Difference between revisions of "E-Paper ESP32 Driver Board"
(→FAQ) |
|||
| (93 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | <div class=" | + | <div class="wiki-pages jet-green-color"> |
{{Infobox item | {{Infobox item | ||
| − | |img=[[File:e-Paper-ESP32-Driver-Board- | + | |img=[[File:e-Paper-ESP32-Driver-Board-01.jpg|300px|{{Amazon_nolink|default={{#ifeq: {{#urlget:amazon|0}}|{{#urlget:Amazon|0}}| default|}}|url=link=https://www.waveshare.com/e-paper-esp32-driver-board.htm}}]] |
| − | |caption=Universal e-Paper Driver HAT | + | |caption=Universal e-Paper Driver HAT<br/>supports various Waveshare SPI e-Paper raw panels |
|category=[[:Category:Expansions|Expansions]], [[:Category:e-Paper|e-Paper]], [[:Category:Raspberry Pi|Raspberry Pi]] | |category=[[:Category:Expansions|Expansions]], [[:Category:e-Paper|e-Paper]], [[:Category:Raspberry Pi|Raspberry Pi]] | ||
|brand=Waveshare | |brand=Waveshare | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
{{Product List|OLEDs / LCDs/e-Paper}} | {{Product List|OLEDs / LCDs/e-Paper}} | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | =Note= | ||
| + | This Wiki mainly introduces the specific operation of this product, if you want to get the product support ink screen models please go to the bottom of the official website product details to get.<br/> | ||
| + | {{E-paper Demo Table}} | ||
| − | < | + | =Overview= |
| − | + | ==Version Guide== | |
| − | = Introduction = | + | <font color="#FF0000">20220728: The serial port chip is changed from CP2102 to CH343, please pay attention to the driver selection.</font> |
| − | Universal e-Paper Driver HAT | + | ==Introduction== |
| + | Universal e-Paper Driver HAT features ESP32 and supports various Waveshare SPI interfaces in e-Paper raw panels. It also supports refreshing images to e-paper via WIFI or Bluetooth and Arduino. | ||
{{Amazon|{{#ifeq: {{#urlget:amazon|0}}|{{#urlget:Amazon|0}}| default|}}=display | {{Amazon|{{#ifeq: {{#urlget:amazon|0}}|{{#urlget:Amazon|0}}| default|}}=display | ||
|More = [https://www.waveshare.com/e-paper-esp32-driver-board.htmm More]}} | |More = [https://www.waveshare.com/e-paper-esp32-driver-board.htmm More]}} | ||
| + | |||
==Parameter== | ==Parameter== | ||
*WiFi Standard: 802.11b/g/n | *WiFi Standard: 802.11b/g/n | ||
| − | *Communication Interface: SPI | + | *Communication Interface: SPI/IIC |
| − | *Bluetooth Standard: 4.2, BR/EDR and BLE included | + | *Bluetooth Standard: 4.2, BR/EDR, and BLE included |
*Communication Interface: 3-Wire SPI, 4-wire SPI (default) | *Communication Interface: 3-Wire SPI, 4-wire SPI (default) | ||
| − | * | + | *Operating Voltage: 5V |
| − | * | + | *Operating Current: 50mA-150mA |
| − | *Outline | + | *Outline Dimensions: 29.46mm x 48.25mm |
| − | + | *Flash Size: 4 MB | |
| + | *SRAM Size: 520 KB | ||
| + | *ROM Size: 448 KB | ||
| + | |||
==Pin== | ==Pin== | ||
| − | {| | + | {|border=1; style="width:700px;" align="center" |
| − | + | |-style="background:green; color:white;" align="center" | |
| − | |- | + | |Pin||ESP32||Description |
| − | |VCC|| | + | |-align="center" |
| − | |- | + | |VCC||3V3||Power input (3.3V) |
| − | |GND||GND|| | + | |-align="center" |
| − | |- | + | |GND||GND||Ground |
| − | | | + | |-align="center" |
| − | |- | + | |DIN||P14||SPI MOSI pin, data input |
| − | | | + | |-align="center" |
| − | |- | + | |SCLK||P13||SPI CLK pin, clock signal input |
| − | |CS||P15||Chip | + | |-align="center" |
| − | |- | + | |CS||P15||Chip selection, low active |
| − | | | + | |-align="center" |
| − | |- | + | |DC||P27||Data/command, low for commands, high for data |
| − | |RST||P26||Reset, active | + | |-align="center" |
| − | |- | + | |RST||P26||Reset, low active |
| − | | | + | |-align="center" |
| + | |BUSY||P25||Busy status output pin (means busy) | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | PS: The above is the board fixed connection, no additional operation by the user | + | '''PS: The above is the board fixed connection, with no additional operation by the user.''' |
==Feature== | ==Feature== | ||
| − | *Onboard ESP32, support Arduino development | + | *Onboard ESP32, support Arduino development. |
| − | *Provide Android mobile APP program, which can update the display content through Bluetooth EDR, easy to use | + | *Provide an Android mobile APP program, which can update the display content through Bluetooth EDR, easy to use. |
| − | *Provide HTML host computer program, which can remotely update the display content through the web page, which is convenient to integrate into various network applications | + | *Provide HTML host computer program, which can remotely update the display content through the web page, which is convenient to integrate into various network applications. |
| − | *Supports Floyd-Steinberg dithering algorithm for more color combinations and better | + | *Supports Floyd-Steinberg's dithering algorithm for more color combinations and better shadows of the original image. |
| − | *Supports many common image formats (BMP, JPEG, GIF, PNG, etc.) | + | *Supports many common image formats (BMP, JPEG, GIF, PNG, etc.). |
| − | *Factory built-in e-ink screen driver (open source) | + | *Factory built-in e-ink screen driver (open source). |
| − | *5V pin supports 3.6V to 5.5V voltage input | + | *5V pin supports 3.6V to 5.5V voltage input and can be powered by a lithium battery. |
| − | * | + | *Comes with online resources and manuals. |
