SIM8200EA-M2 5G HAT
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
SIM8202G-M2:4x antennas, size:30×42mm,
compatible hardware interface, identical software function.
Overview
Introduction
SIM8200EA-M2 5G HAT With Antennas, 5G/4G/3G Support, Snapdragon X55 Onboard, Multi Mode Multi Band, Applicable For China, Europe, The Middle East, South America, Etc.
| More |
Feature
- Standard Raspberry Pi 40PIN GPIO extension header, supports Raspberry Pi series boards, Jetson Nano.
- Comes with SIM8200EA-M2 core module, based on Qualcomm snapdragon X55 platform, with multi mode multi band support.
- 5G/4G/3G communication support.
- USB3.1 port for testing AT commands, sending messages, cloud communication, making a phone call, getting GNSS positioning data, etc.
- SIM card slot, supports 1.8V / 3V SIM card.
- 2 x LED indicators, easy to monitor the working status.
- AT command support, based on 3GPP TS 27.007, 27.005, and V.25TER command set.
- Onboard audio jack and audio decoder, allow audio operation like making a phone call.
- Multi-constellation dual-band positioning: GPS, GLONASS, Beidou, Galileo, and QZSS.
- Operating system support: Windows/Linux/Android.
- Comes with high-quality acrylic case and cooling fan, nice looking, better heat dissipation.
Parameter
|
Working Frequency | |
|
Sub-6G(SA) |
n1, n2, n3, n5, n7, n8, n12, n20, n28, n40, n41,n48, n66, n71, n77, n78, n79 (n79 is only available for SIM8202G-M2) |
|
Sub-6G(NSA) |
n41, n77, n78, n79 (n79 is only available for SIM8202G-M2) |
|
LTE-FDD |
B1/B2/B3/B4/B5/B7/B8/B12/B13/B14/B17/B18/B19/B20/B25/B26/B28/B29/B30/B66/B71 |
|
LTE-TDD |
B34/B38/B39/B40/B41/B42/B48 |
|
WCDMA |
B1/B2/B3/B4/B5/B8 |
|
GNSS |
GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, Galileo and QZSS |
|
Data Transmission | |
|
Sub-6G |
2.4 Gbps (DL) / 500 Mbps (UL) |
|
LTE |
1 Gbps (DL) / 200 Mbps (UL) |
|
HSPA |
42 Mbps (DL) / 5.76 Mbps (UL) |
|
Software Function | |
|
Operating system |
Windows/Linux/Android |
|
Protocols |
TCP/IP/IPV4/IPV6/Multi-PDP/FTP/FTPS/HTTP/HTTPS/MQTTS/DNS/SSL3.0 |
|
Text Message (SMS) |
Support MT, MO, CB, Text, PDU |
|
Firmware upgrade |
Supports firmware upgrade via USB interface |
|
Hardware Description | |
|
SIM card |
1.8V/3.0V |
|
Antenna interface |
6 × IPEX-4 ports for 3G/4G/5G/GNSS |
|
Supply voltage |
5V 3A |
|
Application Scenario | |
|
Applicable area |
Countries or regions that cover the 5G Sub-6G frequency band, such as China, the United States, Japan and South Korea, Europe, the Middle East, and the Americas |
|
Typical application |
CPE/Intelligent Gateway/UAV/Live Video/Telemedicine/Intelligent Security |
Assembly drawing
Working with Windows PC
Install Driver
Download the SIM8200 Driver from the Resources part to your PC and unzip it.
Enter the SIM8200_OS_Driver\Windows directory.
Enter the 1_install directory and run the setup.exe file to install.

After connecting, a mobile network icon appears, and you can disconnect the other networks and test the mobile network.
Install Driver Manually
For most hosts, although 1_install is installed, there are no COM ports shown. In this case, you need to manually add the 2_AddManully file folder. Here is the way to add: find the unrecognized device in Device Manager, right-click to add the driver as shown below:
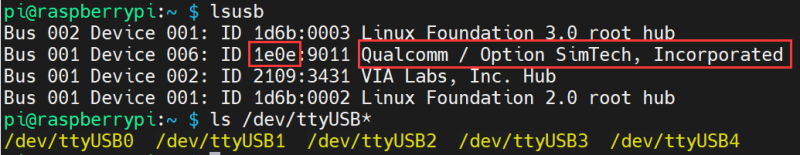
Power on the G module, switch it ON and the module boots, and then the PC will recognize four unrecognized devices (5 or 6 devices are recognized). Here the picture only shows 5 devices.
