ESP32-S3-Pico
| ||
Overview
Introduction
The ESP32-S3-Pico is a low-cost, high-performance microcontroller development board with a compact size and rich peripheral interfaces.
Adopts ESP32-S3R2 as the main chip, which is an MCU chip with integrated 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi and Bluetooth 5 (LE).
The interface chips are CH343 and CH334, so you can experience the fun of USB and UART development with a single USB-C port, and no more trouble switching interfaces.
The DC-DC chip adopts MP28164, a high-efficiency buck-boost chip, which adopts PWM fixed-frequency current control mode to optimize circuit stability and response speed.
You can choose ESP-IDF, Arduino, MicroPython, or other development environments in software so that you can easily and quickly get started and apply it to the product.
Features
- Adopts ESP32-S3R2 as the main chip.
- Comes with Xtensa 32-bit LX7 dual-core processor, capable of running at 240 MHz.
- Integrated 512KB SRAM, 384KB ROM, 2MB PSRAM, 16MB Flash memory.
- Type-C connector, easier to use.
- Onboard CH343 and CH334 chips can meet the needs of USB and UART development via a Type-C interface.
- Onboard DC-DC chip MP28164, high-efficiency DC-DC buck-boost chip with load current up to 2A.
- Supports multiple low-power operating states, the adjustable balance between communication distance, data rate, and power consumption to meet the power requirements of various application scenarios.
- 27 × multi-function GPIO headers.
- Castellated module allows soldering directly to carrier boards.
- Rich peripheral interfaces, including full-speed USB OTG, SPI, I2C, UART, ADC, PWM, and DVP (8-bit ~ 16-bit camera interface), LCD interfaces (8-bit ~ 16-bit parallel RGB, I8080, MOTO6800), etc. to achieve various functions flexibly.
Pinout Definition
- Note: SPI, I2C, UART, and other interfaces can be mapped to most GPIOs through the GPIO Matrix and IO MUX, see the ESP32-S3 datasheet for details.
Dimensions
Development Environment Configuration
- The following development system is Windows by default.
ESP-IDF
- It is recommended to develop with the VSC plug-in.
Develop with VSCode
Install VSCode
- 1. Open the download page of the official VSCode website, and select the corresponding system and system bit to download.

- 2. After running the installation package, the rest can be installed by default, but here for the subsequent experience, it is recommended to check boxes 1, 2, and 3.

- After the first two items are enabled, you can open VSCode directly by right-clicking files or directories, which can improve the subsequent user experience.
- After the third item is enabled, you can select VSCode directly when you choose how to open it.
Install Espressif IDF Plug-in
- Note: The latest version of the current plug-in is V1.6.0, for a consistent experience, users can choose the same version as us.
- 1. Open VSCode and use the shortcut key Shift + Ctrl + X to enter the plugin manager.
- 2. In the search bar, type Espressif IDF, select the corresponding plug-in, and click install.
- 3. Press F1 to enter:
esp-idf: configure esp-idf extension
- 4. Choose express (This tutorial is for users who install it for the first time, so only the first general installation tutorial is covered.)
- 5. Open and display this screen.
- 6. Choose a server to download.
- 7. Select the ESP-IDF version you want now, we choose the latest V5.0.1 (note that ESP-IDF started to support ESP32-S3 only after V4.4).
- 8. The following two are the ESP-IDF directory installation address and the ESP-IDF required tools installation address respectively.
- Note: If you have installed ESP-IDF before, or if it has failed, please make sure to delete the file completely or create a new path.
- 9. Once the configuration is finished, click "install" to download.
- 10. Enter the download page, and it will automatically install the corresponding tools and environment, just wait a moment.
- 11. After the installation is completed, it will enter the following screen, indicating that the installation is finished.
Official Demo Usage
- Click here to view more details provided by the official ESP.
Creating a Demo
- 1. Using the shortcut F1, type:
esp-idf:show examples projects
- 2. Choose your current IDF version:
- 3. Take "Hello World" as an example:
- 4. ① Choose the corresponding demo.
- 5. ② The readme file will explain which chip the demo is suitable for (the following section will introduce how to use the demo and its file structure, which is omitted here).
- 6. ③ Click to create the demo.
- 7. Choose the path to place the demo and ensure that there is no folder with the same name as the demo.