==Application== | ==Application== | ||
| − | This product cooperates with the ink screen and is suitable for the application scenario of wireless | + | This product cooperates with the ink screen and is suitable for the application scenario of wireless refreshing. |
*Supermarket electronic price tag | *Supermarket electronic price tag | ||
*Electronic name card | *Electronic name card | ||
| Line 68: | Line 77: | ||
=Preparation= | =Preparation= | ||
{{E-paper setup}} | {{E-paper setup}} | ||
| − | *Turn on the serial port module: Toggle the No. 2 switch to "ON", this switch controls the power supply of the | + | {|border=1; style="border:#green; width:800px; line-height:200%" align="center" |
| − | *Use a micro USB cable to connect the ESP32 driver board to a computer or 5V power supply<br/> | + | |- style="background:green; color:white;" align="center" |
| + | | Resistor (Display Config) || Screen | ||
| + | |- style="background:white; color:black;" align="center" | ||
| + | |rowspan="7"| 0.47R (A) | ||
| + | | 2.13inch e-Paper (D), 2.7inch e-Paper, 2.9inch e-Paper (D) | ||
| + | |- style="background:white; color:black;" align="center" | ||
| + | | 3.7inch e-Paper, 4.01inch e-Paper (F), 4.2inch e-Paper | ||
| + | |- style="background:white; color:black;" align="center" | ||
| + | | 4.2inch e-Paper (B), 4.2inch e-Paper (C), 5.65inch e-Paper (F) | ||
| + | |- style="background:white; color:black;" align="center" | ||
| + | | 5.83inch e-Paper, 5.83inch e-Paper (B), 7.3inch e-Paper (G) | ||
| + | |- style="background:white; color:black;" align="center" | ||
| + | | 7.3inch e-Paper (F), 7.5inch e-Paper, 7.5inch e-Paper (B) | ||
| + | |- style="background:white; color:black;" align="center" | ||
| + | | 1.64inch e-Paper (G), 2.36inch e-Paper (G), 3inch e-Paper (G) | ||
| + | |- style="background:white; color:black;" align="center" | ||
| + | | 4.37inch e-Paper (G)<br> | ||
| + | |- style="background:#efefef; color:black;" align="center" | ||
| + | |rowspan="3"| 3R (B) | ||
| + | | 1.54inch e-Paper, 1.54inch e-Paper(B), 2.13inch e-Paper | ||
| + | |- style="background:#efefef; color:black;" align="center" | ||
| + | | 2.13inch e-Paper (B), 2.66inch e-Paper, 2.66inch e-Paper (B) | ||
| + | |- style="background:#efefef; color:black;" align="center" | ||
| + | | 2.9inch e-Paper, 2.9inch e-Paper (B) | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Turn on the serial port module: Toggle the No. 2 switch to "ON", this switch controls the power supply of the USB to the UART module. When you don't need to use it, you can manually turn off the module to save power (if switch 2 is in the OFF state, you cannot upload the program.)<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Use a micro USB cable to connect the ESP32 driver board to a computer or 5V power supply.<br/> | ||
| + | |||
==Download Demo== | ==Download Demo== | ||
| − | We provide three kinds of demos: local, | + | We provide three kinds of demos: local, Bluetooth, and WiFi. The sample program can be found in [[#Resources]], or click [https://files.waveshare.com/upload/5/50/E-Paper_ESP32_Driver_Board_Code.7z the sample demo] to download.<br/> |
| − | Unzip the downloaded compressed package, you can get the following files: | + | Unzip the downloaded compressed package, you can get the following files:<br/> |
[[File:esp32 download de.png]]<br/> | [[File:esp32 download de.png]]<br/> | ||
*ePape_Esp32_Loader_APP: Bluetooth App source code (Android Studio)<br/> | *ePape_Esp32_Loader_APP: Bluetooth App source code (Android Studio)<br/> | ||
| Line 78: | Line 116: | ||
*Loader_esp32bt: Bluetooth demos<br/> | *Loader_esp32bt: Bluetooth demos<br/> | ||
*Loader_esp32wf: WiFi demo<br/> | *Loader_esp32wf: WiFi demo<br/> | ||
| − | *app-release.apk: Bluetooth | + | *app-release.apk: Bluetooth demo App installation package<br/> |
| + | |||
==Environment Configuration== | ==Environment Configuration== | ||
| + | *[https://www.waveshare.com/wiki/Arduino_ESP32/8266_Online_Installation Arduino ESP32/8266 Online Installation] | ||
| + | <!-- | ||
*If the Arduino IDE is not installed on your computer before, or the version of the IDE is older. It is recommended to go to the Arduino official website to download the latest IDE and install it according to your own system.<br/> | *If the Arduino IDE is not installed on your computer before, or the version of the IDE is older. It is recommended to go to the Arduino official website to download the latest IDE and install it according to your own system.<br/> | ||
Official link: https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software<br/> | Official link: https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software<br/> | ||
'''Download the ESP32 Dev Module management tool:''' | '''Download the ESP32 Dev Module management tool:''' | ||
| − | 1. Open the preferences of the | + | 1. Open the preferences of the Arduino software and add a link to the add-on board manager URL: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/gh-pages/package_esp32_index.json |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
[[File:esp32 dev.png]]<br/> | [[File:esp32 dev.png]]<br/> | ||
| Line 91: | Line 132: | ||
[[File:ide.png]]<br/> | [[File:ide.png]]<br/> | ||
If the installation cannot be completed due to repeated errors, please contact the after-sales technicians.<br/> | If the installation cannot be completed due to repeated errors, please contact the after-sales technicians.<br/> | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | |||