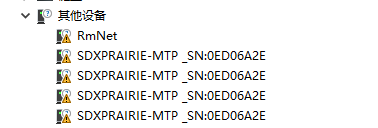
Right-click to update the driver demo, choose to add it manually, and select the path as SIM8200_OS_Driver\Windows. Please select it according to your system (WIN7\WIN8\WIN10), and there are up to 6 devices that can be selected, and then the PC will generate the following devices.

Four COM ports: AT is used for AT command control, Audio is used for dialing, Diagnostics is used for debugging, and NMEA is used for GPS.

![]()
A mobile network will be set up automatically after updating, you can disconnect other networks and test it.
Manual NDIS Dial-up Internet
After installing the driver, some computers cannot automatically dial up to access the Internet, so you need to dial manually, the operation is as follows:
Download SSCOM software, open the sim8200 AT port to send the following command:
AT$QCRMCALL=1,1 //carrier return required

At this point, NDIS dial-up is active, and the computer can connect to the network. If it returns "No Carrier", the dial-up may have already occurred. Try accessing the internet directly.
GPS Positioning
Connect the passive GPS antenna to the ANT5 of the module, and place the antenna outdoors facing the sky. Then send the AT command to turn on the GPS:
AT+CGPS=1
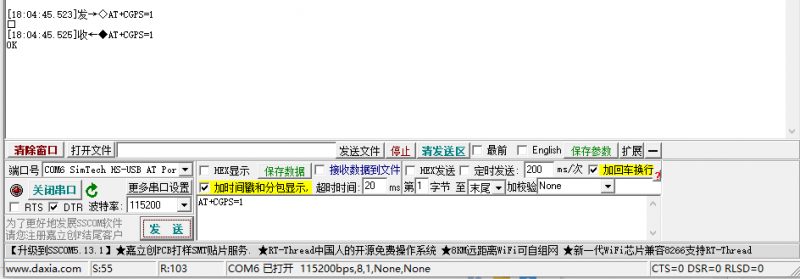
Now open the NEMA port, and you can get GPS data:
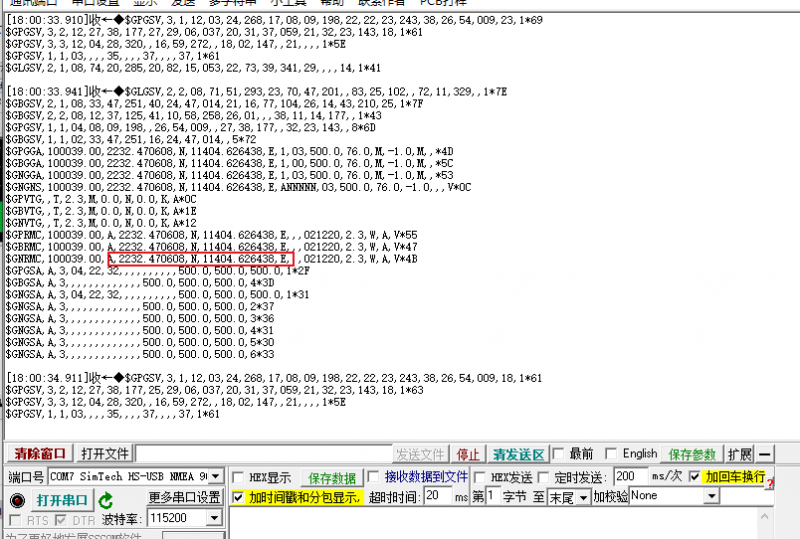
Finally, turn off the GPS, you can use the AT command:
AT+CGPS=0
SIM Card Config
- SIM card 1 is used by default, and you can use the following commands to switch to SIM1 when it is SIM2.
