Difference between revisions of "Current/Power Monitor HAT"
(Created page with "{{infobox item| |img=400px|alt=Power Management HAT|link=https://www.waveshare.com/current-power-monitor-hat.htm |capation=4-ch Curren...") |
(→FAQ) |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <div class="wiki-pages jet-green-color"> | ||
{{infobox item| | {{infobox item| | ||
| − | |img=[[File:Current-Power-Monitor-HAT-1.jpg|400px|alt=Power Management HAT|link=https://www.waveshare.com/current-power-monitor-hat.htm]] | + | |img=[[File:Current-Power-Monitor-HAT-1.jpg|400px|alt=Power Management HAT|{{Amazon_nolink|default={{#ifeq: {{#urlget:amazon|0}}|{{#urlget:Amazon|0}}| default|}}|url=link=https://www.waveshare.com/current-power-monitor-hat.htm}}]] |
|capation=4-ch Current/Voltage/Power Monitor HAT for Raspberry Pi, I2C/SMBus Interface | |capation=4-ch Current/Voltage/Power Monitor HAT for Raspberry Pi, I2C/SMBus Interface | ||
|category=[[:Category:Raspberry Pi|Raspberry Pi]] | |category=[[:Category:Raspberry Pi|Raspberry Pi]] | ||
| Line 7: | Line 8: | ||
|interfaca2=I2C | |interfaca2=I2C | ||
|interface3=SMBus | |interface3=SMBus | ||
| − | |{{#urlget:amazon|default}}=display | + | |{{#ifeq: {{#urlget:amazon|0}}|{{#urlget:Amazon|0}}| default|}}=display |
|website_cn=[http://www.waveshare.net/ 微雪电子] | |website_cn=[http://www.waveshare.net/ 微雪电子] | ||
|website_en=[https://www.waveshare.com/current-power-monitor-hat.htm Waveshare website] | |website_en=[https://www.waveshare.com/current-power-monitor-hat.htm Waveshare website] | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | =Instruction= | |
This is a 4-ch current and power monitor HAT designed for Raspberry Pi. Via the I2C or SMBus interface, it is easy to monitor each channel's current, voltage, and power consumption, as well as the voltage between both sides of the sampling resistor. | This is a 4-ch current and power monitor HAT designed for Raspberry Pi. Via the I2C or SMBus interface, it is easy to monitor each channel's current, voltage, and power consumption, as well as the voltage between both sides of the sampling resistor. | ||
| − | + | ==Features== | |
| − | *Standard Raspberry Pi 40PIN GPIO extension header, supports Raspberry Pi series boards | + | *Standard Raspberry Pi 40PIN GPIO extension header, supports Raspberry Pi series boards. |
| − | *4-ch monitoring, via I2C/SMBus interface | + | *4-ch monitoring, via I2C/SMBus interface. |
| − | *Onboard 0.1Ω 1% sampling resistor, allows measuring bi-directional current up to 3.2A | + | *Onboard 0.1Ω 1% sampling resistor, allows measuring bi-directional current up to 3.2A. |
| − | *Embedded 12-bit ADC, supports multiple successive converting, 0~26V voltage measuring range | + | *Embedded 12-bit ADC, supports multiple successive converting, 0~26V voltage measuring range. |
| − | *Directly calculate and output measured power value through additional multiply register | + | *Directly calculate and output measured power value through additional multiply register. |
| − | *I2C control pins for connecting with other host boards | + | *I2C control pins for connecting with other host boards. |
| − | *Comes with development resources and manual (examples for Raspberry Pi/Arduino/STM32) | + | *Comes with online development resources and manual (examples for Raspberry Pi/Arduino/STM32). |
| − | + | ||
| + | ==Specification== | ||
*Operating voltage: 3.3V/5V | *Operating voltage: 3.3V/5V | ||
*Control interface: I2C/SMBus | *Control interface: I2C/SMBus | ||
| Line 33: | Line 35: | ||
[[File:Current-Power-Monitor-HAT-2.jpg|600px]] | [[File:Current-Power-Monitor-HAT-2.jpg|600px]] | ||
| − | This module can be used to test currents and voltages of four channels, they are (IN1+ IN1-), (IN2+ IN2-), (IN3+ IN3-) and (IN4+ IN4-). | + | This module can be used to test currents and voltages of four channels, they are (IN1+ IN1-), (IN2+ IN2-), (IN3+ IN3-), and (IN4+ IN4-). |
| − | INx+ is the current input, and INx- is the current output. | + | INx+ is the current input, and INx- is the current output. The module measures the differential voltage of the sample resistor connected between INx+ and INx-, with the voltage, we can measure the working current. |
The module supports measuring bidirectional current, so users can invert the input and output. | The module supports measuring bidirectional current, so users can invert the input and output. | ||
| − | '''Note that you must connect GND when testing different power | + | '''Note that you must connect GND when testing different power adapters, otherwise, the VBus voltage cannot be measured. |
| − | + | =Raspberry Pi examples= | |
| − | + | ==Enable the I2C Interface== | |
| + | |||
| + | Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and enter the following command to access the configuration screen:<br/> | ||
| + | sudo raspi-config | ||
| + | Select Interfacing Options -> I2C -> yes to start the i2C kernel driver | ||
| + | [[File:Current Serial.png]]<br/> | ||