==Image Processing Algorithms== | ==Image Processing Algorithms== | ||
| − | In the Bluetooth and WiFi demos, two image processing algorithms are provided, namely Level and Dithering<br/> | + | In the Bluetooth and WiFi demos, two image processing algorithms are provided, namely Level and Dithering.<br/> |
| − | === | + | ===Color scale method=== |
| − | An image can be divided into several large color gamuts, and each pixel on the image is divided into these color gamuts according to how close the color is to these color gamuts. This method is more suitable for images with few colors, such as bright or tri-color shapes or text images. Taking the black and white and red ink screen as an example, when processing the image, we hope to process it into black, white and red, so for an image, we can divide all the colors of the image into three large color areas: the black area , white area, red area.<br/> | + | An image can be divided into several large color gamuts, and each pixel on the image is divided into these color gamuts according to how close the color is to these color gamuts. This method is more suitable for images with few colors, such as bright or tri-color shapes or text images. Taking the black and white and red ink screen as an example, when processing the image, we hope to process it into black, white, and red, so for an image, we can divide all the colors of the image into three large color areas: the black area, white area, red area.<br/> |
| − | For example, according to the figure below, if the value of a pixel in the grayscale image is equal to or less than 127, we regard this pixel as a black pixel, otherwise, it is white<br/> | + | For example, according to the figure below, if the value of a pixel in the grayscale image is equal to or less than 127, we regard this pixel as a black pixel, otherwise, it is white.<br/> |
[[File:colorscale.png]]<br/> | [[File:colorscale.png]]<br/> | ||
| − | For color images, we all know that RGB has three color channels. Compared with the red channel, we can refer to blue and green as the blue-green channel | + | For color images, we all know that RGB has three color channels. Compared with the red channel, we can refer to blue and green as the blue-green channel or the non-red channel. According to the figure below, a pixel on a color image, if it has a high value in the red channel, but a low value in the blue-green channel, we classify it as a red pixel; if its red channel and blue- If the green channel has low values, we classify it as a black pixel; if the red and blue-green channel values are high, we classify it as white.<br/> |
[[File:colordoth.png]]<br/> | [[File:colordoth.png]]<br/> | ||
| − | In the algorithm, the color definition is calculated based on the difference between the RGB value and the sum of the squares of the expected color value. The expected color value refers to the color value that the pixel is closest to, and these values are stored in the curPal array<br/> | + | In the algorithm, the color definition is calculated based on the difference between the RGB value and the sum of the squares of the expected color value. The expected color value refers to the color value that the pixel is closest to, and these values are stored in the curPal array.<br/> |
[[File:colordoth2.png]]<br/> | [[File:colordoth2.png]]<br/> | ||
===Dithering=== | ===Dithering=== | ||
| − | For those images with more colors or more gradient areas, the above gradation method is not suitable. In many cases, the pixels in the gradient area in the image may be very close to all color gamuts. If you use the gradation method to draw The image will lose a lot of image details. Many images taken by cameras, by mixing colors to paint shadows and transition areas, in these images, the gradient area accounts for the majority | + | For those images with more colors or more gradient areas, the above gradation method is not suitable. In many cases, the pixels in the gradient area in the image may be very close to all color gamuts. If you use the gradation method to draw The image will lose a lot of image details. Many images are taken by cameras, by mixing colors to paint shadows and transition areas, in these images, the gradient area accounts for the majority. |
For the human eye, it is easy to confuse a particularly small color. For example, two colors, red and blue, are juxtaposed. If you reduce it to a small enough hand, it will appear to the human eye as a mixture of red and blue. into color. The defect of the human eye means that we can deceive the human eye and use the "mixing" method to obtain more colors that can be expressed. The dithering algorithm uses this phenomenon. | For the human eye, it is easy to confuse a particularly small color. For example, two colors, red and blue, are juxtaposed. If you reduce it to a small enough hand, it will appear to the human eye as a mixture of red and blue. into color. The defect of the human eye means that we can deceive the human eye and use the "mixing" method to obtain more colors that can be expressed. The dithering algorithm uses this phenomenon. | ||
| − | The | + | The demo we provide uses the Floyd-Steinberg dithering algorithm - based on error diffusion (published by Robert Floy and Louis Steinberg in 1976). The formula is for error diffusion according to the image below:<br/> |