AT+SMSIMCFG=1,1
- Or you can directly switch to SIM2:
AT+SMSIMCFG=1,2
- If it still does not work, consider that the flight mode is on, and turn off the flight mode with the following command:
AT+CFUN=1
Working with Raspberry Pi
The use of Raspberry Pi OS
First-time Configuration
Please don't type the wrong letter, it's better to copy and paste.
sudo apt-get install p7zip-full wget https://files.waveshare.com/upload/8/89/SIM8200_for_RPI.7z 7z x SIM8200_for_RPI.7z -r -o./SIM8200_for_RPI sudo chmod 777 -R SIM8200_for_RPI cd SIM8200_for_RPI sudo ./install.sh
Please do not delete or modify the "option" directory, "qmi_wwan_simcom" directory, "default.script", "install.sh" files, otherwise it will affect the loading of the driver.
If there is an error, please confirm whether the system is "2020-08-20-raspios-buster-armhf", and take a screenshot of the error message so that engineers can help you analyze and solve the problem.
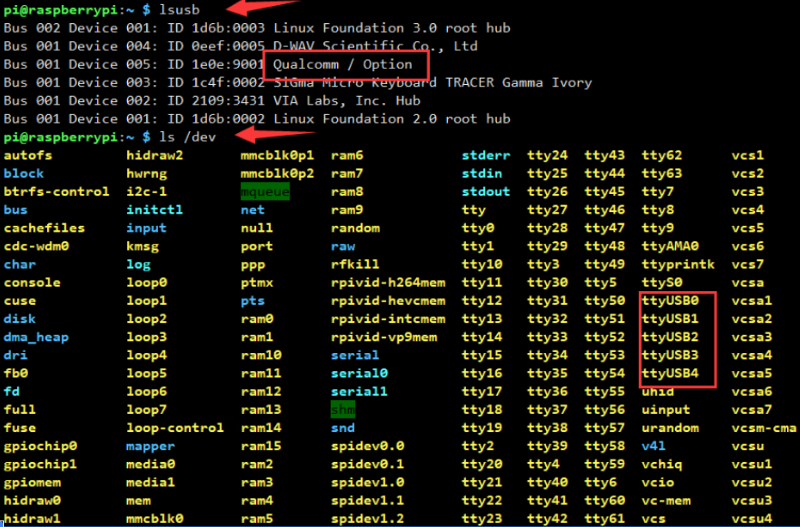
Run "ifconfig -a" to see that "WWAN0" has been generated.

Test AT Command
sudo apt-get install minicom sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyUSB2
NIDS Dial-up
cd Goonline make sudo ./simcom-cm
After running codes, DNS information is shown in the figure below:

After connecting two SIM820X to the Raspberry Pi through USB, two network cards—wwan0 and wwan1 can be recognized. The two network cards can be dialed at the same time through the following commands: (The network speed cannot be superimposed)
sudo ./simcom-cm -i wwan0 sudo ./simcom-cm -i wwan1
- Note: If the IP cannot be obtained or the networking is not successful, use the following commands to obtain the IP and set the DNS networking:
sudo dhclient -v wwan0 sudo route add -net 0.0.0.0 wwan0
Auto-run
If you want to set the codes auto-run after booting, you can modify rc.local file:
sudo nano /etc/rc.local
Add the line to file as below:
sudo /home/pi/SIM8200-M2_5G_HAT_code/Goonline/simcom-cm &
Note that you have to add "&" to the end of the command, make sure that the command can be run in the background, or the Pi may not boot normally.
Live streaming with ffmpeg
If you are using the 2020-08-20-raspios-buster-armhf image, then you don't need to install anything as the system already comes with ffmpeg.
Going straight to the topic, assuming you already have a camera and it's properly connected to the Raspberry Pi, then proceed with the tutorial.
- The camera must be enabled by running the raspi-config command before using it:
sudo raspi-config Select Enable Camera, select YES
- If it is a camera using the CSI interface, the system cannot find the device node of /dev/video0. A line for bcm2835-v4l2 needs to be added to the /etc/modules file:
sudo nano /etc/modules
add:
bcm2835-v4l2

Then after the system starts, the system will load the module name in this file and restart the system:
sudo reboot ls /dev/video*
The video0 device node is found below.
![]()
Note: If after performing the first steps, please confirm that the operation and instructions are correct.
Suppose you are using Douyu Live now, register your account and enable the host function, open Douyu Live Host Center, and find the live broadcast settings.