| + | And then reboot the Raspberry Pi: | ||
| + | sudo reboot | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="cautionSec">PS: If you are using the system of the Bullseye branch, you need to change "apt-get" to "apt". The system of the Bullseye branch only supports Python3.</div> | ||
| − | Open the terminal of Raspberry Pi and | + | To test the example, you should first attach the monitor HAT to Raspberry Pi, or you can connect the monitor HAT to the I2C interface of Raspberry Pi by wires. |
| + | |||
| + | Open the terminal of Raspberry Pi and follow the commands: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | |||
sudo apt-get install p7zip | sudo apt-get install p7zip | ||
| − | wget | + | wget https://files.waveshare.com/upload/6/69/Current-Power_Monitor_HAT_Code.7z |
7zr x Current-Power_Monitor_HAT_Code.7z -r -o./Current-Power_Monitor_HAT | 7zr x Current-Power_Monitor_HAT_Code.7z -r -o./Current-Power_Monitor_HAT | ||
cd Current-Power_Monitor_HAT/RaspberryPi | cd Current-Power_Monitor_HAT/RaspberryPi | ||
python3 ina219.py | python3 ina219.py | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | You can get data | + | You can get data on the VBus voltage, the differential voltage of the sampling resistor, voltage input, power, and current. |
| − | + | ||
| − | The examples | + | =STM32 examples= |
| + | The examples provided are based on NUCLEO-F103RB, you can connect it to the table. | ||
{|class="wikitable" | {|class="wikitable" | ||
!PIN!!NUCLEO | !PIN!!NUCLEO | ||
| Line 64: | Line 77: | ||
|SDA||SDA/D14/PB9 | |SDA||SDA/D14/PB9 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |SCL||SCL | + | |SCL||SCL/D15/PB8 |
|} | |} | ||
| − | Download the demo code from [[# | + | Download the demo code from [[#Resources]], unzip and go to the directory of the STM32 project. Open the project by Keil5. |
| − | Program the demo codes to your NUCLEO board and test | + | Program the demo codes to your NUCLEO board and test. |
| − | The data of the VBus voltage, differential voltage of | + | The data of the VBus voltage, the differential voltage of the sampling resistor, voltage input, power, and current will be printed to the serial port. |
| − | + | ||
| + | =Arduino= | ||
The example provided is based on Waveshare UNO Plus. | The example provided is based on Waveshare UNO Plus. | ||
{|class='wikitable' | {|class='wikitable' | ||
| Line 84: | Line 98: | ||
|SCL||SCL/D15 | |SCL||SCL/D15 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | If you use other Arduino | + | If you use other Arduino boards, please check the working voltage of your Arduino board, and change the VCC to 5V/3.3V according to it. |
| − | Download the demo codes from [[#Resouces]]. unzip and go to the directory of Arduino codes. Open it | + | Download the demo codes from [[#Resouces]]. unzip and go to the directory of Arduino codes. Open it with Arduino IDE and program it to your board. |
| − | The data of the VBus voltage, differential voltage of sample resistor, voltage input, power, and current will be printed to serial port. | + | The data of the VBus voltage, the differential voltage of the sample resistor, voltage input, power, and current will be printed to the serial port. |
| − | + | =Resources= | |
| − | + | ==Documents== | |
| − | *[https:// | + | *[https://files.waveshare.com/upload/d/d4/Current-Power_Monitor_HAT_Schematic.pdf Schematic] |
| − | + | ==Demo codes== | |
| − | *[https:// | + | *[https://files.waveshare.com/upload/6/69/Current-Power_Monitor_HAT_Code.7z Demo codes] |
| − | + | ==Datasheet== | |
| − | *[https:// | + | *[https://files.waveshare.com/upload/1/10/Ina219.pdf INA219 Datasheet] |
| + | =FAQ= | ||
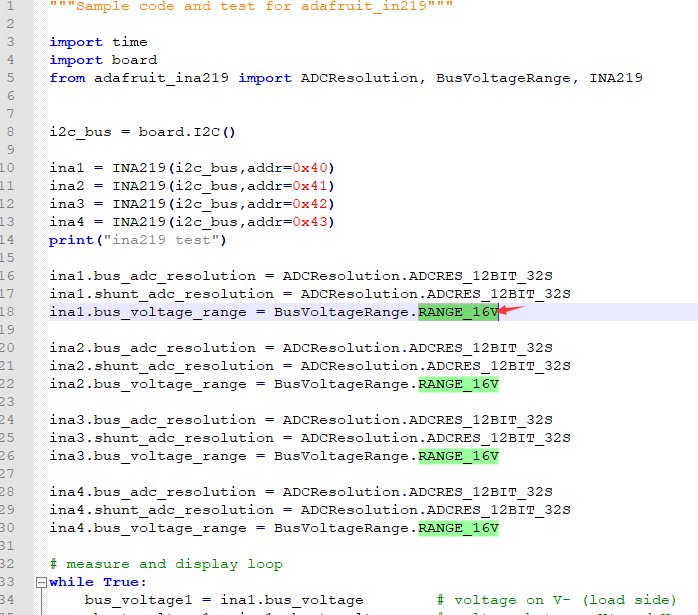
| + | {{FAQ|Why can't I measure above 16V? | ||
| + | |Open ina219.py and find the following:<br/> | ||
| + | [[File:Power Monitor HAT01.png]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{FAQ|Can the Current/Power Monitor HAT be used in case of AC current? | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | The monitor HAT uses INA219 IC, which is used for DC power monitors only. | ||
| + | ||}} | ||
| + | {{FAQ|Is it possible to use multiple "Current/Power Monitor HAT" on the same Raspberry Pi System? Maybe if the I2C address of the ina219 somehow could be modified? | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | The current power monitor HAT doesn't support changing the I2C address.<br> | ||
| + | PCB doesn't reverse pad for modifying I2C address, in this case, you cannot stack them for more channels. | ||
| + | ||}} | ||
| − | = | + | =Support= |
| − | + | {{Servicebox1}} | |
| − | |||
| − | {{ | ||
Latest revision as of 06:50, 18 March 2024
| ||
Instruction
This is a 4-ch current and power monitor HAT designed for Raspberry Pi. Via the I2C or SMBus interface, it is easy to monitor each channel's current, voltage, and power consumption, as well as the voltage between both sides of the sampling resistor.