[[File:dither.png]]<br/> | [[File:dither.png]]<br/> | ||
| − | X is the error (a scalar (vector) difference between the original color and the gray value (color value)), this error will spread to the right, lower right, lower, and lower left four directions, respectively 7/16, 1/16, 5/16 and 3/16 weights are added to the values of these four pixels. Interested users can go to understand the algorithm, there are many resources on the Internet.<br/> | + | X is the error (a scalar (vector) difference between the original color and the gray value (color value)), this error will spread to the right, lower right, lower, and lower left in four directions, respectively 7/16, 1/16, 5/16 and 3/16 weights are added to the values of these four pixels. Interested users can go to understand the algorithm, there are many resources on the Internet.<br/> |
| + | |||
===Comparison=== | ===Comparison=== | ||
Original image<br/> | Original image<br/> | ||
| Line 116: | Line 160: | ||
[[File:gr.png]]<br/> | [[File:gr.png]]<br/> | ||
| − | |||
{{ESP32 e-Paper BT-Example}} | {{ESP32 e-Paper BT-Example}} | ||
| − | |||
{{ESP32 e-Paper WiFi-Example}} | {{ESP32 e-Paper WiFi-Example}} | ||
| − | |||
{{ESP32 e-Paper Offline-Example}} | {{ESP32 e-Paper Offline-Example}} | ||
= Resources= | = Resources= | ||
== Documentation == | == Documentation == | ||
| − | * [https:// | + | * [https://files.waveshare.com/upload/8/80/E-Paper_ESP32_Driver_Board_Schematic.pdf Schematic] |
| + | *[https://files.waveshare.com/upload/4/4a/E-Paper_ESP32_Driver_Board_user_manual_en.pdf User Manual] | ||
| + | *[https://www.espressif.com.cn/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-wroom-32_datasheet_en.pdf ESP32 datasheet] | ||
== Demo Code == | == Demo Code == | ||
| − | *[ | + | *[https://files.waveshare.com/upload/5/50/E-Paper_ESP32_Driver_Board_Code.7z Sample demo] |
| + | |||
| + | == Software Driver== | ||
| + | |||
| + | CP2102 (Old version, used before July 2022) | ||
| + | *[https://files.waveshare.com/upload/f/f1/CH343SER.7z CH343 VCP driver for Windows] | ||
| + | *[https://files.waveshare.com/upload/0/04/CH34XSER_MAC.7z CH343 driver for MacOS] | ||
| + | *[https://files.waveshare.com/upload/1/1a/CH34X_DRV_INSTALL_INSTRUCTIONS.pdf MacOS guide] | ||
| + | |||
| + | CH343 (New version, used after July 2022) | ||
| + | *[https://files.waveshare.com/upload/6/6a/CH343SER_%282%29.7z Windows VCP driver] | ||
| + | *[https://files.waveshare.com/upload/5/50/CH34XSER_MAC_%285%29.7z MAC driver] | ||
| + | |||
==Related Resources== | ==Related Resources== | ||
| − | This is a post in Arduino Form about our SPI e-Paper thanks to ZinggJM, maybe you want to refer to. | + | *[https://www.espressif.com.cn/en/support/download/all ESP32 Resouces] |
| + | *[https://www.waveshare.com/wiki/E-Paper_Floyd-Steinberg E-Paper Floyd-Steinberg] | ||
| + | *[https://files.waveshare.com/upload/c/c6/Zimo221.7z Zimo221] | ||
| + | *[https://www.waveshare.com/wiki/Image2Lcd_Image_Modulo Image2Lcd Image Modulo] | ||
| + | *[https://www.waveshare.com/wiki/Image2Lcd_Image_Modulo Image Modulo] | ||
| + | <!-- | ||
| + | This is a post in Arduino Form about our SPI e-Paper thanks to ZinggJM, which maybe you want to refer to. | ||
*[https://forum.arduino.cc/index.php?topic=487007.0 Waveshare e-Paper display with SPI] | *[https://forum.arduino.cc/index.php?topic=487007.0 Waveshare e-Paper display with SPI] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[https://www.espressif.com/en/support/download/all ESP32 Resouces] | ||
| + | *[https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-wroom-32_datasheet_en.pdf ESP32 Datasheet] | ||
| + | --> | ||
=FAQ= | =FAQ= | ||
| − | {{FAQ|If you don't have a V2 logo on the back of your 2. | + | {{FAQ|Which one is used in the ESP32 module? |
| − | * Open | + | | |
| + | ESP32 Flash: 4M<br> | ||
| + | SRAM: 520KB<br> | ||
| + | ROM: 448KB<br> | ||
| + | PARAM: 0<br> | ||
| + | Freq.: 240MHz<br> | ||
| + | [[File:E-Paper ESP32 FAQ011.png]] | ||
| + | ||}} | ||
| + | {{FAQ|The Arduino software does not detect the port number? | ||
| + | |Open the Device Manager and check if the corresponding port number is used for the corresponding location.<br/> | ||
| + | [[File:E-Paper ESP32 FAQ012.png]]<br/> | ||
| + | If the corresponding driver is not installed, it will be displayed as follows, or in the unknown device.<br/> | ||
| + | [[File:E-Paper ESP32 FAQ013.png]]<br/> | ||
| + | Possible reasons for such illumination:<br/> | ||
| + | 1. the computer port is bad.<br/> | ||
| + | 2. the data line has problems.<br/> | ||
| + | 3. the switch on the board is not dialed to ON.<br/> | ||
| + | [[File:E-Paper ESP32 FAQ014.jpg]]<br/> | ||
| + | ||}} | ||
| + | {{FAQ|If you don't have a V2 logo on the back of your 2.13-inch e-paper screen, how do I use it?| | ||
| + | * Open epd2in13.h in the project and change the following value to 1. | ||
[[File:epd2in13_esp_chose.png|400px]] | [[File:epd2in13_esp_chose.png|400px]] | ||
|||}} | |||}} | ||
| − | {{FAQ|If you don't have a V2 logo on the back of your 1. | + | {{FAQ|If you don't have a V2 logo on the back of your 1.54-inch e-paper screen, how do I use it? |
| − | |* Open epd1in54.h in the project and change the following value to 1 | + | |* Open epd1in54.h in the project and change the following value to 1. |
[[File:in54.png]]<br/> | [[File:in54.png]]<br/> | ||
|||}} | |||}} | ||