Open video plug flow setting:
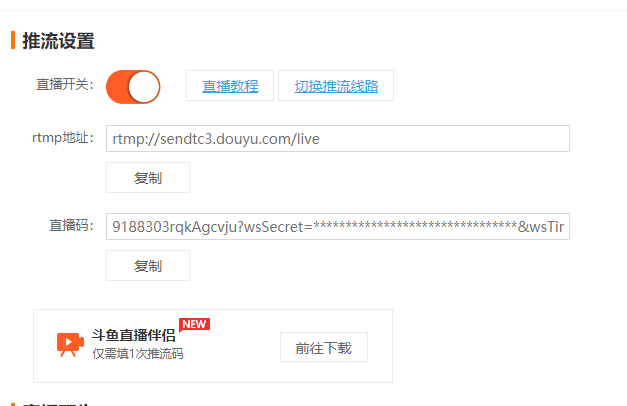
The rtmp address and live code will be obtained, and the Raspberry Pi will execute the command:
ffmpeg -f video4linux2 -s 640x480 -r 25 -i /dev/video0 -c:v h264_omx -f flv "rtmp address/live code"
For example: open a terminal first, runs the 5G network:
cd Goonline sudo ./simcom-cm
and then open another terminal, run the following command:
ffmpeg -f video4linux2 -s 640x480 -r 25 -i /dev/video0 -c:v h264_omx -f flv "rtmp://sendtc3.douyu.com/live/9188303rTNGmU7CS?wsSecret=ef762877aae120262eaf23c3f60a28bf&wsTime=5f59dbf0&wsSeek=off&wm=0&tw=0&roirecognition=0"
rtmp://sendtc3.douyu.com/live is the address, and the next section is the live code. Enter the room number at this time, you can observe the live broadcast, the delay is about 1-2S.
The use of OpenWrt
Introduction to OpenWrt
Soft routing is using desktops or servers and other equipment with software. It mainly depends on the settings of the software to achieve the functions of the router. The hard routing is a unique hardware device, including a processor, power supply, and embedded software to provide router functionality.
OpenWrt is a very popular soft routing system. It is a highly modular and highly automated embedded Linux system with powerful network components and scalability. It is often used in industrial control equipment, routers, and other equipment.
In addition to the functions of general home routers, OpenWrt soft routing can also achieve port forwarding, intranet penetration, 4G networking, FTP server and more powerful functions.
Burn the image
Download the RPI OpenWrt system, unzip the system in the Imgs directory, and use the burning tool to burn the system to the SD card.
Login and initial settings
- After the OpenWrt system is turned on, the Raspberry Pi is equivalent to a router. Therefore, use a network cable to connect the Raspberry Pi to the computer according to the use of the router (you can also use the mobile phone to search for WIFI, the default name is "OpenWrt").
- You can set the language to auto first.
- Enter 192.168.1.1 on the web page, the default user name: root, and the default password: password, enter the OpenWrt web management interface.
- Set WIFI password: Network —> Wireless —> interface configuration —> Wireless security.
- Create the new interface: Network -> Interface -> Create interface.
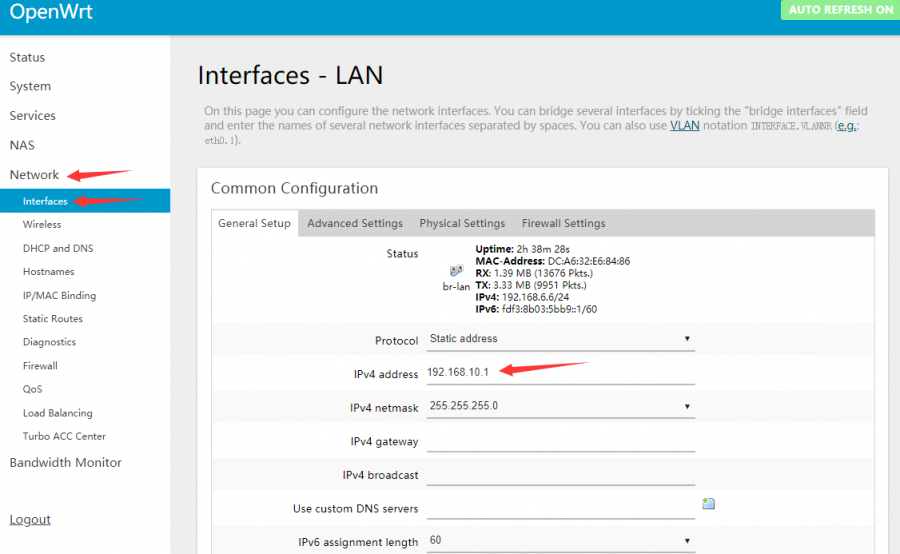
- Modify the IPv4 address of the LAN port to a different IP that is not the same as the LAN port IP of other routers in your home. (Many routers default the LAN port IP to 192.168.1.1. If you do not modify the IP of the OpenWrt, it will easily lead to conflicts and failure to connect to the Internet).