Modify COM Port
- 1. The corresponding COM port is displayed here, click on it to modify.
- 2. We check the device manager COM port, and select COM5, please select according to your corresponding COM port:
- 3. Choose the project and demo.
- 4. Then the COM port is modified.
Modify the Driver
- 1. Here shows the driver used, click here to modify the corresponding driver:
- 2. Choose the project or demo:
- 3. Wait for a few seconds after clicking.
- 4. Choose the driver we need, that is, the main chip ESP32S3.
- 5. Choose the openocd path, we can just choose one as it doesn't matter.
The Rest of the Status Bar Introduction
- ① SDK configuration editor: many functions and configurations of ESP-IDF can be modified within it.
- ② Clean up everything and delete all compiled files.
- ③ Compile.
- ④ Current download method, default is UART.
- ⑤ Program the current firmware, please do it after compiling.
- ⑥ Open the serial monitor to view serial information.
- ⑦ Combined button for compiling, programming, and opening the serial monitor (most commonly used during debugging).
Compile, Program, and Serial Port Monitoring
- 1. Click on the Compile, Program, and Open Serial Monitor buttons we described earlier.
- 2. It may take a long time to compile, especially for the first time.
- During this process, ESP-IDF may take up a lot of CPU resources and therefore may cause system lag.
- 3. If it fails to download, you can hold the boot button to power on and then release the button, and then program the download.
- 4. After successful download, it will automatically enter the serial monitor, and you can see the corresponding information output from the chip and prompt to reboot after 10s.
Arduino
- If you do not use arduino-esp32 before, you can refer to this link.
Install Arduino
- 1. Open the official software download webpage, and choose the corresponding system and system bits to download.
- 2. You can choose "Just Download", or "Contribute & Download".
- 3. Run to install the program and install it all by default.
Install arduino-esp32
- 1. Open Preferences.
- 2. Add the corresponding board manager URLs and click it.
- 3. Add the following content in the blank.
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/gh-pages/package_esp32_index.json
- 4. Save the setting.
- 5. Open the board manager and enter ESP32 in the search bar.
- 6. Wait for downloading.
- 7. arduino-esp32 is downloaded.
Use Arduino Demo
- 1. Select the demo, here we choose the demo to get the chip ID.
- 2. Select the board as ESP32S3 Dev Module.
- 3. Choose the COM5 port of ESP32-S3 USB.
- 4. Click the download button, then it compiles and downloads automatically.
- 5. Finish.
- 6. Open the Serial Port Monitor.
- 7. See the chip ID of the loop output.
MicroPython
Flash Firmware
- 1. For ESP32-S3-Pico, please download firmware: Click here to download the burner and firmware.
For ESP32-S3-DEV-KIT-N8R8, please download firmware: ESP32-S3-DEV-KIT-N8R8-micropython-firmware.zip or download from micropython - 2. Unzip the package downloaded before and enter.
- 3. Enter flash_download_tool_3.9.4 folder and open flash_download_tool_3.9.4.exe.
- 4. Choose the corresponding chip, choose ESP32-S3.
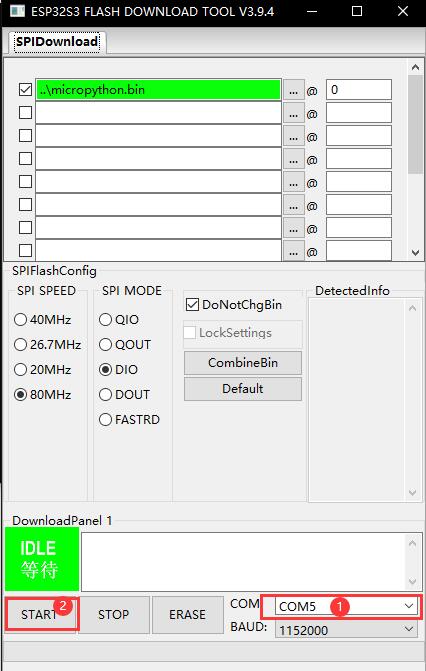
- 5. Choose the corresponding COM port, we have configured it and you just click Start to download.
- ①Choose the COM port.
- ②Download key.
Install Thonny
- 1. Open official Thonny website.
- 2. Select the corresponding system and version, here I choose "Windows", and the mouse has to move to Windows, only then will the corresponding information be displayed.