{{FAQ|ESP32 downloads the Bluetooth demo, and the module reports an error: "Guru Meditation Error: Core 0 panic'ed (LoadProhibited). Exception was unhandled." and the Bluetooth cannot be turned on successfully. What should I do? | {{FAQ|ESP32 downloads the Bluetooth demo, and the module reports an error: "Guru Meditation Error: Core 0 panic'ed (LoadProhibited). Exception was unhandled." and the Bluetooth cannot be turned on successfully. What should I do? | ||
| − | |Download [https:// | + | |Download [https://files.waveshare.com/wiki/E-Paper-ESP32-Driver-Board/Arduino-esp32-master.zip Arduino-ESP32 Package]. Unzip the files in the compressed package to the hardware\espressif\esp32 path in the Arduino IDE installation directory, select "OK to overwrite the file" (remember to back up the original file), and then re-run the routine after powering off. (Note: If the path does not exist in the installation directory, you can create it manually).<br/> |
|||}} | |||}} | ||
{{FAQ|Downloading ESP32 program with Arduino sometimes succeeds and sometimes fails, how to solve it? | {{FAQ|Downloading ESP32 program with Arduino sometimes succeeds and sometimes fails, how to solve it? | ||
| − | |Try to reduce the baud rate, you can try to adjust to 115200, as shown in the figure below<br/> | + | |Try to reduce the baud rate, you can try to adjust to 115200, as shown in the figure below:<br/> |
[[File:FAQ arduino.png]]<br/> | [[File:FAQ arduino.png]]<br/> | ||
|||}} | |||}} | ||
| − | {{FAQ|The wifi routine upload is normal, the serial port outputs the | + | {{FAQ|The wifi routine upload is normal, the serial port outputs the IP address, but the computer input IP address cannot be accessed, it is necessary to check that the network segment of the IP is consistent with the network segment value of the wifi, and the IP does not conflict? |
| − | |Modify the | + | | |
| + | Modify the IP network segment, as shown in the following figure:<br/> | ||
[[File:wifi faq.png]]<br/> | [[File:wifi faq.png]]<br/> | ||
|||}} | |||}} | ||
{{FAQ|If the computer does not recognize the driver board, first confirm whether the serial port driver has been installed, and then try to replace the USB cable and USB interface as much as possible. | {{FAQ|If the computer does not recognize the driver board, first confirm whether the serial port driver has been installed, and then try to replace the USB cable and USB interface as much as possible. | ||
| − | |mac serial driver: https://www.silabs.com/documents/public/software/Mac_OSX_VCP_Driver.zip<br/> | + | | |
| − | Windows serial port driver: https://www.silabs.com/documents/public/software/CP210x_Universal_Windows_Driver.zip<br/> | + | *[https://files.waveshare.com/upload/f/f1/CH343SER.7z CH343 VCP driver for Windows] |
| + | *[https://files.waveshare.com/upload/0/04/CH34XSER_MAC.7z CH343 driver for MacOS] | ||
| + | *[https://files.waveshare.com/upload/1/1a/CH34X_DRV_INSTALL_INSTRUCTIONS.pdf MacOS guide] | ||
| + | <!--mac serial driver: https://www.silabs.com/documents/public/software/Mac_OSX_VCP_Driver.zip<br/> | ||
| + | Windows serial port driver: https://www.silabs.com/documents/public/software/CP210x_Universal_Windows_Driver.zip<br/>--> | ||
|||}} | |||}} | ||
| − | {{FAQ|Burning and uploading program error: | + | {{FAQ|Burning and uploading program error: Connecting........................................................................................................................................................................_____....._____.... .____Error uploading project_A fatal error occurred: Failed to connect to ESP32: Timed out waiting for packet header |
| − | |You need to press and hold the boot button on the ESP32 baseboard when the Connecting... prompt appears | + | | |
| + | You need to press and hold the boot button on the ESP32 baseboard when the Connecting... prompt appears. | ||
|||}} | |||}} | ||
| − | {{FAQ|Bluetooth demo stuck at 0% | + | {{FAQ|Bluetooth demo stuck at 0%? |
| − | |It is necessary to confirm that the hardware connection is correct | + | |It is necessary to confirm that the hardware connection is correct and select the corresponding ink screen model.<br/> |
|||}} | |||}} | ||
{{FAQ|When uploading the program, an error is reported that the development board does not exist or is empty, you need to confirm that the port and development board are selected correctly, you need to confirm that the hardware connection is correct, and select the corresponding ink screen model | {{FAQ|When uploading the program, an error is reported that the development board does not exist or is empty, you need to confirm that the port and development board are selected correctly, you need to confirm that the hardware connection is correct, and select the corresponding ink screen model | ||
| − | |Select the port and driver board as shown below<br/> | + | |Select the port and driver board as shown below.<br/> |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:port.png]]<br/> |
|||}} | |||}} | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | {{FAQ|E-Paper ESP32 driver board A, B key function. | |
| − | + | |Compatible with more ink screen models, which can be adjusted according to the display effect.<br/> | |
| − | {{FAQ|E-Paper ESP32 driver board A, B key function | ||
| − | |Compatible with more ink screen models, which can be adjusted according to the display effect<br/> | ||
|||}} | |||}} | ||