If necessary, it is also recommended to disable the IPv6 allocation length. After the modification is completed, click "Save & Apply", and re-use 192.168.10.1 to access the OpenWrt console.
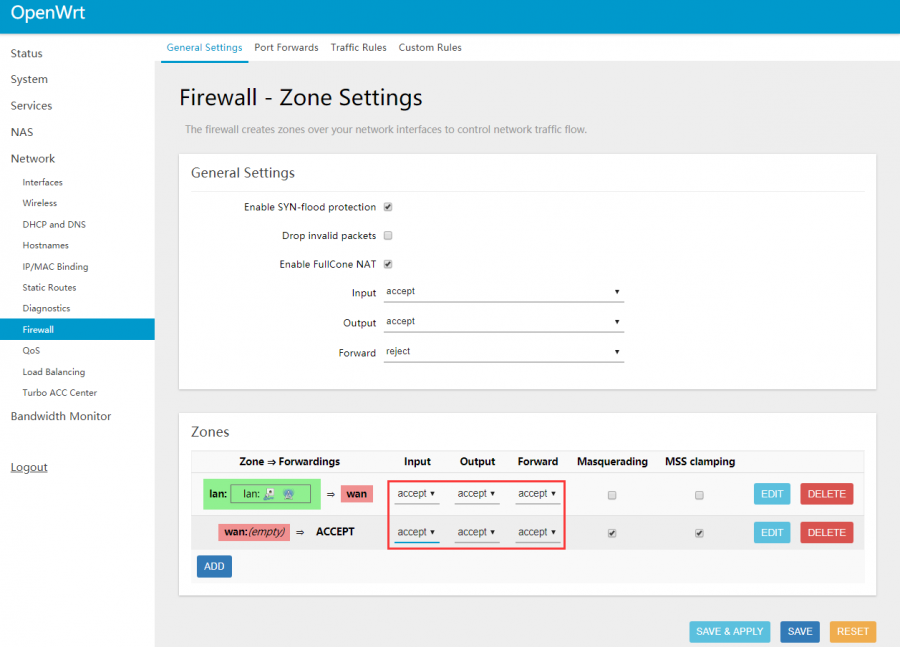
- In addition, it is recommended to adjust the Firewall setting to connect the OpenWrt terminal and Web management interface through the local area.
Network —> Firewall, change all "reject" to "accept", and click "Save & Apply" after modification, as shown in the picture below:
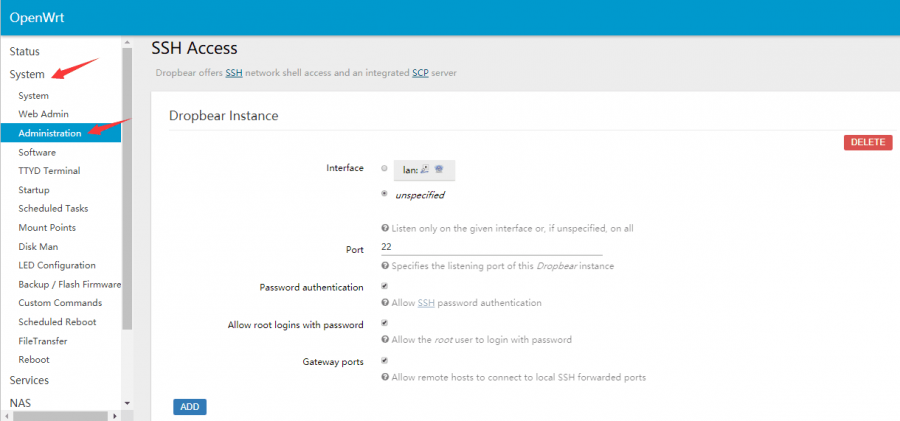
- And then select System -> Administration, modify the allowed interface for SSH access to "unspecified" (that is, any interface can be accessed by ssh), check the Gateway port, and click "Save & Apply" after the modification is completed.