Features
- Standard Raspberry Pi 40PIN GPIO extension header, supports Raspberry Pi series boards.
- 4-ch monitoring, via I2C/SMBus interface.
- Onboard 0.1Ω 1% sampling resistor, allows measuring bi-directional current up to 3.2A.
- Embedded 12-bit ADC, supports multiple successive converting, 0~26V voltage measuring range.
- Directly calculate and output measured power value through additional multiply register.
- I2C control pins for connecting with other host boards.
- Comes with online development resources and manual (examples for Raspberry Pi/Arduino/STM32).
Specification
- Operating voltage: 3.3V/5V
- Control interface: I2C/SMBus
- Sampling resistor: 0.1Ω 1%
- Voltage range: 0~26V
- Current range: ±3.2A
- Resolution: 0.8mA (±3.2A range) OR 0.1mA (±400mA range)
- Dimensions: 65mm × 30mm
- Mounting hole size: 3.0mm
Hardware
This module can be used to test currents and voltages of four channels, they are (IN1+ IN1-), (IN2+ IN2-), (IN3+ IN3-), and (IN4+ IN4-).
INx+ is the current input, and INx- is the current output. The module measures the differential voltage of the sample resistor connected between INx+ and INx-, with the voltage, we can measure the working current.
The module supports measuring bidirectional current, so users can invert the input and output.
Note that you must connect GND when testing different power adapters, otherwise, the VBus voltage cannot be measured.
Raspberry Pi examples
Enable the I2C Interface
Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and enter the following command to access the configuration screen:
sudo raspi-config Select Interfacing Options -> I2C -> yes to start the i2C kernel driver

And then reboot the Raspberry Pi:
sudo reboot
To test the example, you should first attach the monitor HAT to Raspberry Pi, or you can connect the monitor HAT to the I2C interface of Raspberry Pi by wires.
Open the terminal of Raspberry Pi and follow the commands:
sudo apt-get install p7zip wget https://files.waveshare.com/upload/6/69/Current-Power_Monitor_HAT_Code.7z 7zr x Current-Power_Monitor_HAT_Code.7z -r -o./Current-Power_Monitor_HAT cd Current-Power_Monitor_HAT/RaspberryPi python3 ina219.py
You can get data on the VBus voltage, the differential voltage of the sampling resistor, voltage input, power, and current.
STM32 examples
The examples provided are based on NUCLEO-F103RB, you can connect it to the table.
| PIN | NUCLEO |
|---|---|
| VCC | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| SDA | SDA/D14/PB9 |
| SCL | SCL/D15/PB8 |
Download the demo code from #Resources, unzip and go to the directory of the STM32 project. Open the project by Keil5.
Program the demo codes to your NUCLEO board and test.
The data of the VBus voltage, the differential voltage of the sampling resistor, voltage input, power, and current will be printed to the serial port.
Arduino
The example provided is based on Waveshare UNO Plus.
| PIN | UNO Plus |
|---|---|
| VCC | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| SDA | SDA/D14 |
| SCL | SCL/D15 |
If you use other Arduino boards, please check the working voltage of your Arduino board, and change the VCC to 5V/3.3V according to it.
Download the demo codes from #Resouces. unzip and go to the directory of Arduino codes. Open it with Arduino IDE and program it to your board.
The data of the VBus voltage, the differential voltage of the sample resistor, voltage input, power, and current will be printed to the serial port.
Resources
Documents
Demo codes
Datasheet
FAQ
The monitor HAT uses INA219 IC, which is used for DC power monitors only.
{{{5}}}
The current power monitor HAT doesn't support changing the I2C address.
PCB doesn't reverse pad for modifying I2C address, in this case, you cannot stack them for more channels.
{{{5}}}
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 PM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)