| − | {{FAQ|What is the spacing between J3 and J4 of the E-Paper ESP32 driver board | + | {{FAQ|What is the spacing between J3 and J4 of the E-Paper ESP32 driver board? |
|Spacing is 22.65mm<br/> | |Spacing is 22.65mm<br/> | ||
[[File:22.65.png]]<br/> | [[File:22.65.png]]<br/> | ||
|||}} | |||}} | ||
| + | {{FAQ|What is the thickness of the 2.13-inch e-paper cloud module? | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Without battery, around 6mm; with battery, around 14.5mm. | ||
| + | ||}} | ||
| + | {{FAQ|Why cannot the ESP32 board be selected in the Arduino IDE when using Mac OS? | ||
| + | |If the ESP32 device is recognized by your Mac PC but fails in Arduino IDE, please check the security settings, it maybe blocked while installing the required driver. Please check the driver in the system settings, details list. | ||
| + | :[[File:ESP32-driver-install-Mac.png|300px]] | ||
| + | ||}} | ||
| + | {{FAQ|The full pinout for the ESP32 e-paper driver board? | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Check with the image below.<br> | ||
| + | [[File:ESP32 driver board faq.png]] | ||
| + | ||}} | ||
| + | {{FAQ|The board manager cannot search for esp32? | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Open File -> Preferences, you need to fill in the esp32 development board management URL: https://dl.espressif.com/dl/package_esp32_index.json <br> | ||
| + | (esp8266:http://arduino.esp8266.com/stable/package_esp8266com_index.json):<br> | ||
| + | [[File: FAQ-developboa09.png]] | ||
| + | ||}} | ||
| + | |||
=Support= | =Support= | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Servicebox1}} |
</div> | </div> | ||
[[Category:Expansions|Expansions]] [[Category:e-Paper|e-Paper]] [[Category:Raspberry Pi|Raspberry Pi]] | [[Category:Expansions|Expansions]] [[Category:e-Paper|e-Paper]] [[Category:Raspberry Pi|Raspberry Pi]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:44, 19 April 2024
| ||
Note
This Wiki mainly introduces the specific operation of this product, if you want to get the product support ink screen models please go to the bottom of the official website product details to get.
| Model | Demo |
| 1.54inch e-Paper | epd1in54_V2-demo |
| 1.54inch e-Paper (B) | epd1in54b_V2-demo |
| 2.13inch e-Paper | epd2in13_V3-demo |
| 2.13inch e-Paper (B) | epd2in13b_V4-demo |
| 2.13inch e-Paper (D) | epd2in13d-demo |
| 2.66inch e-Paper | epd2in66-demo |
| 2.66inch e-Paper (B) | epd2in66b-demo |
| 2.7inch e-Paper | epd2in7_V2-demo |
| 2.7inch e-Paper (B) | epd2in7b_V2-demo |
| 2.9inch e-Paper | epd2in9_V2-demo |
| 2.9inch e-Paper (B) | epd2in9b_V3-demo |
| 3.7inch e-Paper | epd3in7-demo |
| 4.01inch e-Paper (F) | epd4in01f-demo |
| 4.2inch e-Paper | epd4in2-demo |
| 4.2inch e-Paper (B) | epd4in2b_V2-demo |
| 5.65inch e-Paper (F) | epd5in65f-demo |
| 5.83inch e-Paper | epd5in83_V2-demo |
| 5.83inch e-Paper (B) | epd5in83b_V2-demo |
| 7.5inch e-Paper | epd7in5_V2-demo |
| 7.5inch e-Paper (B) | epd7in5b_V2-demo |
Note: The corresponding demo only takes the latest version of the screen as an example, if you are using an older version, please refer to the version label on the back of the screen.
Overview
Version Guide
20220728: The serial port chip is changed from CP2102 to CH343, please pay attention to the driver selection.
Introduction
Universal e-Paper Driver HAT features ESP32 and supports various Waveshare SPI interfaces in e-Paper raw panels. It also supports refreshing images to e-paper via WIFI or Bluetooth and Arduino.
| More |
Parameter
- WiFi Standard: 802.11b/g/n
- Communication Interface: SPI/IIC
- Bluetooth Standard: 4.2, BR/EDR, and BLE included
- Communication Interface: 3-Wire SPI, 4-wire SPI (default)
- Operating Voltage: 5V
- Operating Current: 50mA-150mA
- Outline Dimensions: 29.46mm x 48.25mm
- Flash Size: 4 MB
- SRAM Size: 520 KB
- ROM Size: 448 KB
Pin
| Pin | ESP32 | Description |
| VCC | 3V3 | Power input (3.3V) |
| GND | GND | Ground |
| DIN | P14 | SPI MOSI pin, data input |
| SCLK | P13 | SPI CLK pin, clock signal input |
| CS | P15 | Chip selection, low active |
| DC | P27 | Data/command, low for commands, high for data |
| RST | P26 | Reset, low active |
| BUSY | P25 | Busy status output pin (means busy) |
PS: The above is the board fixed connection, with no additional operation by the user.
Feature
- Onboard ESP32, support Arduino development.
- Provide an Android mobile APP program, which can update the display content through Bluetooth EDR, easy to use.
- Provide HTML host computer program, which can remotely update the display content through the web page, which is convenient to integrate into various network applications.
- Supports Floyd-Steinberg's dithering algorithm for more color combinations and better shadows of the original image.
- Supports many common image formats (BMP, JPEG, GIF, PNG, etc.).
- Factory built-in e-ink screen driver (open source).
- 5V pin supports 3.6V to 5.5V voltage input and can be powered by a lithium battery.
- Comes with online resources and manuals.
Application
This product cooperates with the ink screen and is suitable for the application scenario of wireless refreshing.
- Supermarket electronic price tag
- Electronic name card
- Serial information display board, etc.
Preparation
Hardware Connection
This product is shipped with an ESP32 network driver board, an adapter board, and an FFC extension cable.
When using it, you can directly connect the screen to the driver board, or connect it through extension cables and adapter boards.