At this point, you can connect to the OpenWrt web management interface or terminal through the IP address of the LAN port or wan port.
Check the working status of the drive
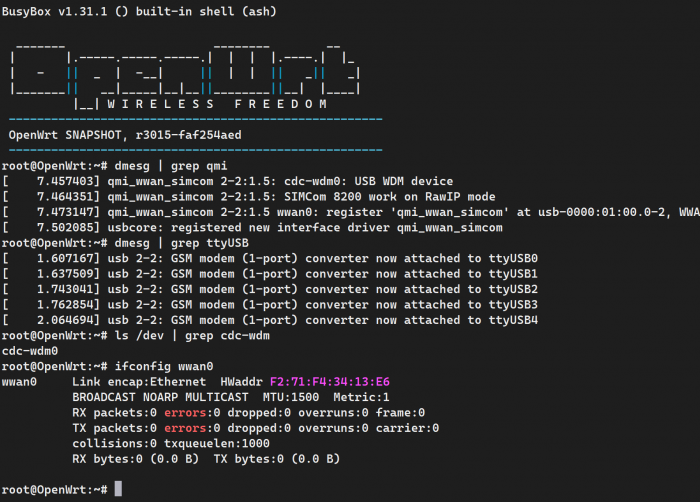
Connect to the OpenWrt terminal via SSH, and run the following commands to view the qmi driver, USB device, network port registration, and network port status:
dmesg | grep qmi dmesg | grep ttyUSB ls /dev | grep cdc-wdm ifconfig wwan0
Configure networking
- Select System -> FileTransfer, select and upload simcom-cm in the simcom-cm directory of the folder:
Use the above "File Transfer" to upload, the uploaded program is located in "simcom-cm" under the /tmp/upload/ directory.
Enter the following commands in the terminal:
cp /tmp/upload/simcom-cm / chmod a+x simcom-cm ./simcom-cm
【Note】: Closing this terminal will cause the networking program to stop, which will cause the network to be disconnected. It is recommended to run in the background.
- At this time, open a new terminal of OpenWrt and enter the command: ifconfig wwan0. You can see that the wwan0 network port has successfully obtained the operator IP and can ping the external network.
- Enter the Web management interface of OpenWrt, click Network —>Interface —>Create a new interface.
- Enter the interface as shown in the picture below and confirm that the interface selection in "Physical Settings" is "wwan0".
- Confirm that the interface selection in "Firewall Settings" is "wan".
- Click "Save & Apply" to complete the network port settings, then return to the interface below, network-interface, you can see that the network port has been correctly identified.
Then the other devices can be connected to the OpenWrt wireless "OpenWrt" or through the network cable to connect to OpenWrt's own network port for networking.
5G Network Speed Test
In the speed measurement part, because the Raspberry Pi comes with a Gigabit Ethernet port, and there are few USB network cards above Gigabit, we use the SpeedTest For Python tool to perform speed measurement by the commands. Connect to the terminal of OpenWrt and enter the commands one by one to measure the speed:
## OpenWRT opkg update opkg install python3 opkg install python3-pip pip install speedtest_cli speedtest # or use speedtest_cli
Raspberry Pi minicom Serial Port Debugging
1. Insert the module into the Raspberry Pi and set the S_TX and S_RX of the dipswitch to ON.

2. Install minicom, minicom is the serial port debugging tool for Linux.
- Use minicom to open ttyUSB2:
sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyUSB2
Send to enable the UART serial port:
AT+CCUART=1
3. Open ttyS0 via minicom - ttyS0 is the serial port of the Raspberry Pi 3B/3B+/4B, and the default baud rate is 115200.
sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyS0
4. Raspberry Pi 2B/zero, the user serial device number is ttyAMA0; you can use the following command line to confirm that serial0 is the selected serial device number, as follows:
ls -l /dev/serial*
Use with Jetson Nano
It is recommended that you use the system image jetson-nano-sd-card-image (updated in October 2020). The Linux kernel version of this system is 4.9.140-tegra. The previous system is 4.4. This tutorial is based on the 4.9 kernels. If there is a difference, please update to the same version as this one, which will minimize the chance of your using it incorrectly.
