5) 随着传感器与金属接触与分离,终端输出的数据会发生相应改变。
6) 按Ctrl+C结束程序。
- Infrared Reflective Sensor
1) 把ARPI600插入到树莓派。
2) 按照下表连接传感器和ARPI600的管脚:
| Infrared Reflective Sensor管脚 | ARPI600 |
| DOUT | NC |
| AOUT | T_A6 |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
3) 把Infrared_Reflective_Sensor文件夹复制到树莓派系统内,上电之后,终端执行:
cd Infrared_Reflective_Sensor sudo ./General_Sensor
4) 传感器靠近障碍物时,模块上的信号指示灯点亮。传感器远离障碍物时,模块上的信号指示灯熄灭。
5) 随着传感器与障碍物距离的变化,终端输出的数据也会发生改变。
6) 按Ctrl+C结束程序。
- Laser Sensor
1) 把ARPI600插入到树莓派。
2) 按照下表连接传感器和ARPI600的管脚:
| Laser Sensor管脚 | ARPI600 |
| DOUT | NC |
| AOUT | T_A6 |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
3) 把Laser_Sensor文件夹复制到树莓派系统内,在终端运行程序
cd Laser_Sensor sudo ./General_Sensor
4) 把障碍物置于激光传感器上方,此时模块上的信号指示灯会被点亮,把障碍物远离激光传感器上方,此时模块上的信号指示灯熄灭。由此可知激光传感器是否探测到障碍物。
5) 按Ctrl+C结束程序。
- Moisture Sensor
1) 把ARPI600插入到树莓派。
2) 按照下表连接传感器和ARPI600的管脚:
| Moisture Sensor管脚 | ARPI600 |
| DOUT | NC |
| AOUT | T_A6 |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
3) 把Moisture_Sensor文件夹复制到树莓派系统内,上电之后,终端执行:
cd Moisture_Sensor sudo ./General_Sensor
4) 把传感器插入土壤中,然后逐渐往土壤中加水,终端输出数据变化。
5) 按Ctrl+C结束程序。
- Rotation Sensor
1) 把ARPI600插入到树莓派。
2) 按照下表连接传感器和ARPI600的管脚:
| Moisture Sensor管脚 | ARPI600 |
| SIA | P0 |
| SIB | P1 |
| SW | P2 |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
3) 把Rotation_Sensor文件夹复制到树莓派系统内,上电之后,终端执行:
cd Rotation_Sensor sudo ./Rotation_Sensor
4) 分别顺时针旋转,逆时针旋转和按下编码器,端口分别输出数据:
Turn right! Turn left! Turn down!
5) 把模块的SIA,SIB,SW端口分别连接逻辑分析仪(需另外选购)的CH0,CH1,CH2。
顺时针旋转编码器,波行输出如下:
![]()
逆时针转编码器,波行输出如下:
![]()
按下编码器上的按键:
![]()
6) 按Ctrl+C结束程序。
- Sound Sensor
1) 把ARPI600插入到树莓派。
2) 按照下表连接传感器和ARPI600的管脚:
| Sound Sensor管脚 | ARPI600 |
| DOUT | NC |
| AOUT | T_A6 |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
3) 把Sound_Sensor文件夹复制到树莓派系统内,上电之后,终端执行:
cd Sound_Sensor sudo ./General_Sensor
4) 当模块的咪头靠近发声源时,模块上的信号指示灯点亮。当模块的咪头远离发声源时,模块上的信号指示灯熄灭。
5) 随着传感器与发声源距离的变化,终端输出数据有相应的变化。
6) 按Ctrl+C结束程序。
- Temperature-Humidity Sensor
1) 把ARPI600插入到树莓派。
2) 按照下表连接传感器和ARPI600的管脚:
| 管脚 | ARPI600 |
| DOUT | P0 |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
3) 把Temperature-Humidity_Sensor文件夹复制到树莓派系统内,上电之后,终端执行:
cd Temperature-Humidity_Sensor sudo ./DHT11
4) 终端输出温度和湿度。例如:
Humidity=33 Temperature=28
5) 按Ctrl+C结束程序。
- MQ-5 Gas Sensor
1) 把ARPI600插入到树莓派。
2) 按照下表连接传感器和ARPI600的管脚:
| 管脚 | ARPI600 |
| DOUT | NC |
| AOUT | T_A6 |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
3) 把MQ-5_Gas_Sensor文件夹复制到树莓派系统内,上电之后,终端执行:
cd MQ-5_Gas_Sensor sudo ./General_Sensor
4) 让传感器先预热一分钟。
5) 把传感器放入含有敏感气体(该气体传感器对液化气,天然气和煤气敏感)的装置中,模块上的信号指示灯点亮。把传感器从敏感气体装置中取出,模块上的信号指示灯熄灭。由此可判断敏感气体的浓度是否超标。
6) 按Ctrl+C结束程序。
- Tilt Sensor
1) 把ARPI600插入到树莓派。
2) 按照下表连接传感器和ARPI600的管脚:
| 管脚 | ARPI600 |
| DOUT | T_A6 |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
3) 把Tilt_Sensor文件夹复制到树莓派系统内,上电之后,终端执行:
cd Tilt_Sensor sudo ./General_Sensor
4) 晃动模块或使模块倾斜时,模块上的信号指示灯点亮。模块平行放置时,模块上的信号指示灯熄灭。由此可判断模块的状态是否发生晃动或倾斜。
5) 按Ctrl+C结束程序。
- UV Sensor
1) 把ARPI600插入到树莓派。
2) 按照下表连接传感器和ARPI600的管
脚:
| 管脚 | ARPI600 |
| T_A6 | |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
3) 把UV_Sensor文件夹复制到树莓派系统内,上电之后,终端执行:
cd UV_Sensor sudo ./General_Sensor
4) 让传感器靠近阳光,终端输出的数据会发生改变。
5) 按Ctrl+C结束程序。
- Liquid Level Sensor
1) 把ARPI600插入到树莓派。
2) 按照下表连接传感器和ARPI600的管脚:
| 管脚 | ARPI600 |
| AOUT | T_A6 |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
3) 把Liquid_Level_Sensor文件夹复制到树莓派系统内,上电之后,终端执行:
cd Liquid_Level_Sensor sudo ./General_Sensor
4) 把传感器插入一定深度的水中,终端输出的数据会发生改变。
5) 按Ctrl+C结束程序。