Direct access to the driver board:

Access via extension cord:

- Set the mode switch: Set the No. 1 switch according to the model of the EPD used. There are many screens. If it is not listed, please use 'A' to try. If the display effect is poor or cannot be driven, please try switching the switch.
| Resistor (Display Config) | Screen |
| 0.47R (A) | 2.13inch e-Paper (D), 2.7inch e-Paper, 2.9inch e-Paper (D) |
| 3.7inch e-Paper, 4.01inch e-Paper (F), 4.2inch e-Paper | |
| 4.2inch e-Paper (B), 4.2inch e-Paper (C), 5.65inch e-Paper (F) | |
| 5.83inch e-Paper, 5.83inch e-Paper (B), 7.3inch e-Paper (G) | |
| 7.3inch e-Paper (F), 7.5inch e-Paper, 7.5inch e-Paper (B) | |
| 1.64inch e-Paper (G), 2.36inch e-Paper (G), 3inch e-Paper (G) | |
| 4.37inch e-Paper (G) | |
| 3R (B) | 1.54inch e-Paper, 1.54inch e-Paper(B), 2.13inch e-Paper |
| 2.13inch e-Paper (B), 2.66inch e-Paper, 2.66inch e-Paper (B) | |
| 2.9inch e-Paper, 2.9inch e-Paper (B) |
- Turn on the serial port module: Toggle the No. 2 switch to "ON", this switch controls the power supply of the USB to the UART module. When you don't need to use it, you can manually turn off the module to save power (if switch 2 is in the OFF state, you cannot upload the program.)
- Use a micro USB cable to connect the ESP32 driver board to a computer or 5V power supply.
Download Demo
We provide three kinds of demos: local, Bluetooth, and WiFi. The sample program can be found in #Resources, or click the sample demo to download.
Unzip the downloaded compressed package, you can get the following files:

- ePape_Esp32_Loader_APP: Bluetooth App source code (Android Studio)
- examples: local demo
- Loader_esp32bt: Bluetooth demos
- Loader_esp32wf: WiFi demo
- app-release.apk: Bluetooth demo App installation package
Environment Configuration
Image Processing Algorithms
In the Bluetooth and WiFi demos, two image processing algorithms are provided, namely Level and Dithering.
Color scale method
An image can be divided into several large color gamuts, and each pixel on the image is divided into these color gamuts according to how close the color is to these color gamuts. This method is more suitable for images with few colors, such as bright or tri-color shapes or text images. Taking the black and white and red ink screen as an example, when processing the image, we hope to process it into black, white, and red, so for an image, we can divide all the colors of the image into three large color areas: the black area, white area, red area.
For example, according to the figure below, if the value of a pixel in the grayscale image is equal to or less than 127, we regard this pixel as a black pixel, otherwise, it is white.

For color images, we all know that RGB has three color channels. Compared with the red channel, we can refer to blue and green as the blue-green channel or the non-red channel. According to the figure below, a pixel on a color image, if it has a high value in the red channel, but a low value in the blue-green channel, we classify it as a red pixel; if its red channel and blue- If the green channel has low values, we classify it as a black pixel; if the red and blue-green channel values are high, we classify it as white.

In the algorithm, the color definition is calculated based on the difference between the RGB value and the sum of the squares of the expected color value. The expected color value refers to the color value that the pixel is closest to, and these values are stored in the curPal array.

Dithering
For those images with more colors or more gradient areas, the above gradation method is not suitable. In many cases, the pixels in the gradient area in the image may be very close to all color gamuts. If you use the gradation method to draw The image will lose a lot of image details. Many images are taken by cameras, by mixing colors to paint shadows and transition areas, in these images, the gradient area accounts for the majority.
For the human eye, it is easy to confuse a particularly small color. For example, two colors, red and blue, are juxtaposed. If you reduce it to a small enough hand, it will appear to the human eye as a mixture of red and blue. into color. The defect of the human eye means that we can deceive the human eye and use the "mixing" method to obtain more colors that can be expressed. The dithering algorithm uses this phenomenon.
The demo we provide uses the Floyd-Steinberg dithering algorithm - based on error diffusion (published by Robert Floy and Louis Steinberg in 1976). The formula is for error diffusion according to the image below:

X is the error (a scalar (vector) difference between the original color and the gray value (color value)), this error will spread to the right, lower right, lower, and lower left in four directions, respectively 7/16, 1/16, 5/16 and 3/16 weights are added to the values of these four pixels. Interested users can go to understand the algorithm, there are many resources on the Internet.
Comparison
Original image

"Black and white grading" and "Multicolor grading"

"Black and White Dithering" and "Multicolor Dithering"

Bluetooth Demo
Download example
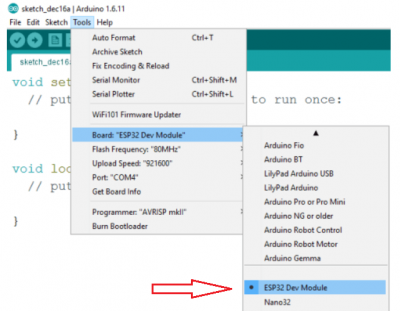
- Go to the Loader_esp32bt directory, double click the Loader_esp32bt.ino file to open the example.
- Choose Tools -> Boards -> ESP32 Dev Module and select the correct Port according to Device Manager: Tools -> Port.
- Click the Upload icon to build the project and upload it to the ESP32 driver board.
- Install the APP to the Android board and open it:
- APP has five buttons on the main page:
- BLUETOOTH CONNECTION: This button is used to connect the ESP32 device via Bluetooth.
- SELECT DISPLAY TYPE: This button is used to select the type of display according to what you buy.