- 3. Just install it all the way by default.
- 4. Finish.
Get the Demo
- 1. Click here to download the demo.
- 2. Unzip the demo zip file.
Run the Demo
- 1. Open Thonny and choose Configure Interpreter.
- 2. Choose MicroPython (ESP32) as the Interpreter.
- 3. Click OK to save.
- 4. Click Stop or Ctrl + F2.
- 5. You can see the MicroPython version information and the board name.
- 6. Open the files.
- 7. Choose our demo file and open a demo, here we choose a wifi-scan demo.
- ①Current local file directory.
- ②The demo we want to open is wifi-scan.py.
- ③ESP32-S3-PICO directory.
- 8. Click to run or press F5.
- 9. Please wait a moment, and you can see the wifi output information of esp32-s3-pico.
MicroPython Demo Description
- Most of the demos are based on Pico-Sensor-Kit-B.
For better using experience, we include a py file in the firmware。 The following code is used to organize scattered GPIO pins in the order of Pico pins. The source code is shown below:
from micropython import const D0 = const(11) D1 = const(12) D2 = const(13) D3 = const(14) D4 = const(15) D5 = const(16) D6 = const(17) D7 = const(18) D8 = const(33) D9 = const(34) D10= const(35) D11= const(36) D12= const(37) D13= const(38) D14= const(39) D15= const(40) D16= const(42) D17= const(41) D18= const(1) D19= const(2) D20= const(4) D21= const(5) D22= const(6) D26= const(7) D27= const(8) D28= const(9) A1= const(7) A2= const(8) A3= const(9) RGB_PIN= const(21) USB_ADC= const(3)
1-GPIO
Blink
- Blink the GPIO10 corresponding to the Raspberry Pi PICO (GP35 corresponding to the ESP32-S3) at 1-sec interval.
Key
- Read the level of GPIO3 corresponding to Raspberry Pi PICO (corresponding to GP13 of ESP32-S3).
- If it is low level, press the key to flip the LED level.
2-PWM
fade
- Output PWM frequency of GPIO12 corresponding to Raspberry Pi PICO (GP37 corresponding to ESP32-S3) at 1000Hz, with duty cycle increasing or decreasing between 0% and 100%.
Siren
- Configure GPIO12 of the corresponding Raspberry Pi PICO (corresponding to GP37 of ESP32-S3) to output PWM with a duty cycle of 30%, and increase or decrease the frequency between 600-1400Hz.
3-UART
uart
- Using GPIO0 of Raspberry Pi Pico (corresponding to GP11 of ESP32-S3) and GPIO1 (corresponding to GP12 of ESP32-S3) as the TX and RX pins for UART, perform UART echo.
4-I2C
I2C-OLED
- Using GPIO6 of Raspberry Pi Pico (corresponding to GP17 of ESP32-S3) and GPIO7 (corresponding to GP18 of ESP32-S3) as the SDA and SCL pins for I2C, drive the 1.5-inch OLED module.
I2C-SCAN
- Using GPIO8 of Raspberry Pi Pico (corresponding to GP33 of ESP32-S3) and GPIO9 (corresponding to GP34 of ESP32-S3) as the SDA and SCL pins for I2C, scan the device addresses on the I2C bus.
5-SPI
Pico-LCD-1.3
- Drive the PICO-LCD-1.3 module.
6-ADC
adc
- Sequentially read the voltage values of GPIO pins 26-29 of the Raspberry Pi PICO and output the information.
7-RGB
rgb
- Lights up the on-board RGB-LEDs and keeps on converting colors.
8-SYS
FLASH-SIZE
- Output remaining FLASH memory.
RAM-SIZE
- Output the remaining and used RAM space.
RTC
- Set RTC time and read the RTC value in a loop.
SLEEP
- Set the ESP32-S3 to deep sleep for 10 seconds, it will automatically reset and reboot when it reaches the sleep time.
WDT
- Set watchdog and wait for watchdog reset.
9-WIFI
scan
- Scan the surrounding wifi signal and display the related information.
Resource
Schematic
Demo
Software
ESP32-S3
CH343
UART
Datasheet
ESP32-S3
CH343
Official Documentation
Official ESP32 Document
Official MicroPython Document
FAQ
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 AM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)