If you are using other Linux systems, please download the driver under SIM8200_OS_Driver\linux and port it according to the documentation under it.
Configuration Required for First Use
- Please don't type the wrong letter, it's better to copy and paste:
sudo apt-get install p7zip-full wget https://files.waveshare.com/upload/0/07/Sim8200_for_jetsonnano.7z 7z x Sim8200_for_jetsonnano.7z -r -o./Sim8200_for_jetsonnano sudo chmod 777 -R Sim8200_for_jetsonnano cd Sim8200_for_jetsonnano sudo ./install.sh
Please do not delete or modify the options directory, qmi_wwan_simcom directory, default. script, install.sh these four directory files, otherwise it will affect the loading of the driver.
If there is an error, please confirm whether the system kernel is 4.9.140-tegra, and take a screenshot of the error message so that engineers can help you analyze and solve the problem.
Run ifconfig -a to see that WWAN0 has been generated.

AT Test Command
sudo apt-get install minicom sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyUSB2
5G Network
cd Goonline make sudo ./simcom-cm
You can successfully see that DNS has been generated at the bottom.

About the Speed
Due to the differences between actual and laboratory conditions, the 5G speed will not be ideal and stable at 100MBPS. There are the following points:
- Base station distance, the closer to the 5G base station, the better the signal and the faster the speed;
- Base station load, the fewer people using it, the faster the speed will be, and the rush hour will be slower;
- Number of base stations: Due to spectrum relationships, the same amount of 4G coverage requires double the number of 5G base stations.
- Operator: You need to confirm whether your 5G card is limited in speed, you can periodically ask the operator to reset your network.
- Indoors is worse than outdoor: building penetration loss, and indoor diffraction loss.
- PS: The current number of base stations still does not have good coverage, and the speed measurement in different locations is not the same.
Resouces
Schematic
Assembly drawing
Demo Codes
Software
Document
- SIm8200 Series AT Command Manual
- SIM8200EA-M2 Hardware Design Manual
- SIMcom SIM8200EA-M2 resources
- SIMcom SIM8202G-M2 resources
- SIM820X RNDIS Dial-Up
Related application cases
FAQ
{{{5}}}
AT+CNBP? //(you can copy the band to notepad) backup band AT+CNBP=0x100600000FC00000,0x00000000000000460000A7E2BB0F38DF,0x0000000000000000,0x00000000003FFE63000681E2090828D7. 0x00000000003FFE63000681E2090828D7 //assign the band to SIM820X or AT+CNBP=0x100600000FC00000,0x0000000000000046000001E2000908DD,0x00000000000000000000,0x00000000000000007042000081A0080808D7. 0x00000000000070000000010000000000 //give the frequency band to SIM820X AT+CNMP=71 // Fixed 5G
{{{5}}}
It may be that the APN is not acquired, generally, the APN is able to be acquired automatically, some areas (IoT cards) need to be acquired manually, for example, can be set by the following instructions:
AT+CGDCONT=1, "IP", "APN" // different operators APN is different, here the APN is changed to the corresponding operator
You can check the APNs of major carriers at the following websites: APN Search Website
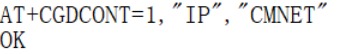
{{{5}}}
- The default is to use SIM card 1, it may be switched to SIM card 2, please use the following command to switch to SIM card 1:
AT+SMSIMCFG=1,1
- Or directly switch to SIM card 2:
AT+SMSIMCFG=1,2
- If it still doesn't work, consider that the airplane mode is turned on, and use the following command to turn off the airplane mode:
AT+CFUN=1
Question: What should I do if the SIM820X module NDIS dial fails and the driver cannot be installed?
- You can program the newest Raspbian system and reconfigure NDIS dial-up.
- Also, you can use the pre-configured image.
{{{5}}}
In this case, the network connection may not be successful. Follow the steps below to troubleshoot:
1. First confirm the hardware problem:
- Check whether the connected SIM card can communicate and surf the Internet normally on mobile phones and other devices:
- Check whether the antenna is connected properly;
- Check that the NET light is flashing, and it is always on, indicating that it is not registered to the network
2. After confirming that the hardware is OK, you can use the following command (AT LOG) to further confirm the network situation:
*Check the firmware version information: AT+SIMCOMATI *Check if the sim card is in good contact: AT+CPIN? *Turn the radio on (turn off airplane mode): AT+CFUN=1 *Check that the network mode is set to auto-seek: AT+CNMP=2 *Check the signal quality of the current environment: AT+CSQ *Check if the registration to the network is successful: AT+CGREG? *Check internet connection: AT+CPSI? *Check if the APN corresponds to the operator of the SIM card: AT+CGDCONT? *Check operator access: AT+COPS?