- LOAD IMAGE FILE: Click it and choose a picture to open. It is only available after choosing the display type.
- SELECT IMAGE FILTER: This button is used to choose the image process method.
- UPLOAD IMAGE: Upload the processed image to the ESP32 driver board and update to e-Paper display.
- BLUETOOTH CONNECTION: This button is used to connect the ESP32 device via Bluetooth.
- Please first open the Bluetooth function of your phone. Click the BLUETOOTH CONNECTION button -> Click the SCAN icon on the top-right to scan the Bluetooth device.
- Find the ESP32 device and connect. If your phone is the first time to connect this device, it requires pairing, complete the pairing process according to the prompt. (Note: The APP cannot work with pairing.)
- Click "SELECT DISPLAY TYPE" to choose the display type.
- Click "LOAD IMAGE FILE" To choose a picture from your phone and cut it.
- Click " SELECT IMAGE FILTER" to choose a process algorithm and confirm.
- "LEVEL: MONO": This option will process the picture to a monochrome image.
- "LEVEL" COLOR": This option will process the picture to the tricolor image according to the display colors of the display (only valid for colorful displays).
- "DITHERING: MONO": This option will process the picture to a monochrome image.
- "DITHERING: COLOR": This option will process the picture to the tricolor image according to the display colors of the display (only valid for colorful displays).
- Click "UPLOAD IMAGE" to upload the image to the ESP32 device and display it.
WiFi Demo
Provide WiFi demos with an HTML host computer.
Note: The module only supports the 2.4G network band.
How to Use
- Go to the Loader_esp32wf directory, double click Loader_esp32wf.ino file to open the project.
- Choose Tools -> Boards -> ESP32 Dev Module in the IDE menu, and select the correct COM port: Tools -> Port.
- Open the srvr.h file and change the ssid and password to the actual WiFi username and password used.
- Modify the WiFi username and password here to match the WiFi username and password of your router or mobile hotspot. In this program, the ESP32 acts as a slave, not a host, so it will not transmit the WiFi hotspot message outward.
- Press win + R and type CMD to open the command line and get the IP of your computer.
- Open the srvr.h file, modify the network segment in the location shown in the picture to the corresponding network segment.
- Note: the IP address of ESP32 (that is, the fourth bit) should not be the same as the address of the computer, and the rest should be the same as the IP address of the computer.
- Then click upload to compile and download the demo to the ESP8266 driver board.
- Open the serial monitor and set the baud rate to 115200, you can see the serial port print out the IP address of the ESP32 driver board as follows:
- Open the browser on your computer or cell phone (note that the network you are accessing needs to be on the same network segment as the wifi connected to the ESP8266), enter the IP address of the ESP8266 in the URL input field, and open it, you can see the operation interface as follows.
- The entire operation interface is divided into five areas:
- Image Operation Area:
Select Image file: Click to choose an image from your computer or phone
Level: mono: Black and white image processing algorithm
Level: color: Multi-color image processing algorithm (only effective for multi-color screens)
Dithering: mono: Black dithering image processing algorithm
Dithering: color: Multi-color dithering image processing algorithm (only effective for multi-color screens)
Update image: Upload image - IP information display area: This displays the IP address information of the module you are currently connected to
- Image size setting area: Here, x and y can be set to specify the starting position of the display, which is relative to the image file you have selected. For example, if you choose an 800x480 image but the e-Paper screen you are connected to is 2.9 inches, the screen will not be able to display the entire image. In this case, the processing algorithm will automatically crop the image from the upper left corner and send a portion of it to the e-ink screen for display. You can set x and y to customize the starting position of the cropping. W and h represent the resolution of the current e-ink screen. Note: If you modify the x and y coordinates, you need to click on the processing algorithm again to generate a new image.
- Model selection area: Here, you can choose the e-ink screen model you are connected to.
- Image display area: Here, the selected image and the processed image will be displayed.
- PS: During image upload, the upload progress will be displayed at the bottom.
- Image Operation Area:
- Area ①: Click "Select Image file" to choose an image, or drag and drop the image directly into the "Original image" area.
- Area ④: Choose the corresponding e-Paper model, for example, 1.54b.
- Area ①: Click on an image processing algorithm, for example, "Dithering: color".
- Area ①: Click "Upload image" to upload the image to the e-ink screen display.
Offline Demo
Provides offline ESP32-based demos without WiFi, Bluetooth, and other devices.
Demo Usage
- Open Arduino IDE to view the project file folder location (please do not modify it).
- Go to the E-Paper_ESP32_Driver_Board_Code\examples directory and copy the entire esp32-waveshare-epd folder to the libraries directory in the project folder.
- Close all Arduino IDE windows, reopen the Arduino IDE, and select the corresponding example demo as shown:
- Choose the corresponding board and COM port.
Resources
Documentation
Demo Code
Software Driver
CP2102 (Old version, used before July 2022)
CH343 (New version, used after July 2022)
Related Resources
FAQ

If the corresponding driver is not installed, it will be displayed as follows, or in the unknown device.

Possible reasons for such illumination:
1. the computer port is bad.
2. the data line has problems.
3. the switch on the board is not dialed to ON.

{{{5}}}
You need to press and hold the boot button on the ESP32 baseboard when the Connecting... prompt appears.
Without battery, around 6mm; with battery, around 14.5mm.
{{{5}}}
Open File -> Preferences, you need to fill in the esp32 development board management URL: https://dl.espressif.com/dl/package_esp32_index.json
(esp8266:http://arduino.esp8266.com/stable/package_esp8266com_index.json):

{{{5}}}
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 AM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)