{{{5}}}
- After confirming that the SIM card is normal and the local 5G network is covered, follow the steps below to fix 5G (to increase the network speed).
AT+CNBP? //(Can copy the frequency band to Notepad) Backup frequency band AT+CNBP = 0x100600000FC00000, 0x000000000000000046004600001e2000908dd, 0x00000000000000000000000000000070420081a00808d7, 0x0000000000000000000000 // AT+CNMP=71 // Fixed 5G
- The 5G operator's SIM card frequency band should cover the SIM820X frequency band; sometimes the 4G network is queried, and the speed has reached 5G. You can directly measure the speed to confirm that the 5G network speed is available.
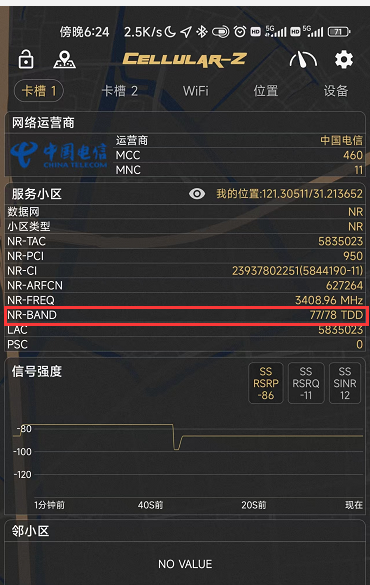
- To confirm whether the test environment has 5G network coverage, you can install Cellular-Z on a 5G mobile phone (all major app stores can download it) to view the detailed network information:
- Apple phones can follow the following steps to obtain band information:
- Open the phone dialer, enter *3001#12345#*, then click the dialer button.
- In the pop-up page, first, find and click "Serving Cell Info", then find and click "Freg Band Indicator.
- Check according to the table issued by the operator, and you will know.
{{{5}}}
- It is recommended to use the more convenient RNDIS dial-up.
- You can burn the latest Raspberry Pi Raspbian system and reconfigure the NDIS dial-up.
- Or you can use the image of the RNDIS dial-up with drivers already configured and boot the Raspbian system image (with drivers installed).
{{{5}}}
AT+CSYSSEL="nr5g_band",41:78
{{{5}}}
{{{5}}}
{{{5}}}
{{{5}}}
{{{5}}}
The following commands can be used to save the SMS to the module memory:
AT+CPMS="MT"
{{{5}}}
at+voltesetting=1 at+cnv=/nv/item_files/modem/mmode/ue_usage_setting,1,01,1
The VOLTE function can be turned off with the following command:
at+voltesetting=0 at+cnv=/nv/item_files/modem/mmode/ue_usage_setting,0,01,1
{{{5}}}
- Insert the GPS antenna into the GNSS antenna holder (SIM8200EA is ANT5; SIM8202G is ANT2), and place the receiver in the open outdoors (note that the test cannot be done in rainy weather), the power needs to wait for about 1 minute before the positioning signal is received;
- M2 module needs a passive antenna to obtain positioning information, if you do not have a passive positioning antenna, the matching 5G antenna is also available, replace the 5G antenna and put the module into outdoor positioning (the 5G antenna does not come with an extension cable)::
{{{5}}}
USB, Raspberry Pi runs "sudo. /install" will load the USB driver, and we connect communication with a 3B/4B USB connector. According to the tutorial, you can load the USB driver on Windows, and it will display as an unknown device when there is no driver.
{{{5}}}
{{{5}}}
{{{5}}}
After prolonged operation, the lubricating oil in the rolling bearing fan may evaporate, leading to increased noise. This is a common phenomenon with rolling bearing fans and does not indicate a malfunction of the fan.
{{{5}}}
We use the RTL8125 network port solution.
Theoretically, RTL8125 supports 2.5G, but it depends on the 5G module and the network condition of the test environment.
{{{5}}}
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 AM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)